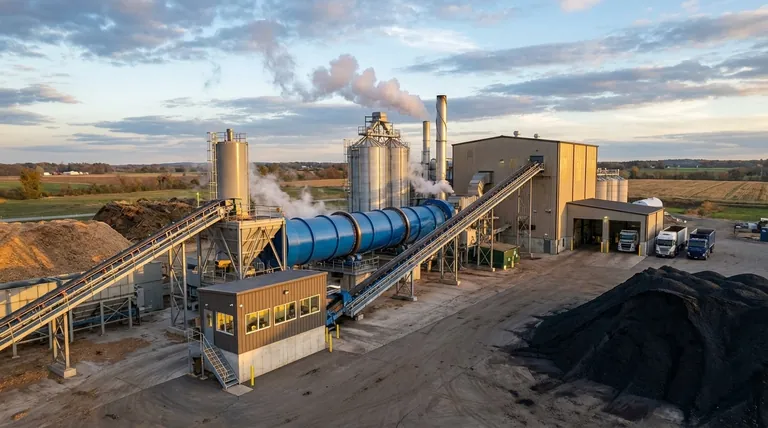
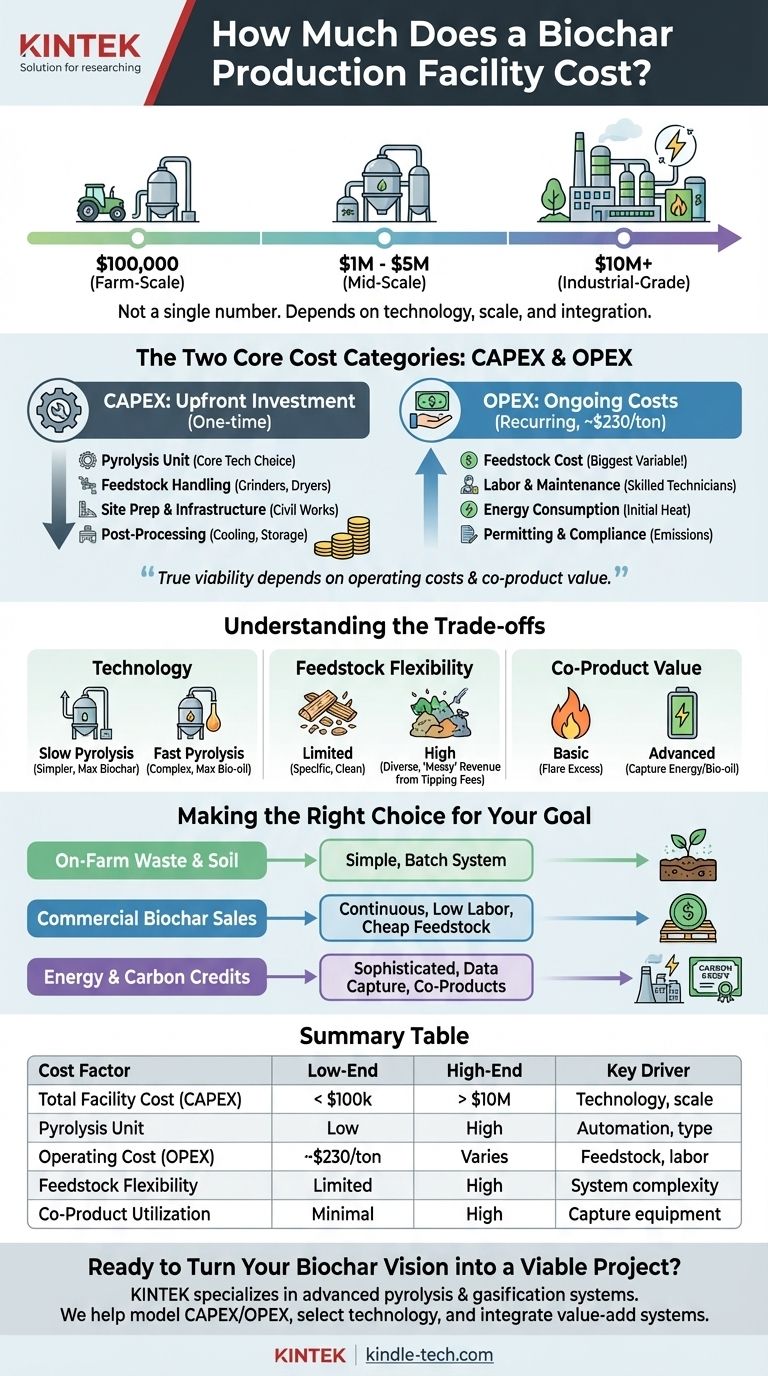
The cost of a biochar production facility is not a single number, but a wide spectrum determined by technology, scale, and integration. A small, farm-scale unit might cost under $100,000, while a large, industrial-grade plant integrated with energy recovery can easily exceed $10 million. The final investment depends entirely on your production goals and operational context.
The capital cost of the pyrolysis equipment is only one part of the financial puzzle. True viability is determined by a holistic analysis of operating costs—especially feedstock—and the value of all potential co-products, not just the biochar itself.

