While many experts lean towards HPHT for inherent quality, neither method is definitively "better" than the other for the end consumer. HPHT diamonds are grown in a high-purity environment that often results in a higher-quality stone without further treatment, but this process is more expensive. CVD diamonds are cheaper to produce but frequently require post-growth treatments to enhance their color and clarity.
The choice between HPHT and CVD is not about which is superior, but about understanding their different manufacturing philosophies. HPHT mimics nature's force to create a high-quality diamond from the start, while CVD uses a more controlled, additive process that is often refined with treatment to achieve its final, excellent quality.
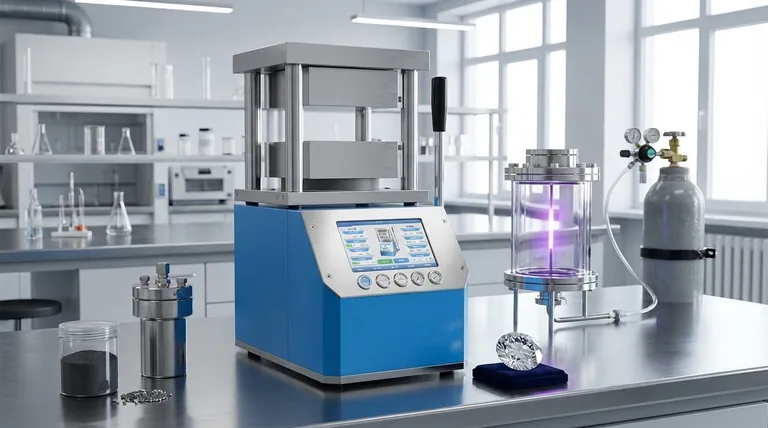

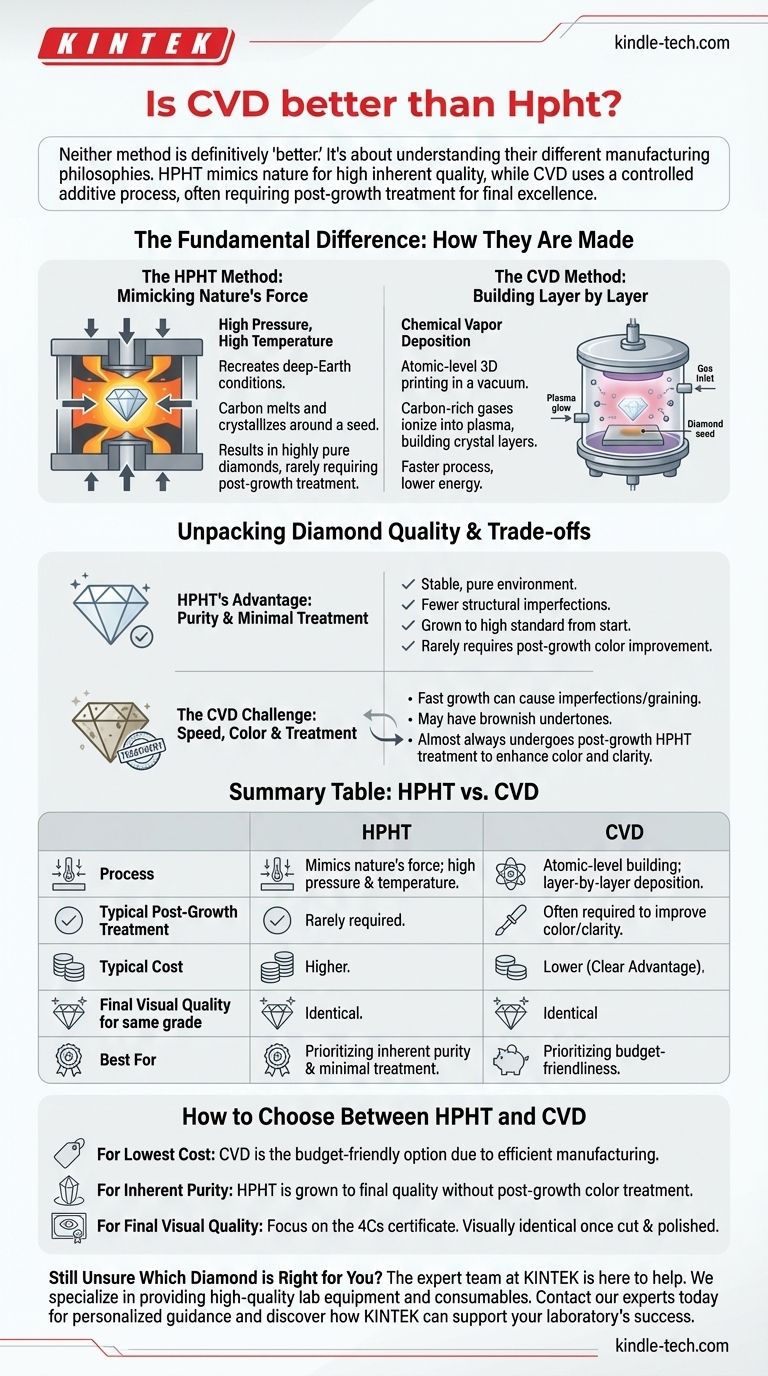
The Fundamental Difference: How They Are Made
To understand the difference in quality and cost, you must first understand the two distinct creation processes. Each method is a technological marvel that recreates conditions that take nature millions of years to achieve.
