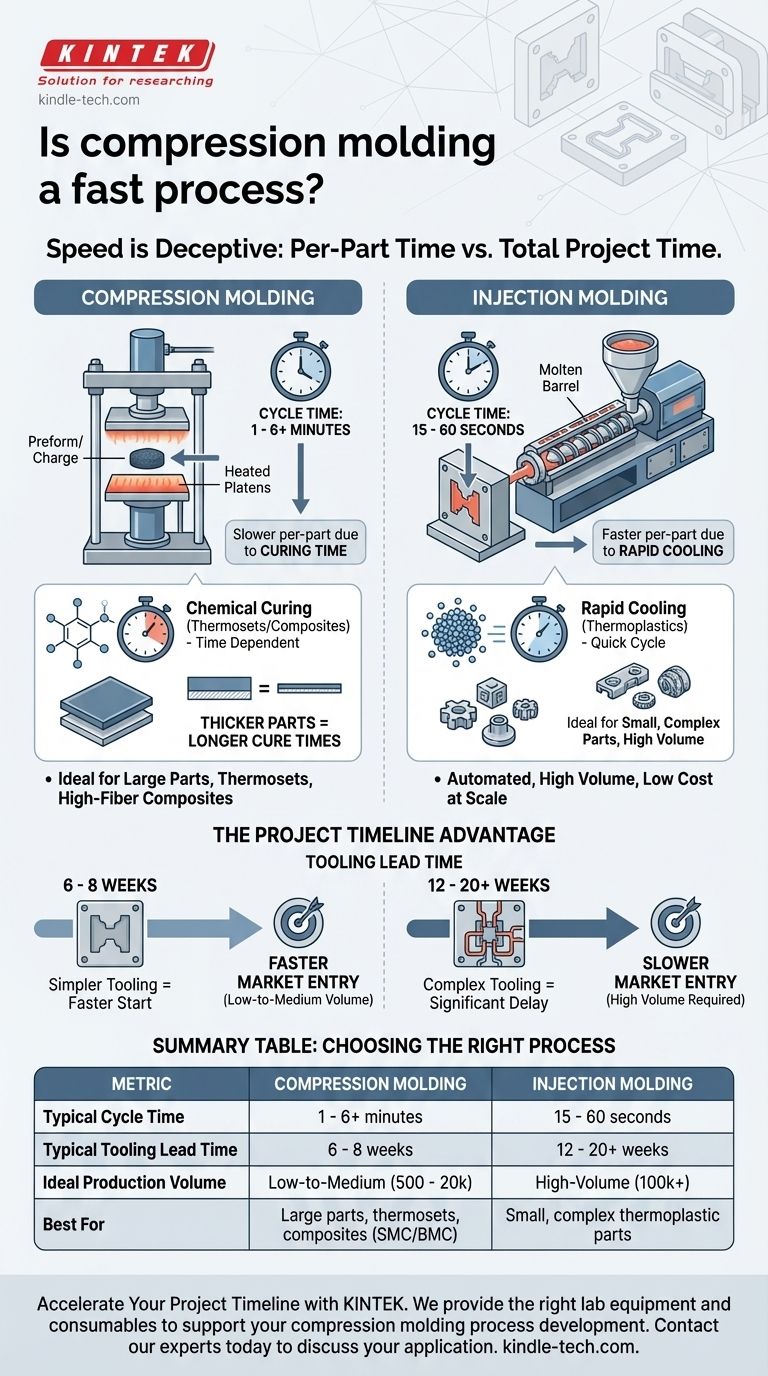
To be direct: compression molding is generally considered a slower process on a per-part basis when compared to high-volume methods like injection molding. Its cycle times are measured in minutes rather than seconds. However, this perspective is incomplete, as its simpler tooling requirements can significantly shorten the overall project timeline from design to first production run.
The speed of compression molding is deceptive. While individual part cycle times are longer, its faster and less expensive tooling can make it the quickest path to market for low-to-medium volume production, especially for large parts or specific composite materials.

What Defines the Speed of Compression Molding?
To understand the speed of the process, you must first understand its fundamental steps. The total cycle time is a sum of several distinct, often manual, stages.