The Two Core Cost Categories: CAPEX and OPEX
Understanding the cost of a facility requires breaking it down into two distinct categories: the upfront investment (CAPEX) and the ongoing costs to run it (OPEX).
Capital Expenditures (CAPEX): The Upfront Investment
This is the total one-time cost to get your facility built and commissioned. It goes far beyond the price of the main reactor.
The Pyrolysis Unit: The Heart of the Operation
The core technology choice—typically slow or fast pyrolysis, or gasification—is the primary driver of cost. A simple, low-tech drum or kiln is vastly cheaper than a sophisticated, automated continuous system with precise temperature controls.
Feedstock Handling and Preparation
Raw biomass is rarely ready for pyrolysis. You must budget for essential support equipment like grinders, chippers, and dryers. Conveyor systems to move material automatically also add significant cost.
Site Preparation and Infrastructure
A facility requires a prepared site, often with a concrete slab, a protective structure or building, and access to utilities like electricity and water. These civil engineering costs are a major and often underestimated expense.
Post-Processing and Value-Add Systems
After production, biochar must be quenched (cooled safely), potentially ground or pelletized, and stored. If you plan to capture and use co-products like syngas for heat or bio-oil, the necessary capture, cleaning, and storage equipment will add to the initial CAPEX.
Operating Expenditures (OPEX): The Ongoing Costs
These are the recurring costs required to produce each ton of biochar. While a market price of $1,000/ton seems attractive, profitability hinges on keeping your production cost, estimated to be around $230/ton, as low as possible.
Feedstock Cost: The Biggest Variable
This is the most critical factor in your business model. If you are using a waste product you already own (e.g., manure, crop residue), your cost is near zero. If you have to purchase and transport biomass, it becomes your largest operating expense.
Labor and Maintenance
Automated systems require fewer operators but demand more skilled technicians for maintenance and troubleshooting. You must account for salaries, training, and the cost of routine upkeep and spare parts.
Energy Consumption
Pyrolysis requires an initial energy input to reach operating temperature. While many modern systems can then run on the syngas they produce, some still require a consistent external energy source, which is a direct cost.
Permitting and Compliance
Operating a pyrolysis plant involves environmental permits, particularly for air emissions. The costs for initial permitting, testing, and ongoing monitoring can be substantial and vary significantly by location.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right system involves balancing upfront cost with long-term capability and profitability. The cheapest option is rarely the most profitable.
Technology: Slow vs. Fast Pyrolysis
Slow pyrolysis systems are generally less complex and less expensive. They maximize the yield of biochar (the solid product).
Fast pyrolysis systems are more expensive and technologically complex. Their primary goal is to maximize the yield of liquid bio-oil, with biochar being a secondary product.
Feedstock Flexibility vs. Cost
A cheaper, simpler machine may only be able to process a very specific type of clean, dry wood chip. A more expensive and robust system might handle diverse and "messy" feedstocks like manure, biosolids, or mixed plastics, which could provide you with a revenue stream from tipping fees.
Co-Product Value: Beyond Just Biochar
A basic system burns off the excess heat and gas produced during pyrolysis. A more sophisticated—and expensive—facility captures this energy. This captured heat can be used to dry feedstock (lowering OPEX) or sold to a neighboring facility (creating a new revenue stream), dramatically improving the overall economics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your ideal facility depends entirely on your primary objective. Evaluate your project through one of these lenses.
- If your primary focus is on-farm waste management and soil improvement: A smaller, simpler, batch-style system is likely your most cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is commercial biochar sales: You must prioritize a continuous system with low labor needs and secure a cheap, long-term feedstock source, as this will be the key to profitability.
- If your primary focus is energy production or carbon credits: You need a sophisticated, instrumented system capable of capturing co-products and providing the verifiable data required by energy buyers and carbon registries.
Ultimately, a successful biochar project is built on a comprehensive business model, not just the purchase of a machine.
Summary Table:
| Cost Factor | Low-End Estimate | High-End Estimate | Key Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Facility Cost (CAPEX) | < $100,000 | > $10,000,000 | Technology, scale, and integration level |
| Pyrolysis Unit (Core Reactor) | Low | High | Automation, controls, and technology type (slow vs. fast) |
| Operating Cost (OPEX) per ton | ~$230/ton | Varies significantly | Feedstock cost (biggest variable) and labor |
| Feedstock Flexibility | Limited (e.g., clean wood chips) | High (e.g., manure, mixed waste) | System complexity and robustness |
| Co-Product Utilization | Minimal (syngas often flared) | High (energy recovery, bio-oil) | Additional capture and processing equipment |
Ready to Turn Your Biochar Vision into a Viable Project?
Navigating the complex cost variables of a biochar facility requires expert guidance. KINTEK specializes in advanced pyrolysis and gasification systems, providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed to test, scale, and optimize your operation.
We help our laboratory and industrial partners:
- Accurately model CAPEX and OPEX for your specific feedstock and scale.
- Select the right technology (slow vs. fast pyrolysis) to maximize your target product yield (biochar, bio-oil, energy).
- Integrate value-add systems for co-product utilization to improve overall economics.
Don't leave your project's profitability to chance. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation tailored to your laboratory and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- Iridium Dioxide IrO2 for Water Electrolysis
People Also Ask
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker














