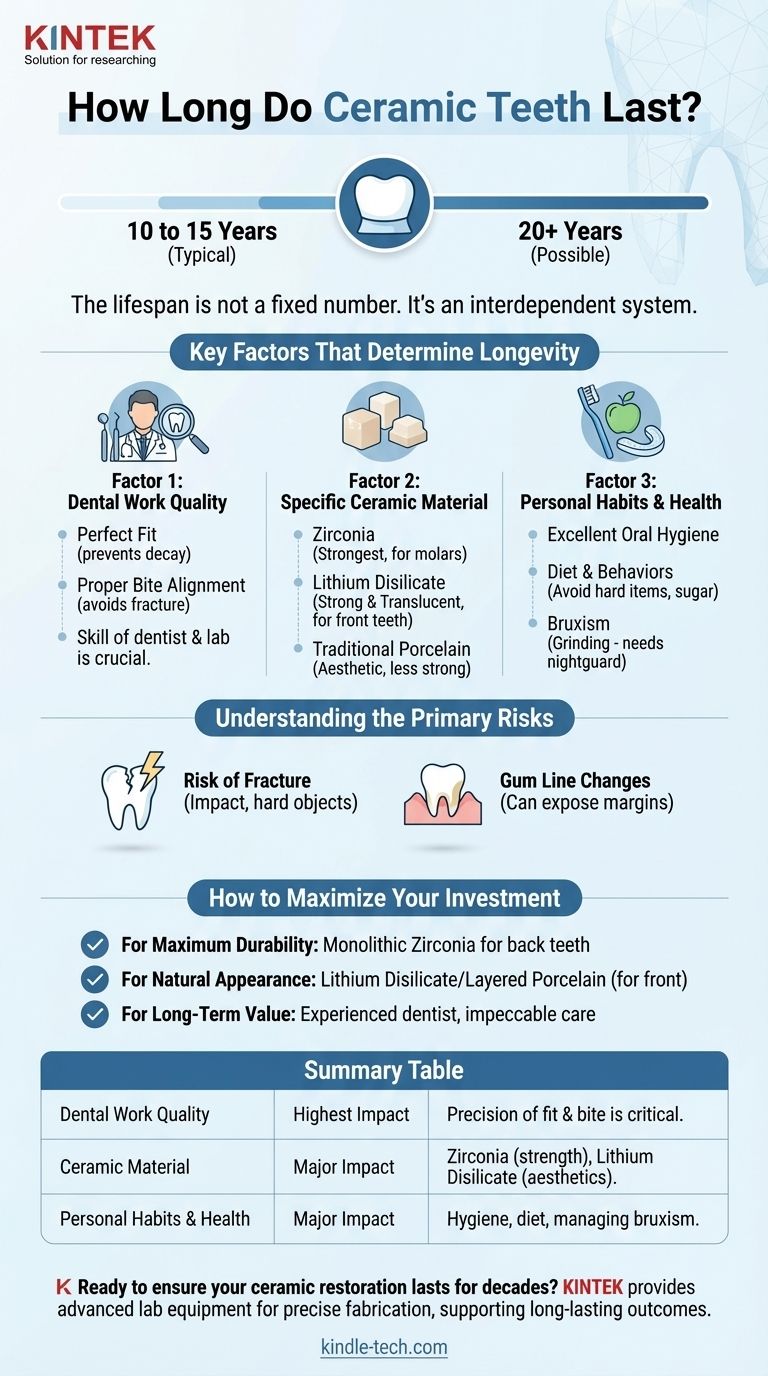
Ceramic dental restorations are designed for remarkable durability. With proper installation and diligent care, you can expect a high-quality ceramic crown, veneer, or implant to last 10 to 15 years. However, it is not uncommon for them to function perfectly for 20 years or even longer.
The lifespan of a ceramic tooth is not a fixed number. It is the result of an interdependent system: the specific material used, the precision of the dental work, and the daily habits of the patient.