The Core Process Steps
The cycle begins by placing a pre-measured amount of molding material, known as the charge or preform, into the heated lower half of a mold cavity.
The mold is then closed, applying immense pressure, which forces the material to fill the entire cavity. The combination of heat and pressure is maintained for a specific duration.
The Critical Role of Curing Time
This holding period, known as curing time, is typically the longest part of the cycle. During this phase, thermoset materials (like rubbers or phenolics) undergo a chemical cross-linking reaction, permanently hardening them.
Unlike the rapid cooling of thermoplastics in injection molding, this chemical curing is a time-dependent process that cannot be rushed without compromising the part's structural integrity.
Material Type and Part Thickness
The required curing time is heavily influenced by two factors: the material being used and the cross-sectional thickness of the part.
Thicker parts require longer cure times to ensure the core of the component reaches the necessary temperature and fully cures. Different materials also have inherently different curing characteristics.
Comparing Cycle Times: Compression vs. Injection Molding
The most common point of comparison for speed is injection molding. The two processes serve different needs and excel in different production scenarios.
The Injection Molding Advantage: Automation & Speed
Injection molding is a highly automated process designed for massive production volumes. Molten plastic is injected into a mold under high pressure, cooled rapidly, and then automatically ejected.
Cycle times for injection molding are incredibly short, often ranging from 15 to 60 seconds. This makes it unbeatable for producing millions of identical parts at a very low cost per piece.
The Compression Molding Niche: Simplicity & Materials
Compression molding cycles are much longer, typically ranging from 1 to 6 minutes, and can be even longer for very large or thick components.
However, it excels at forming materials that are difficult or impossible to injection mold, such as high-fiber composites (SMC/BMC), PTFE, and various thermoset rubbers.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Part Speed vs. Project Speed
Focusing only on the cycle time per part misses a critical part of the manufacturing equation: the time and cost required to get started.
Tooling Lead Time
This is where compression molding often has a significant advantage. The molds are simpler, as they do not require the complex runners, gates, and cooling channels of an injection mold.
A compression mold can often be designed and fabricated in 6-8 weeks. A complex injection mold can easily take 12-20 weeks or more, representing a major delay in getting a product to market.
Cost Per Part at Volume
The initial investment in an injection mold is substantially higher. This cost is justified when spread across hundreds of thousands or millions of parts.
For lower volumes (e.g., 500 to 20,000 units), the high cost of injection molding tooling can make the per-part cost prohibitive. The lower tooling cost of compression molding makes it far more economical for these production runs.
Part Geometry and Size
Compression molding is exceptionally well-suited for producing large, relatively simple parts, such as automotive body panels, electrical enclosures, or large gaskets. The gentle, even pressure is ideal for these geometries.
Injection molding, by contrast, is the superior choice for small, highly complex parts with intricate features and tight tolerances.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "fastest" process is the one that best aligns with your specific project requirements, from volume and material to budget and time-to-market.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production (100,000+ units) of thermoplastic parts: Injection molding's sub-minute cycle time is the clear winner for achieving the lowest cost per part.
- If your primary focus is a rapid launch or low-to-medium volume runs (under 20,000 units): Compression molding's shorter tooling lead time can get your product to market faster and more economically.
- If your primary focus is using specific thermosets or high-fiber composites: Compression molding is often the only viable process, making its cycle time a necessary parameter of working with these advanced materials.
Ultimately, viewing speed through the lens of your total project timeline—from initial tooling to final part—is the key to selecting the most effective process.
Summary Table:
| Metric | Compression Molding | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Cycle Time | 1 - 6+ minutes | 15 - 60 seconds |
| Typical Tooling Lead Time | 6 - 8 weeks | 12 - 20+ weeks |
| Ideal Production Volume | Low-to-Medium (500 - 20,000 units) | High-Volume (100,000+ units) |
| Best For | Large parts, thermosets, composites (SMC/BMC) | Small, complex thermoplastic parts |
Need to get your low-to-medium volume production to market faster?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables to support your material testing and process development for compression molding. Whether you're working with advanced composites, rubbers, or thermosets, our solutions can help you optimize your curing times and ensure part quality.
Let's accelerate your project timeline together. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and how we can support your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy



















