In short, DLC coating is exceptionally strong. It is significantly harder than any steel and stands as one of the most durable coatings commercially available for protecting surfaces from scratches and wear. Its true "strength," however, comes not just from its hardness but from a unique combination of properties, including a very low coefficient of friction, which allows it to shrug off abrasive contact.
The true strength of a DLC coating is not simply its remarkable hardness, but its unique blend of slickness and wear resistance. However, its ultimate real-world durability is critically dependent on the quality of its bond to the underlying material and the toughness of that material itself.

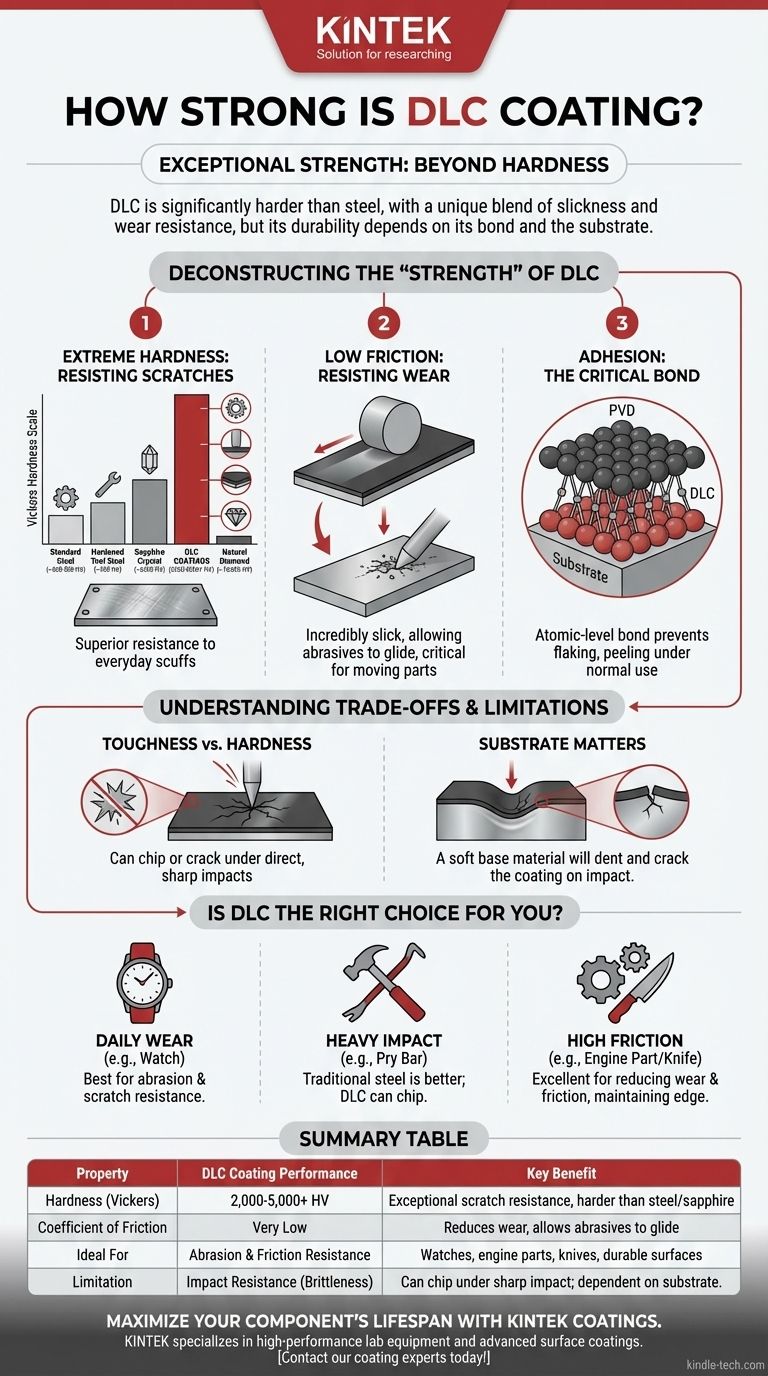
Deconstructing the "Strength" of DLC
To understand the performance of Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC), we must look beyond the single word "strength." Its durability is a result of three distinct, yet interconnected, material properties.
Extreme Hardness: Resisting Scratches
The most cited characteristic of DLC is its incredible hardness. This is the material's ability to resist being scratched or indented by another object.
On the Vickers hardness scale (HV), where a higher number indicates greater hardness, DLC far surpasses traditional metals.