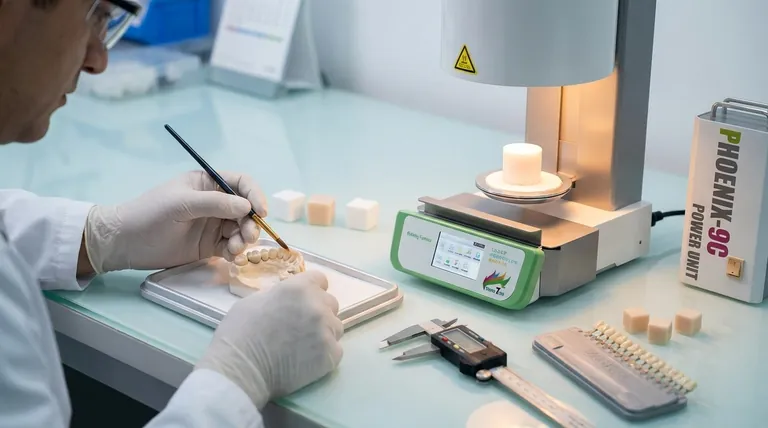

The Key Factors That Determine Longevity
The final outcome depends on a partnership between you and your dental professional. Understanding the key variables will empower you to maximize the life of your restoration.
Factor 1: The Quality of the Dental Work
The skill of your dentist and the lab they work with is the single most important factor.
A perfect fit is non-negotiable. An improperly sealed crown can allow bacteria to seep underneath, leading to decay of the underlying natural tooth and failure of the restoration.
Proper bite alignment, or occlusion, is also critical. If the restoration is too "high," it will absorb excessive force during chewing, significantly increasing the risk of chipping or fracture.
Factor 2: The Specific Ceramic Material
Not all ceramics are the same. They are chosen based on a balance between strength and aesthetics, depending on the tooth's location in your mouth.
Zirconia is an exceptionally strong, tooth-colored ceramic. It is highly resistant to fracture and is often the preferred choice for molars, where biting forces are greatest.
Lithium disilicate (e.g., E-max) offers a superb combination of strength and translucency. It is a popular choice for front teeth because it mimics the appearance of natural enamel almost perfectly.
Traditional porcelain is highly aesthetic but more prone to chipping than modern alternatives. It is often layered over a stronger core material like zirconia.
Factor 3: Your Personal Habits and Health
Once the restoration is in place, its lifespan is largely in your hands.
Excellent oral hygiene is paramount. While the ceramic itself cannot decay, the natural tooth structure underneath and the surrounding gums are still vulnerable to plaque and bacteria.
Your diet and behaviors matter. Chewing on hard items like ice, pens, or fingernails can cause fractures. A diet high in sugar can lead to decay around the margins of the restoration.
Conditions like bruxism (teeth grinding) place extreme stress on any dental work. A protective nightguard is often essential to prevent premature failure.
Understanding the Primary Risks
Even the best ceramic work has potential vulnerabilities. Being aware of them is key to prevention.
The Risk of Fracture
While modern ceramics are incredibly strong, they are not indestructible. A sudden impact from an accident or biting down unexpectedly on a hard object like an olive pit can cause a chip or fracture.
The Issue of Gum Line Changes
The ceramic restoration itself does not change, but your body does. Over many years, gums can naturally recede, which may expose the margin where the crown meets the natural tooth.
This can create an aesthetic issue or a new area where decay can begin, potentially requiring the restoration to be replaced.
The Myth of a "Permanent" Solution
It is crucial to view ceramic restorations as a long-term, but not necessarily permanent, solution. They are durable repairs, much like a high-quality component on a car, and may eventually require replacement due to wear, accident, or changes in your underlying dental health.
How to Maximize the Lifespan of Your Investment
Your choices before, during, and after the procedure directly influence the outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability: Discuss using monolithic (solid) zirconia for back teeth, as it offers the highest resistance to fracture.
- If your primary focus is the most natural appearance: A material like lithium disilicate or layered porcelain on zirconia is often the best choice for front teeth, but requires avoiding risky habits.
- If your primary focus is long-term value: Invest in an experienced dentist with advanced training in cosmetic and restorative dentistry, and commit to impeccable, lifelong oral care.
Ultimately, proactive care and a strong partnership with your dental team are the keys to a long-lasting and successful result.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Lifespan | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Dental Work Quality | Highest Impact | Precision of fit and bite alignment is critical. |
| Ceramic Material | Major Impact | Zirconia for strength, Lithium Disilicate for aesthetics. |
| Personal Habits & Health | Major Impact | Oral hygiene, diet, and managing teeth grinding (bruxism). |
Ready to ensure your ceramic restoration lasts for decades?
At KINTEK, we understand that the longevity of your dental work depends on precision and quality materials. Our advanced lab equipment and consumables are trusted by dental professionals worldwide to create durable, perfectly fitted ceramic crowns, veneers, and implants. By providing reliable tools for precise fabrication, we help dental labs deliver restorations that stand the test of time.
Partner with KINTEK to elevate the quality and durability of your dental solutions. Contact our experts today to learn how our products support long-lasting patient outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs



















