At its core, thermal evaporation is a straightforward process for creating a thin metal film by essentially "boiling" a metal in a vacuum. The source metal is heated until it vaporizes, and this metal vapor then travels and condenses onto a cooler surface, known as a substrate, forming a uniform, solid film. This technique is a fundamental type of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) used widely in manufacturing electronics.
The central principle of thermal evaporation is using resistive heating to convert a solid source material into a vapor within a high-vacuum chamber. This vapor then coats a target substrate, condensing back into a solid to form a precisely controlled thin film.
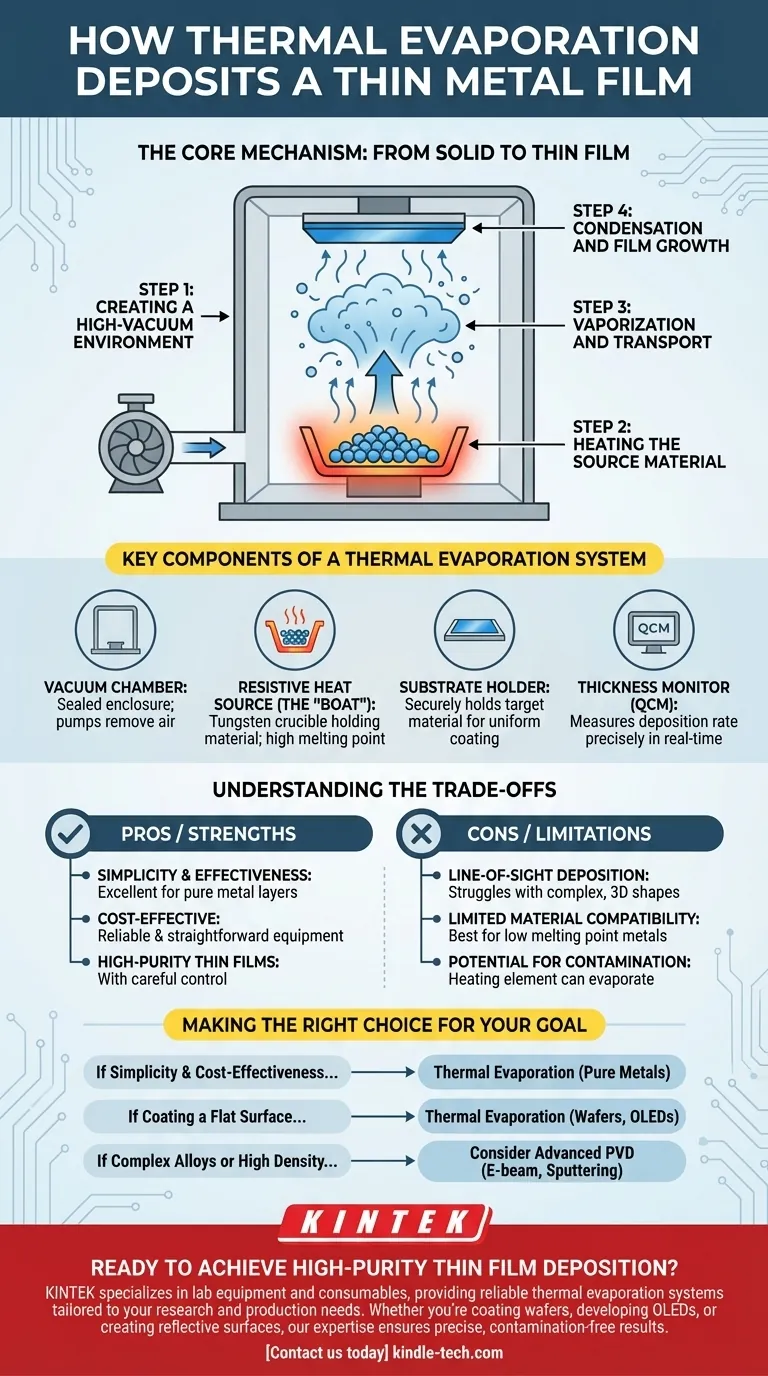
The Core Mechanism: From Solid to Thin Film
Understanding the thermal evaporation process involves breaking it down into four distinct, sequential steps that occur within a controlled environment.
Step 1: Creating a High-Vacuum Environment
The entire process takes place inside a sealed chamber where the pressure is reduced to a high vacuum.