The HPHT Method: Mimicking Nature's Force
HPHT stands for High Pressure, High Temperature. This process mimics the natural geological conditions under which diamonds form deep within the Earth.
A small diamond "seed" is placed in a cell with a carbon source, such as graphite. The cell is then subjected to immense pressure and extreme heat, causing the carbon to melt and crystallize around the seed, forming a new, larger diamond.
The CVD Method: Building Layer by Layer
CVD, or Chemical Vapor Deposition, is more akin to atomic-level 3D printing. This method takes place inside a vacuum chamber at much lower pressures and temperatures than HPHT.
A diamond seed is placed in the chamber, which is then filled with carbon-rich gases. These gases are ionized into plasma, causing carbon atoms to break away and deposit onto the diamond seed, building up the crystal layer by layer.
Unpacking "Diamond Quality"
The term "quality" involves more than just the final look of the stone. It also includes the purity of the creation process and the presence of any structural imperfections.
The Purity Argument: HPHT's Advantage
The extreme environment of the HPHT process is very stable and pure. This results in diamonds that often have fewer structural imperfections.
Because of this, HPHT diamonds are typically grown to a high standard from the beginning and rarely require post-growth treatments to improve their color.
The CVD Challenge: Speed and Color
The CVD growth process is very fast, which can sometimes lead to imperfections like spotty internal marks or graining.
More significantly, CVD diamonds are known to sometimes grow with brownish undertones. To correct this, they almost always undergo a post-growth treatment to enhance their beauty and achieve a colorless state.
The Blurring Line: Post-Growth Treatment
This need for treatment is a critical distinction. Interestingly, the very same HPHT process is often used as a secondary treatment to purify CVD diamonds and improve their color.
This means a finished CVD diamond may have gone through both processes, blurring the lines between the two methods.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between HPHT and CVD requires balancing cost, process philosophy, and the final observable result.
Cost: CVD's Clear Advantage
The CVD method operates at moderate temperatures and lower pressure, requiring significantly less energy and less complex machinery than HPHT.
This efficiency translates directly to a lower production cost, making CVD diamonds generally the more affordable option for consumers comparing stones of the same final grade.
The Visual Reality: Can You Tell?
Here is the most important takeaway for a buyer: once cut, polished, and graded, it is impossible for a consumer to tell the difference between an HPHT and a CVD diamond of the same quality.
Even trained gemologists require sophisticated equipment to definitively identify the growth method. The differences are microscopic, not visible to the naked eye.
How to Choose Between HPHT and CVD
Your final decision should be guided by your personal priorities, not by a technical debate over which process is superior.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible cost for a given grade: CVD is almost always the more budget-friendly option due to its more efficient manufacturing process.
- If your primary focus is a diamond that is "pure" from its creation: HPHT is generally grown to its final quality without the need for post-growth color treatment.
- If your primary focus is simply the final visual quality: Concentrate on the diamond's certificate (the 4Cs), not the growth method, as high-quality examples from both are visually identical.
Ultimately, the "better" diamond is the one that meets your standards for beauty and budget, regardless of how it was grown.
Summary Table:
| Feature | HPHT Diamond | CVD Diamond |
|---|---|---|
| Process Philosophy | Mimics nature's force; high pressure & temperature | Atomic-level building; layer-by-layer deposition |
| Typical Post-Growth Treatment | Rarely required | Often required to improve color/clarity |
| Typical Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Final Visual Quality (for same grade) | Identical | Identical |
| Best For | Prioritizing inherent purity & minimal treatment | Prioritizing budget-friendliness |
Still Unsure Which Diamond is Right for You?
Choosing between HPHT and CVD is a significant decision. The expert team at KINTEK is here to help. We specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories and researchers.
Let us help you make an informed choice. Contact our experts today for personalized guidance and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of chemical vapour deposition techniques? A Guide to Choosing the Right CVD Method
- What is the function of an electro-thermal fluidized bed reactor? Achieve Precise Carbon Coating on Alumina Particles
- What is the difference between chemical vapour deposition and physical Vapour deposition? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Coating Process
- How does Vapour deposition work? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Coating Processes
- What is the CVD method of synthesis? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is meant by chemical vapour deposition? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Growth
- What is the full form of CVD in physics? A Guide to Chemical Vapor Deposition
- What is organic thin film? A Guide to Engineered Molecular Layers for Advanced Tech



















