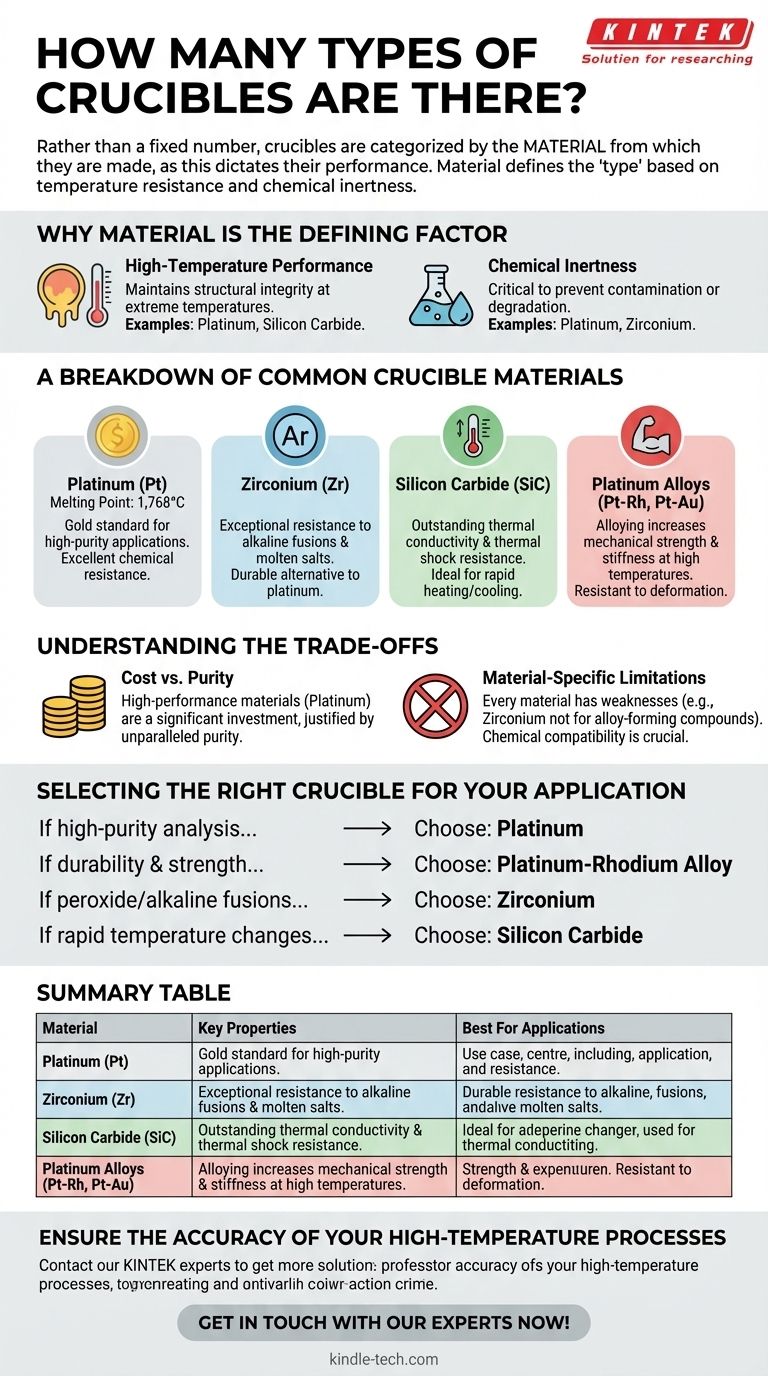
Rather than a fixed number, crucibles are categorized by the material from which they are made, as this dictates their performance. The primary types are constructed from materials chosen for their high melting points and chemical inertness, such as platinum, zirconium, silicon carbide, and specialized platinum alloys like platinum-rhodium and platinum-gold.
The "type" of a crucible is fundamentally defined by its material composition. Your selection should not be based on a name, but on matching the material's specific properties—like temperature resistance and chemical inertness—to the precise demands of your application.

Why Material is the Defining Factor
The function of a crucible is simple: to hold a substance securely during intense heating without reacting with it. Therefore, the material used is the single most important characteristic that differentiates one crucible from another.
High-Temperature Performance
A crucible’s primary requirement is its ability to maintain structural integrity at extreme temperatures.
