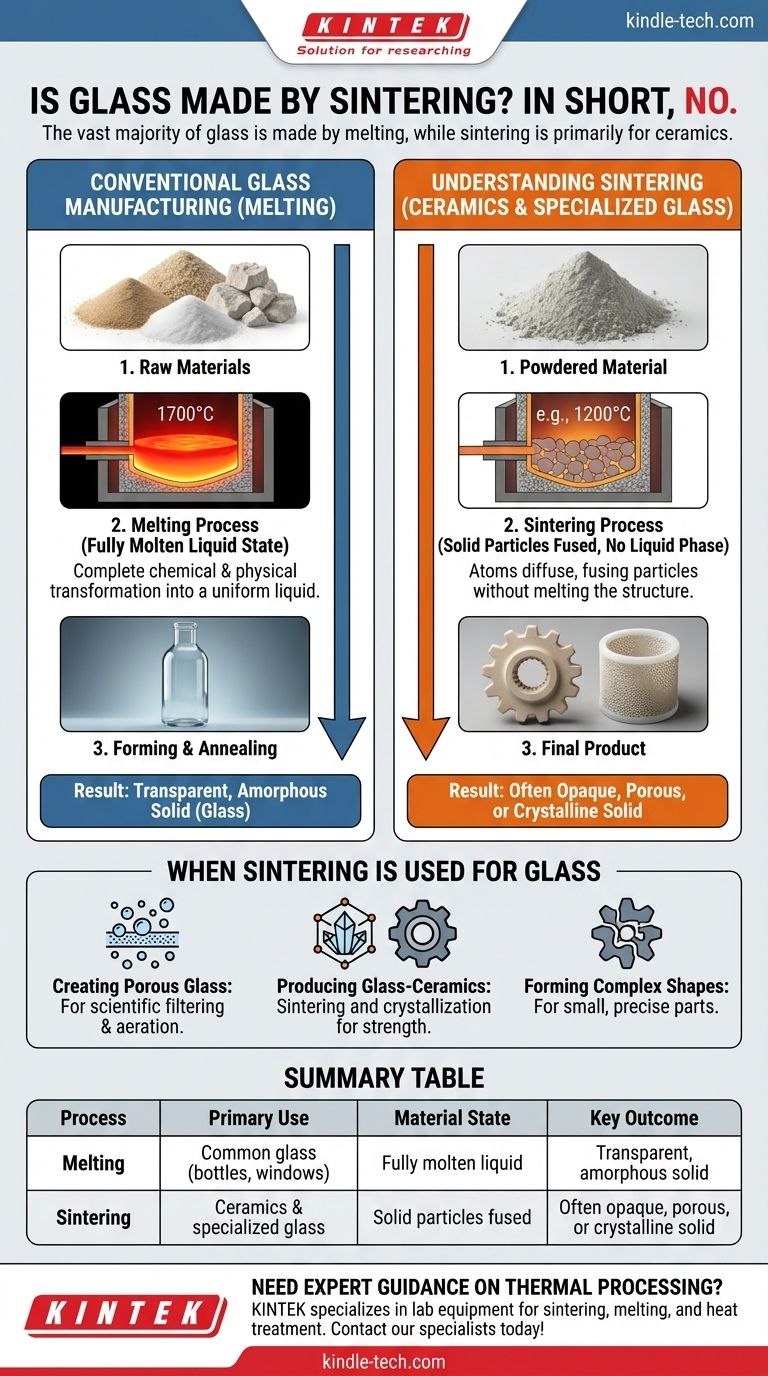
In short, no. The vast majority of glass products, like windows and bottles, are made by completely melting raw materials into a liquid and then cooling it. Sintering is a fundamentally different process used primarily for ceramics, although it is employed to create specialized glass products from powder.
The critical distinction lies in the state of the material: conventional glass manufacturing involves a fully molten liquid state, while sintering fuses solid particles together using heat, without ever reaching a complete liquid phase.
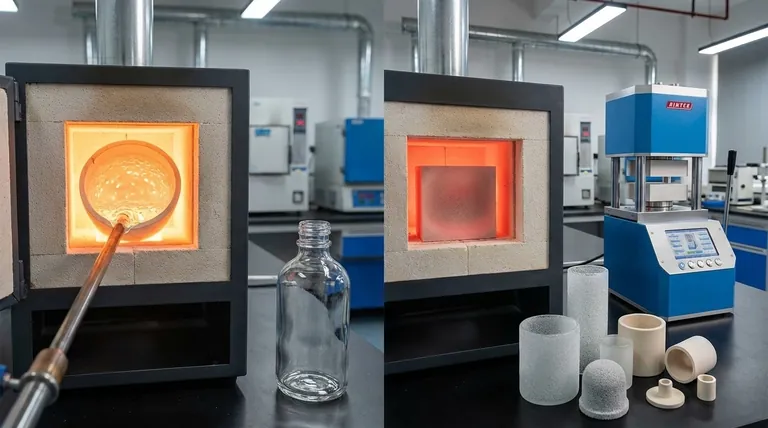
The Conventional Method: Melting and Cooling
To understand why sintering isn't the standard method, it's essential to first grasp how common glass is actually made. The process is one of complete chemical and physical transformation.