This vacuum is critical because it removes air and other particles, preventing the metal vapor from reacting with contaminants and ensuring it can travel unimpeded from the source to the substrate.
Step 2: Heating the Source Material
The metal to be deposited, often in the form of wire, pellets, or shot, is placed in a container.
This container, typically called a "boat" or "basket," is made of a material with a very high melting point, like tungsten. An electric current is passed through the boat, causing it to heat up resistively, much like the filament in an incandescent light bulb.
Step 3: Vaporization and Transport
As the boat heats up, it transfers thermal energy to the source metal, raising its temperature until it begins to evaporate or sublimate, turning directly into a gas.
This creates a cloud of metal vapor that expands throughout the vacuum chamber, traveling in straight lines.
Step 4: Condensation and Film Growth
A cooler substrate (such as a silicon wafer or glass panel) is positioned above the vapor source.
When the atoms or molecules of metal vapor collide with the cooler substrate, they lose energy, condense back into a solid state, and begin to form a thin, uniform film on its surface.
Key Components of a Thermal Evaporation System
A functional thermal evaporation system relies on several critical pieces of hardware working in concert to achieve a precise and clean deposition.
The Vacuum Chamber
This is the sealed enclosure that contains the entire process. It's connected to a series of pumps that remove air to create the necessary high-vacuum conditions.
The Resistive Heat Source (The "Boat")
This is the crucible or filament that holds the source material. It must be able to withstand extreme temperatures without melting or reacting with the material being evaporated.
The Substrate Holder
This component securely holds the target material—the wafer, glass, or other object to be coated. It is often positioned to ensure uniform coating from the vapor cloud below.
The Thickness Monitor (QCM)
To control the final film thickness with high precision, systems use a Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM). This device measures the deposition rate in real-time by detecting the change in the crystal's resonant frequency as mass from the vapor is added to its surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While thermal evaporation is valued for its simplicity and effectiveness, it's essential to understand its inherent limitations.
Line-of-Sight Deposition
Because the metal vapor travels in straight lines from the source to the substrate, this method is considered a line-of-sight technique. This means it is excellent for coating flat surfaces but struggles to uniformly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with undercuts or hidden surfaces.
Limited Material Compatibility
The process is best suited for materials with relatively low melting and boiling points, such as pure metals like aluminum, gold, silver, and indium. Attempting to evaporate materials with extremely high melting points or complex alloys can be difficult or impossible with standard resistive heating.
Potential for Contamination
While the vacuum mitigates most contamination, the heating element (the boat) itself can sometimes contaminate the film if it gets too hot and begins to evaporate alongside the source material. This requires careful control of power and temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting thermal evaporation depends entirely on the specific requirements of your material, substrate, and desired film properties.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and cost-effectiveness: Thermal evaporation is an excellent choice for depositing pure metallic layers for applications like electrical contacts or reflective coatings.
- If your primary focus is coating a flat surface: This method excels at creating uniform films on substrates like wafers, solar cells, and OLED display panels where line-of-sight deposition is sufficient.
- If your primary focus is depositing complex alloys or achieving high film density: You may need to consider more advanced PVD techniques like electron-beam evaporation or sputtering, which offer greater control over material composition and film structure.
Ultimately, thermal evaporation remains a foundational and highly valuable technique for its ability to produce high-purity thin films with reliable and straightforward equipment.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) |
| Core Mechanism | Resistive heating vaporizes metal in a vacuum, which condenses on a substrate |
| Ideal Materials | Pure metals like aluminum, gold, silver, indium |
| Best For | Flat surfaces, electrical contacts, reflective coatings |
| Limitations | Line-of-sight deposition; not ideal for complex 3D shapes |
Ready to achieve high-purity thin film deposition in your lab? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable thermal evaporation systems tailored to your research and production needs. Whether you're coating wafers, developing OLEDs, or creating reflective surfaces, our expertise ensures precise, contamination-free results. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
People Also Ask
- What is thermal effect via evaporation? A Simple Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What is thermal evaporation used to deposit? A Guide to Metals, Compounds, and Key Applications
- What is vacuum thermal evaporation? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What are the drawbacks of thermal evaporation? Understanding the Limitations for High-Performance Applications
- What is the thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition for Your Lab



