Materials like platinum and silicon carbide are selected specifically for their exceptionally high melting points, ensuring they remain solid and stable well beyond the temperatures required for most laboratory and industrial processes.
Chemical Inertness
It is critical that the crucible does not contaminate the sample it holds, or be degraded by it.
Materials such as platinum and zirconium are highly non-reactive. This inertness prevents the crucible from interfering with chemical reactions or leaching impurities into the melt, which is essential for accurate analysis.
A Breakdown of Common Crucible Materials
While many materials can be used, a few stand out in professional and industrial settings for their superior reliability and performance under specific conditions.
Platinum (Pt)
Platinum is often considered the gold standard for high-purity applications. It offers excellent resistance to many chemical agents and has a very high melting point (1,768°C).
Zirconium (Zr)
Zirconium crucibles provide exceptional resistance to alkaline fusions and certain molten salts. They are a durable and often more cost-effective alternative to platinum for specific chemical processes.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Known for its outstanding thermal conductivity and resistance to thermal shock, silicon carbide is well-suited for applications involving rapid heating and cooling cycles.
Platinum Alloys (Pt-Rh, Pt-Au)
Pure platinum can be soft at high temperatures. Alloying it with elements like rhodium (Rh) or gold (Au) significantly increases its mechanical strength and stiffness, making the crucible more resistant to deformation over repeated use.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single crucible material is perfect for every situation. The choice always involves balancing performance requirements against practical limitations, primarily cost and chemical compatibility.
Cost vs. Purity
High-performance materials come at a significant cost. Platinum and its alloys are extremely expensive, making them a major investment. The cost must be justified by the need for unparalleled purity or resistance.
Material-Specific Limitations
Every material has a weakness. For example, while zirconium is excellent for alkaline fusions, it is not suitable for fusions with compounds that can form alloys with it. Understanding these specific chemical incompatibilities is crucial to prevent crucible failure and sample contamination.
Selecting the Right Crucible for Your Application
Your choice should be driven entirely by the specific chemical and thermal environment of your work.
- If your primary focus is high-purity analysis with a wide range of materials: A platinum crucible is the most reliable and versatile choice.
- If your primary focus is durability and strength during repeated high-temperature use: A platinum-rhodium alloy provides superior mechanical performance.
- If you are performing peroxide or other strong alkaline fusions: A zirconium crucible offers the best resistance and longevity for this specific task.
- If your application involves rapid temperature changes: A silicon carbide crucible is engineered to withstand the stress of thermal shock.
Ultimately, choosing the correct crucible is a critical step in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of your high-temperature work.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Properties | Best For Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Platinum (Pt) | High melting point (1,768°C), excellent chemical inertness | High-purity analysis with a wide range of materials |
| Zirconium (Zr) | Exceptional resistance to alkaline fusions | Peroxide or strong alkaline fusions |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Outstanding thermal shock resistance, high thermal conductivity | Applications involving rapid heating and cooling cycles |
| Platinum Alloys (Pt-Rh, Pt-Au) | Increased mechanical strength and stiffness at high temperatures | Repeated high-temperature use requiring superior durability |
Ensure the Accuracy of Your High-Temperature Processes
Choosing the right crucible is critical for achieving reliable results and protecting your samples from contamination. The experts at KINTEK understand that your laboratory's success depends on using the correct equipment for each specific application.
We specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including a comprehensive range of crucibles made from platinum, zirconium, silicon carbide, and specialized alloys. Our team can help you select the perfect crucible based on your specific temperature requirements, chemical compatibility needs, and budget.
Contact us today to discuss your application requirements and get a personalized recommendation. We are here to help you enhance the efficiency and accuracy of your work.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
People Also Ask
- Why are alumina crucibles or baskets essential for Boudouard reaction studies? Ensure Pure Data & Chemical Inertness
- Why use an alumina crucible in a stainless steel autoclave? Ensure Purity in Liquid Lead and LBE Exposure Experiments
- What is the purpose of using an alumina crucible with a lid for g-C3N4 synthesis? Optimize Your Nanosheet Production
- What is a crucible material for a furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right High-Temperature Container
- How does the use of corrosion-resistant ceramic crucibles ensure the chemical purity of materials? | KINTEK



















