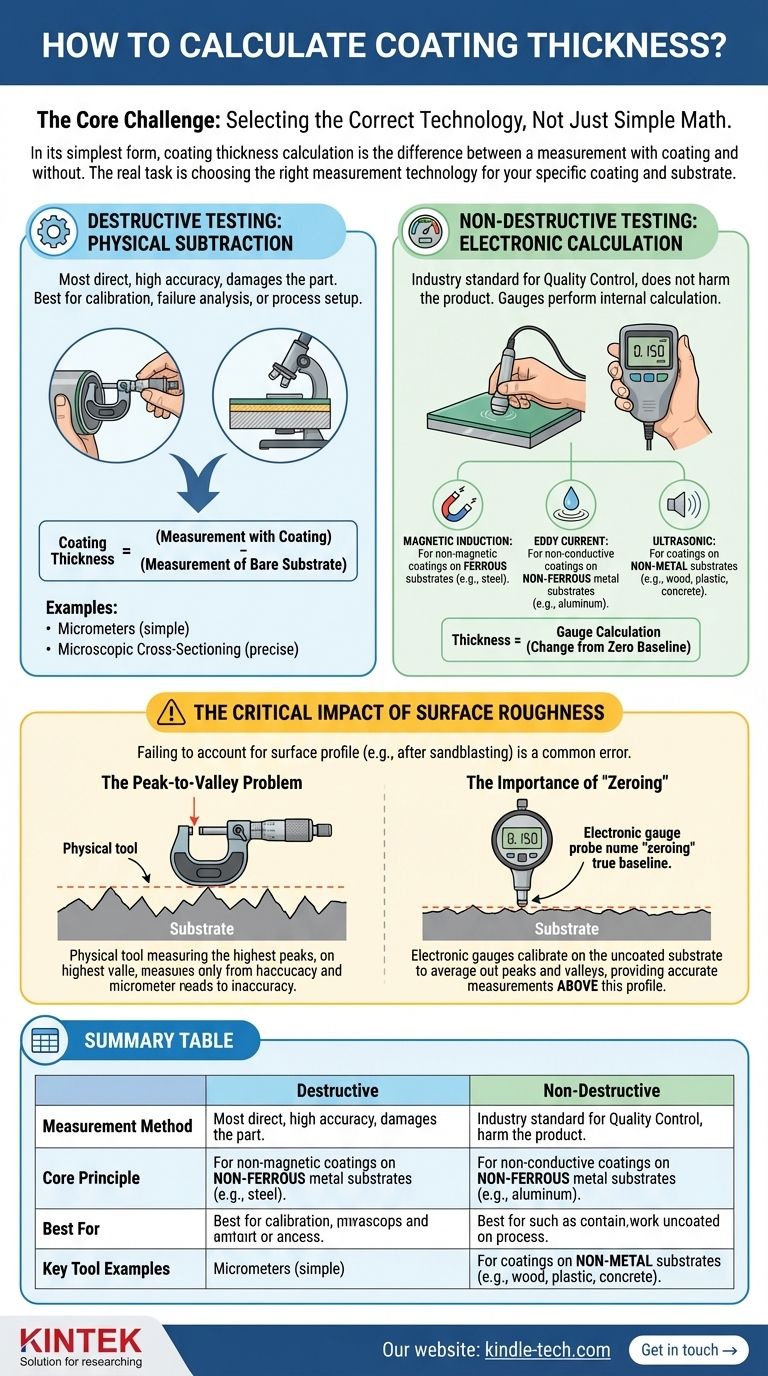
In its simplest form, the calculation for coating thickness is the difference between a measurement taken with the coating and a measurement taken without it. For example, using a micrometer, you would measure the uncoated part, then measure it again in the same spot after coating, with the difference being the thickness.
The core challenge is not the calculation itself, which is often just simple subtraction performed by a gauge. The real task is selecting the correct measurement technology for your specific coating and substrate, as this choice dictates the entire process.

The Two Core Measurement Philosophies
At a high level, all methods fall into one of two categories: destructive testing, which provides high accuracy but damages the part, and non-destructive testing, which is ideal for quality control.
Destructive Testing: Physical Subtraction
This is the most direct way to measure thickness and is often used for calibration, failure analysis, or setting up a new process.
The Method: The principle is based on physically observing the coating. You measure the total thickness of the part with the coating, then remove the coating and measure the substrate alone.