The Raw Materials
The journey begins with a mixture of raw materials, primarily silica sand (silicon dioxide), soda ash (sodium carbonate) to lower the melting point, and limestone (calcium carbonate) to improve stability.
The Melting Process
This mixture is heated in a furnace to extreme temperatures (around 1700°C or 3090°F) until it melts completely into a uniform, molten liquid. At this stage, all individual particles are gone, and the material is homogenous.
Forming and Annealing
This molten liquid is then shaped by blowing, pressing, or floating it on a bed of molten tin. It is then cooled in a controlled manner (annealing) to relieve internal stresses, resulting in the transparent, non-crystalline (amorphous) solid we know as glass.
Understanding Sintering: A Different Approach
Sintering is a thermal treatment for compacting and forming a solid mass of material from powder. It is the cornerstone of ceramic manufacturing.
What is Sintering?
Sintering uses heat to encourage atoms to diffuse across the boundaries of individual particles, fusing them together. Think of it as welding countless tiny particles into a single, solid piece without melting the entire structure.
The Sintering Mechanism
A compacted powder is heated to a temperature below its melting point. At this high temperature, the particles bond at their contact points, gradually reducing the empty space (porosity) between them and causing the object to densify and shrink.
When Sintering Is Used for Glass
While not the primary method, sintering is significant for manufacturing specific types of glass and glass-like materials where the properties of a powder starting material are an advantage.
Creating Porous Glass
Sintering glass powder (often called "frit") allows for the creation of porous glass components. These are used for scientific filtering, aeration (bubblers in fish tanks), and as support structures where fluid or gas flow is required.
Producing Glass-Ceramics
Sintering is a key step in making glass-ceramics. A glass object is first formed from powder, and then a carefully controlled heat treatment process (crystallization) transforms the non-crystalline glass into a fine-grained crystalline ceramic, giving it superior strength and thermal shock resistance.
Forming Complex Shapes
For small, highly intricate shapes that are difficult to mold from a viscous molten liquid, pressing and sintering glass powder can be a more precise and effective manufacturing technique.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Melting vs. Sintering
The choice between these two processes comes down to the desired outcome and the properties of the final product.
Transparency and Homogeneity
Melting is superior for achieving perfect transparency. The liquid state ensures a completely uniform, homogenous material with no internal boundaries to scatter light. Sintering often leaves behind microscopic pores that make the final product translucent or opaque.
Final Product Properties
Melting followed by rapid cooling is how you create an amorphous solid (glass). Sintering is the primary method for creating strong, hard crystalline solids (ceramics).
Energy and Temperature
While both are high-heat processes, sintering typically occurs at a lower temperature than what is required for complete melting. This can offer an energy advantage for materials with extremely high melting points.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The manufacturing method is dictated entirely by the material's intended structure and function.
- If your primary focus is a transparent, amorphous material like a windowpane or bottle: The required process is melting the raw materials into a homogenous liquid and cooling.
- If your primary focus is a strong, opaque, crystalline material like a coffee mug or tile: The required process is sintering a ceramic powder.
- If your primary focus is a specialty product like a lab filter or a high-strength glass-ceramic: The process starts with glass powder and utilizes sintering.
Ultimately, the choice is determined by whether the goal is to form a product from a uniform liquid or to fuse solid particles into a cohesive whole.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Use | Material State | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Melting | Common glass (bottles, windows) | Fully molten liquid | Transparent, amorphous solid |
| Sintering | Ceramics & specialized glass | Solid particles fused | Often opaque, porous, or crystalline solid |
Need expert guidance on thermal processing for your materials?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for sintering, melting, and heat treatment applications. Whether you are developing new glass-ceramics, porous filters, or optimizing a production process, our expertise can help you achieve superior results. Contact our specialists today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
People Also Ask
- What causes hydraulic pressure spikes? Prevent System Damage from Hydraulic Shock
- What are heated hydraulic presses used for? Molding Composites, Vulcanizing Rubber, and More
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- What is a hot hydraulic press? Harness Heat and Pressure for Advanced Manufacturing
- Why do you need to follow the safety procedure in using hydraulic tools? Prevent Catastrophic Failure and Injury



















