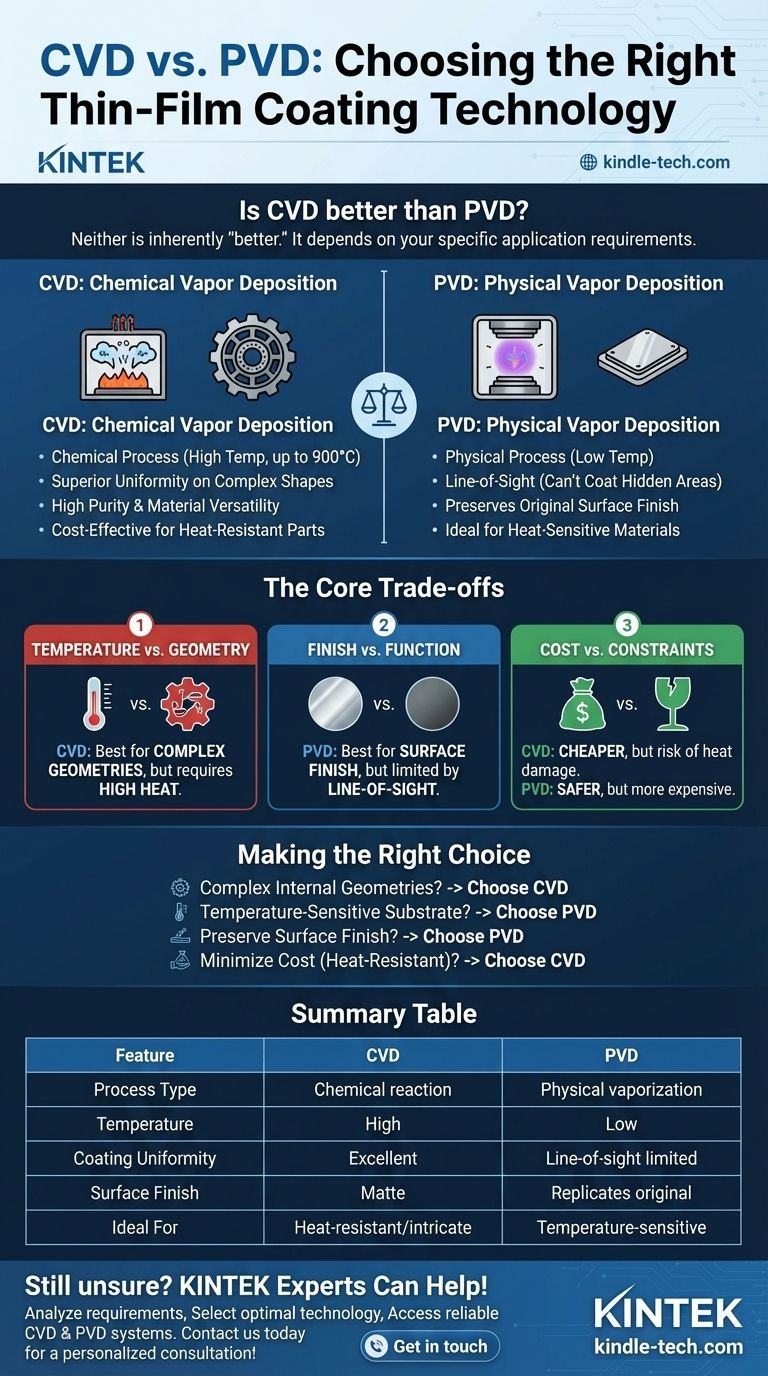
To be direct, neither CVD nor PVD is inherently "better" than the other. The superiority of one process over the other is entirely dependent on the specific requirements of your application. The core difference lies in their operating principles: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) uses a chemical reaction on a heated surface, while Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) uses a physical process to deposit a thin film in a vacuum. This fundamental distinction dictates which method is suitable for your material, geometry, and desired outcome.
The decision between CVD and PVD is a classic engineering trade-off. CVD offers unparalleled uniform coverage on complex shapes at a lower cost, but its high heat restricts its use. PVD operates at much lower temperatures, making it ideal for sensitive materials, but its line-of-sight nature limits its ability to coat intricate geometries.

The Fundamental Difference: Chemical vs. Physical
To choose correctly, you must first understand how each process works at a high level. Their names reveal their core mechanisms.
How Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) Works
CVD is a chemical process. Precursor gases are introduced into a chamber containing the substrate, which is heated to very high temperatures (often up to 900°C). The heat triggers a chemical reaction among the gases, causing a solid material—the coating—to form and deposit onto the substrate surface.