- Standard Steel: ~600-800 HV
- Hardened Tool Steel: ~900 HV
- Sapphire Crystal: ~2000 HV
- DLC Coatings: 2000 to over 5000 HV
- Natural Diamond: ~10,000 HV
This means DLC is highly effective at resisting the everyday scuffs and scratches that would easily mar uncoated steel, titanium, or aluminum.
Low Friction: Resisting Wear
Equally important to its durability is DLC's extremely low coefficient of friction. It creates a surface that is incredibly slick, comparable to Teflon in some environments.
This property is a key contributor to its wear resistance. When an abrasive object moves across a DLC-coated surface, it is more likely to glide over it rather than dig in and remove material. This is critical for moving parts in engines, firearms, and high-performance knife blades.
Adhesion: The Critical Bond
A coating is useless if it does not remain bonded to the material it is protecting. Modern application processes, like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), create an atomic-level bond between the DLC and the substrate.
When applied correctly to a properly prepared surface, the DLC coating will not flake, peel, or blister under normal use. This bond is fundamental to the coating's overall performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. While DLC is exceptionally durable, it is not invincible. Understanding its limitations is crucial for setting realistic expectations.
Toughness vs. Hardness
There is a classic trade-off in material science between hardness and toughness. Hardness resists scratches, while toughness resists chipping and cracking from impacts.
Because DLC is an extremely hard, thin ceramic layer, it can be brittle. A sharp, direct impact can potentially chip or crack the coating, even if the underlying metal is unharmed.
The Substrate Still Matters
The DLC coating is a protective skin, typically only a few microns thick (thinner than a human hair). It does not add structural integrity to the object itself.
If the base material is soft, like aluminum or basic stainless steel, a significant impact can dent the material underneath the coating. This deformation will cause the hard DLC layer on top to crack or fail at the point of impact. The coating is only as impact-resistant as the material it covers.
Coating Application Quality
The final performance of a DLC coating is heavily dependent on the quality of its application. Factors like surface preparation, coating thickness, and the specific type of DLC used can vary dramatically between manufacturers.
A poorly applied coating may have weak adhesion or internal stresses, making it prone to premature failure. This is why the reputation of the company applying the coating is just as important as the coating itself.
Is DLC the Right Choice for You?
Choosing a DLC-coated item depends entirely on what kind of stress you expect it to endure. Its strength is best suited for resisting abrasion and friction, not for withstanding heavy, focused impacts.
- If your primary focus is daily wear and scratch resistance (like a watch or jewelry): DLC offers outstanding protection against common scuffs and will keep the item looking new for much longer.
- If your primary focus is heavy-duty impact resistance (like a pry bar or axe): A traditional, uncoated, through-hardened steel tool is more suitable, as DLC can chip under severe impacts that deform the base metal.
- If your primary focus is performance in a high-friction environment (like an engine part or high-use knife blade): DLC is one of the best choices available for simultaneously reducing wear, lowering friction, and maintaining a sharp edge.
Ultimately, viewing DLC as an incredibly tough, friction-reducing shield, rather than invincible armor, is the key to understanding its true value.
Summary Table:
| Property | DLC Coating Performance | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Vickers) | 2,000 - 5,000+ HV | Exceptional scratch resistance, harder than steel and sapphire |
| Coefficient of Friction | Very Low | Reduces wear by allowing abrasives to glide off the surface |
| Ideal For | Abrasion & Friction Resistance | Watches, engine parts, knives, and applications requiring slick, durable surfaces |
| Limitation | Impact Resistance (Brittleness) | Can chip under sharp, direct impacts; dependent on substrate toughness |
Maximize your component's lifespan with a DLC coating tailored to your needs. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and advanced surface coatings. Our expertise ensures your materials gain superior wear resistance and reduced friction. Let's discuss how our solutions can enhance your project's durability. Contact our coating experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is the role of plasma in PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is Dielectric Blocking Discharge Enhanced Chemical Vapour Deposition (DBD-PECVD)? High-Pressure Film Uniformity
- What temperature is PECVD silicon nitride? A Guide to Low-Temp Deposition for Sensitive Devices
- What is PECVD cluster tool deposition used for? Essential for High-Purity Multi-Layer Device Fabrication
- How does PECVD equipment facilitate the directional growth of carbon nanotubes? Achieve Precision Vertical Alignment
- What is the high temperature for DLC coating? Maximize Performance with the Right Thermal Limits
- Why is plasma a crucial component of the PECVD process? Unlocking Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does PECVD equipment facilitate SiC deposition on sensitive substrates? Unlock Low-Temp Thin Film Solutions









