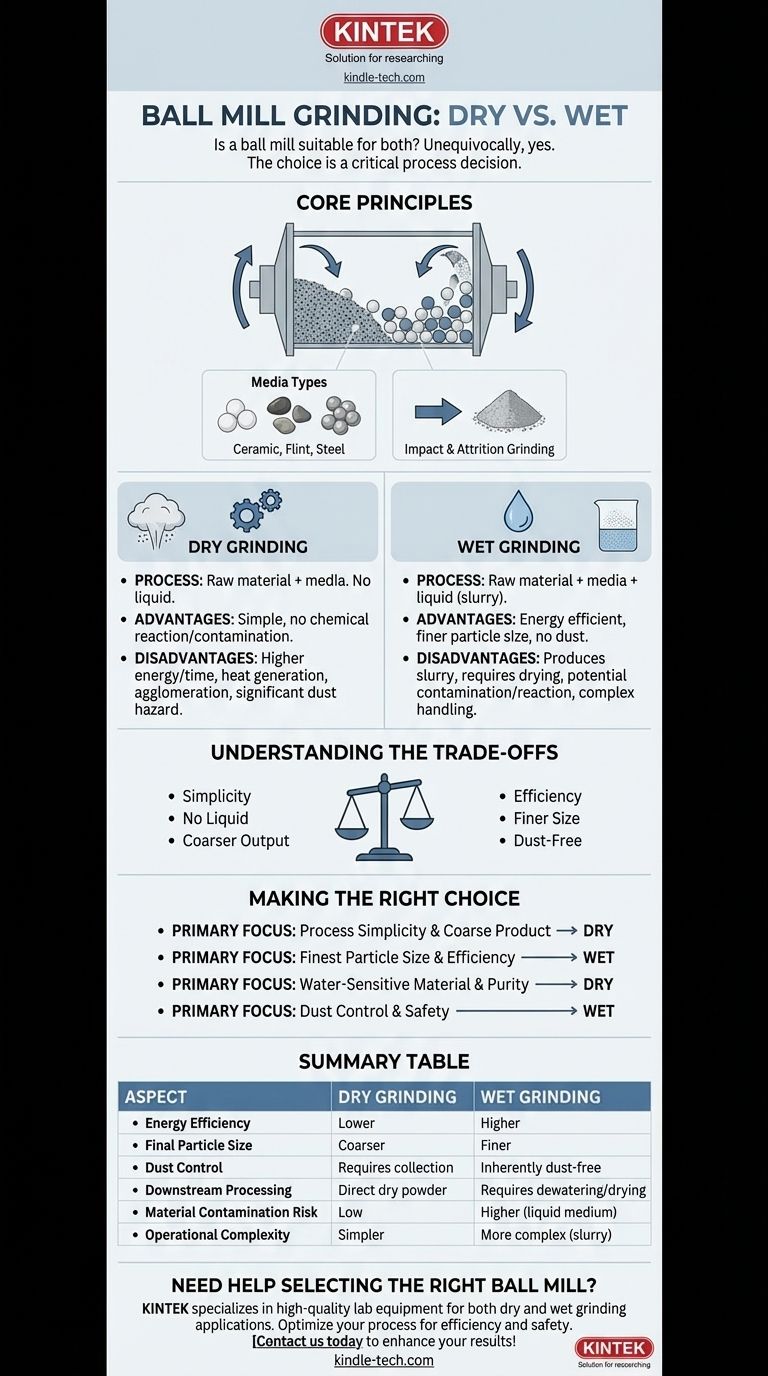
Unequivocally, yes. A ball mill is a highly versatile piece of size-reduction equipment, fundamentally designed to operate in both dry and wet grinding modes. The decision to use one method over the other is not a question of the mill's capability, but rather a critical process choice driven by your material's properties, your desired final particle size, and your operational constraints.
While a ball mill is effective for both dry and wet grinding, the choice is a critical process decision. Wet grinding generally offers finer particle sizes and higher energy efficiency, while dry grinding provides operational simplicity, with each method presenting distinct trade-offs in energy, contamination, and downstream processing.

The Core Principles of Ball Milling
To understand the difference between wet and dry grinding, we must first establish how a ball mill functions. It is a simple, robust technology that relies on a few key principles.
How a Ball Mill Operates
A ball mill is a hollow cylindrical shell that rotates on its horizontal axis. This shell is partially filled with the material to be ground, along with a charge of grinding media.
As the cylinder rotates, the media is lifted up the side of the shell and then cascades or cataracts down, crushing and grinding the material through impact and attrition. The speed of rotation is critical; too slow and the media only tumbles, too fast and it centrifuges, sticking to the shell wall.
The Role of Grinding Media
The grinding media does the actual work. These are typically hard, dense objects whose properties are chosen based on the application.