Because this process relies on a gas that surrounds the part, the coating forms uniformly over every exposed surface, regardless of its shape or complexity.
How Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Works
PVD is a physical process conducted in a vacuum. A solid source material (the coating) is physically vaporized into a plasma through methods like sputtering or evaporation. This vaporized material then travels in a straight line through the vacuum and condenses onto the substrate, forming a thin, hard coating.
Think of PVD as a highly advanced form of spray painting. It is a line-of-sight process, meaning it can only coat surfaces it can "see."
Where CVD Excels
The chemical nature of CVD gives it distinct advantages in specific scenarios.
Superior Conformality and Uniformity
Because the coating is formed from a reactive gas, CVD is not limited by line-of-sight. It can deposit a perfectly even layer inside deep holes, on complex internal features, and around intricate shapes. This is something PVD simply cannot achieve.
High Purity and Material Versatility
The CVD process can produce exceptionally high-purity, fine-grained, and dense coatings. It can also be used with elements that are difficult to evaporate for PVD but are available as volatile chemical compounds.
Cost-Effectiveness
For applications that can tolerate its high heat, CVD is often the cheaper process. It can be performed at atmospheric pressure and generally results in less material waste.
Where PVD Excels
The physical, lower-temperature nature of PVD makes it the only choice for other applications.
Low-Temperature Processing
This is the most significant advantage of PVD. Its operating temperatures are much lower than CVD's, making it safe for temperature-sensitive substrates. This includes hardened steels, aluminum alloys, and other materials that would be softened, warped, or destroyed by CVD's extreme heat.
Preservation of Surface Finish
PVD coatings meticulously replicate the original surface finish of the part. If you coat a polished component, the coated component will be polished. CVD, in contrast, typically creates a dull, matte finish that requires post-processing if a specific aesthetic is required.
No Post-Coating Heat Treatment
Parts coated with PVD are ready to use immediately. Because the process doesn't alter the substrate's heat treatment, no additional steps are needed to restore its material properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Your decision will almost always come down to balancing three key factors.
Temperature vs. Geometry
This is the central conflict. If your part has complex internal geometries but can withstand high heat, CVD is the ideal choice. If your part is made of a heat-sensitive material, PVD is your only viable option, and you must design around its line-of-sight limitations.
Finish vs. Function
You must decide if the final surface appearance is critical. If preserving a polished or specific texture is a requirement, PVD is the clear winner. If the coating's uniform functional performance is the only goal, the matte finish from CVD is often acceptable.
Cost vs. Process Constraints
While CVD can be cheaper per part, the potential cost of a ruined substrate due to heat damage can be immense. PVD is more expensive due to its complex vacuum and loading systems, but it provides a much safer process for valuable or sensitive components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these points as a definitive guide to select the appropriate technology.
- If your primary focus is coating complex internal geometries or deep features: Choose CVD for its superior ability to deposit a uniform layer without being limited by line-of-sight.
- If your primary focus is coating temperature-sensitive substrates (like tempered steel or certain alloys): PVD is the necessary choice due to its significantly lower processing temperatures.
- If your primary focus is preserving the original surface finish of a component: Select PVD, as it replicates the existing finish, whereas CVD typically results in a matte surface.
- If your primary focus is minimizing cost for heat-resistant parts: CVD is generally the more cost-effective option for creating highly uniform and durable coatings.
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently select the deposition technology that aligns perfectly with your material, design, and performance goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Chemical reaction | Physical vaporization |
| Temperature | High (up to 900°C) | Low |
| Coating Uniformity | Excellent on complex geometries | Line-of-sight limited |
| Surface Finish | Matte, may require post-processing | Replicates original finish |
| Ideal For | Heat-resistant parts with intricate shapes | Temperature-sensitive materials |
Still unsure whether CVD or PVD is right for your specific lab application?
KINTEK specializes in providing expert guidance and high-quality lab equipment for all your thin-film deposition needs. Our team can help you:
- Analyze your material properties and geometry requirements
- Select the optimal coating technology for your budget and performance goals
- Access reliable CVD and PVD systems and consumables
Contact our experts today to ensure you choose the perfect coating solution for your laboratory. Get in touch via our Contact Form for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD used for? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Performance Thin Films
- What materials are deposited in PECVD? Discover the Versatile Thin-Film Materials for Your Application
- What is PECVD silicon deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition process? Unlock Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films



