The Calculation: The formula is a straightforward subtraction:
Coating Thickness = (Measurement with coating) - (Measurement of bare substrate)
Common Tools: This category includes micrometers for simple applications and microscopic cross-sectioning for highly precise analysis where a sample is cut, polished, and measured under magnification.
Non-Destructive Testing: Electronic Calculation
This is the industry standard for quality control because it doesn't harm the finished product. Modern gauges perform the calculation internally and provide a direct reading.
The Method: These gauges work by creating a field (magnetic, electrical, or ultrasonic) and measuring how the coating interferes with it. They are first calibrated on the bare, uncoated substrate to establish a "zero" baseline.
The Calculation: The gauge electronically calculates the thickness based on the change from its zeroed baseline. The user does not perform a manual subtraction.
Common Technologies:
- Magnetic Induction: For non-magnetic coatings (paint, powder coat, zinc) over ferrous substrates like steel.
- Eddy Current: For non-conductive coatings over non-ferrous metal substrates like aluminum or copper.
- Ultrasonic: For coatings on non-metal substrates like wood, plastic, or concrete.
The Critical Impact of Surface Roughness
A common point of failure in any calculation is failing to account for the substrate's surface profile, especially after processes like sandblasting.
The "Peak-to-Valley" Problem
A physical tool like a micrometer measures from the highest peak of the rough surface to the top of the coating. This reading ignores the coating that fills the "valleys" of the surface profile, leading to an inaccurate measurement of the true coating volume.
The Importance of "Zeroing"
Electronic gauges solve this problem through calibration, or "zeroing." By placing the gauge probe on the uncoated, rough substrate, you teach the instrument where the true baseline is, averaging out the peaks and valleys.
Every subsequent measurement over the coated surface is then an accurate reading of the thickness above this established surface profile. This is why a simple subtractive measurement on a rough surface is often misleading.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a method requires balancing the need for precision against the practical demands of production.
Accuracy vs. Usability
Destructive testing like cross-sectioning offers the highest possible accuracy and serves as the ultimate proof of thickness. However, it is slow, expensive, and destroys the part.
Non-destructive gauges are fast, portable, and essential for 100% inspection or statistical process control (SPC). Their accuracy depends entirely on proper calibration and using the right gauge for the job.
Substrate is Everything
The most common mistake is using the wrong technology for the substrate. A magnetic gauge will not work on aluminum, and an eddy current gauge will not work on steel. The physical properties of the base material dictate the correct tool.
Calibration is Not Optional
An uncalibrated or improperly zeroed electronic gauge provides meaningless numbers. Any calculation or data derived from it is fundamentally flawed. Calibration on a representative, uncoated part is the first and most critical step.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your objective determines the correct method for calculating or measuring coating thickness.
- If your primary focus is process validation or failure analysis: Use destructive cross-sectioning to get a definitive, microscopic measurement.
- If your primary focus is quality control on steel or iron parts: A properly calibrated magnetic induction gauge is the correct tool.
- If your primary focus is quality control on aluminum, brass, or copper: You must use an eddy current gauge calibrated for that specific substrate.
- If your primary focus is measuring coatings on wood, concrete, or plastic: An ultrasonic coating thickness gauge is the appropriate technology.
Ultimately, achieving an accurate coating thickness value depends less on manual math and more on selecting the right instrument and calibrating it correctly for the surface you are measuring.
Summary Table:
| Measurement Method | Core Principle | Best For | Key Tool Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Destructive Testing | Physical subtraction: (Coated Measurement) - (Bare Substrate) | Calibration, failure analysis, high-precision validation | Micrometers, Microscopic Cross-Sectioning |
| Non-Destructive Testing | Electronic calculation via field interference (magnetic, eddy current, ultrasonic) | Quality control, in-process checks, high-volume inspection | Magnetic Induction, Eddy Current, Ultrasonic Gauges |
Need precise control over your coating processes? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for accurate material analysis. Whether you require calibration standards for your gauges or robust tools for destructive testing, our solutions ensure reliable thickness measurements for your laboratory. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and enhance your quality control protocol. Get in touch →
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Buchner Funnel and Triangular Funnel
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What are the four main types of sensors? A Guide to Power Source and Signal Type
- How are PTFE gaskets utilized for POEGMA electrolyte conductivity? Ensure Precision in Electrochemical Measurements
- Why is PTFE wire used for hanging metal specimens in biodiesel corrosion tests? Ensure Pure Experimental Results
- What is the difference between PPF and coating? Armor vs. Slick Shell for Your Car
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context