Common media includes high-density ceramic balls, naturally-shaped flint pebbles, or heavy stainless steel balls. The size, density, and material of the media are key variables that control the grinding process.
A Closer Look at Dry Grinding
In dry grinding, the raw material is loaded into the mill with the grinding media, and nothing else. The mill rotates, and the dry powder is reduced in size.
Key Advantages of Dry Grinding
The primary benefit of dry grinding is simplicity. The process is straightforward, and the resulting product is a dry powder that is often ready for the next stage without further processing.
This method also avoids any potential chemical reactions or contamination that could occur between your material and a grinding liquid.
Primary Disadvantages of Dry Grinding
Dry grinding typically requires more energy and time to achieve the same particle size compared to wet grinding.
It also generates significant heat, which can be problematic for heat-sensitive materials. Furthermore, very fine dry powders can begin to agglomerate or coat the grinding media, reducing efficiency. Finally, handling fine, dry powders poses a significant dust hazard.
A Closer Look at Wet Grinding
In wet grinding, a liquid—most often water—is added to the material and media inside the mill. This creates a slurry that is ground by the media's action.
Key Advantages of Wet Grinding
Wet grinding is generally more energy efficient. The liquid medium improves the transfer of energy, dissipates heat effectively, and prevents fine particles from clumping together.
This allows the mill to produce a finer final particle size with a narrower particle size distribution. The slurry format also completely eliminates the risk of airborne dust.
Primary Disadvantages of Wet Grinding
The most obvious disadvantage is that the final product is a slurry. This requires an additional, often energy-intensive, dewatering or drying step if a dry powder is the final goal.
The liquid also adds a potential source of contamination and can cause unwanted reactions with certain materials. Handling and pumping slurries can add to the operational complexity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between dry and wet grinding is an exercise in balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" method; there is only the best method for your specific goal.
Energy Consumption vs. Simplicity
Wet grinding is more efficient, lowering your energy cost per ton of processed material. However, this savings can be offset by the energy required for the downstream drying process. Dry grinding consumes more energy in the mill but delivers a finished, dry product.
Final Particle Size and Distribution
If you need to produce ultra-fine particles (in the micron or sub-micron range), wet grinding is almost always superior. The liquid prevents the agglomeration that plagues fine dry grinding and allows the media to work more effectively.
Contamination and Material Purity
Dry grinding's main advantage here is that it introduces no foreign liquids. However, both methods are subject to contamination from wear and tear on the grinding media and the mill's inner lining.
Operational Complexity and Safety
Wet grinding eliminates the explosion and inhalation risks associated with fine dusts. However, it introduces the complexities of slurry handling and drying. Dry grinding is operationally simpler but requires robust dust collection and safety protocols.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The decision between wet and dry grinding depends entirely on your project's specific goals. Use these points as your guide.
- If your primary focus is process simplicity and the final product can be coarse: Dry grinding is often the most direct and cost-effective path.
- If your primary focus is achieving the finest possible particle size and maximizing energy efficiency: Wet grinding is the superior choice, provided you can manage the resulting slurry.
- If your primary focus is preventing any form of contamination in a water-sensitive material: Dry grinding is your only viable option, though you must still account for media wear.
- If your primary focus is controlling dust for health and safety reasons: Wet grinding inherently solves the problem of airborne particulate matter.
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently select the grinding method that aligns perfectly with your technical and operational requirements.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Dry Grinding | Wet Grinding |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
| Final Particle Size | Coarser | Finer |
| Dust Control | Requires dust collection | Inherently dust-free |
| Downstream Processing | Direct dry powder | Requires dewatering/drying |
| Material Contamination Risk | Low (no liquid) | Higher (liquid medium) |
| Operational Complexity | Simpler | More complex (slurry handling) |
Need help selecting the right ball mill for your grinding process? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, offering tailored solutions for both dry and wet grinding applications. Our experts can help you optimize your process for efficiency, particle size, and safety. Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover how our ball mills can enhance your results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a high-energy planetary ball mill in CoCrFeNi preparation? Mastering Mechanical Alloying
- What is the role of high-energy ball milling in producing HEA powders? Achieve Nano-Scale Homogeneity in Alloys
- What are the advantages of planetary ball milling? Achieve High-Energy Grinding and Material Synthesis
- How is a planetary ball mill utilized in preparing iron and yttrium oxide? Achieve High-Energy Mechanical Alloying
- What are the factors affecting grinding in a ball mill? Optimize Your Milling Process for Maximum Efficiency
- What role does a planetary ball mill play in the preparation of nano-sized Li8/7Ti2/7V4/7O2 cathode materials?
- What is the primary function of a planetary ball mill in AlN production? Achieve Perfect Material Dispersion
- Why are zirconia grinding balls selected for milling NaSICON? Optimize Your Solid Electrolyte Purity and Performance



















