Yes, both pyrolysis and gasification are primary methods for the thermochemical conversion of biomass. They are advanced processes that use high heat to break down organic materials like wood waste, agricultural residue, or energy crops into more valuable and usable forms of energy, such as liquid fuels, combustible gases, and solid charcoal.
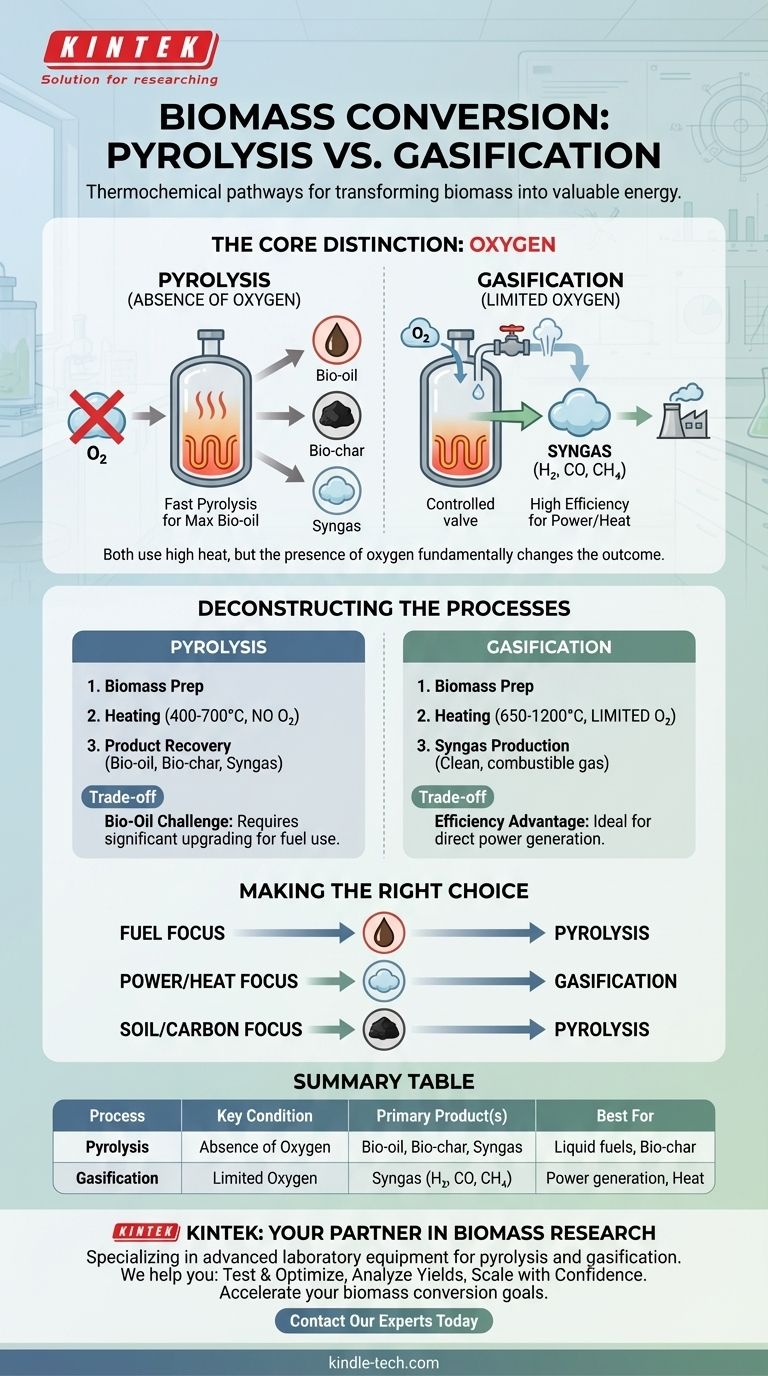
The core distinction between the two processes boils down to one critical element: oxygen. Pyrolysis is thermal decomposition in the complete absence of oxygen, while gasification is partial oxidation with a very limited and controlled supply of oxygen.

What is Biomass Conversion?
The Source Material: Biomass
Biomass is a broad term for any organic material derived from plants or animals.
This includes primary wood waste like chips and sawdust, dedicated energy crops like sugar cane, agricultural waste such as corn husks and nut shells, and even municipal solid waste.
The Goal of Conversion
The objective is to transform this raw, often low-density organic matter into energy-dense and versatile products. Instead of simply burning biomass for heat, these conversion technologies refine it into fuels or valuable chemical precursors.
Deconstructing Pyrolysis
The Core Process: Heating Without Oxygen
Pyrolysis involves heating biomass to high temperatures, typically between 400-700°C, in a reactor that is completely devoid of oxygen.
Think of it as "cooking" the material in a sealed container. Without oxygen, the biomass cannot combust; instead, its complex molecules break down into simpler, smaller components.
Key Outputs: A Mix of Products
This thermal decomposition yields three primary products:
- Bio-oil: A dark, thick liquid that can be upgraded into transportation fuels.
- Bio-char: A stable, carbon-rich solid similar to charcoal, which can be used as a soil amendment or for filtration.
- Syngas: A mixture of combustible gases, though typically in smaller quantities compared to gasification.
The Role of "Fast" Pyrolysis
Fast pyrolysis uses very high heating rates and short residence times (often less than two seconds) to maximize the yield of liquid bio-oil. This is the most common approach when the primary goal is producing a liquid fuel.
Deconstructing Gasification
The Core Process: Heating With Limited Oxygen
Gasification also uses high temperatures, often ranging from 650°C to over 1200°C. However, a controlled, sub-stoichiometric amount of an oxidizing agent (like air, pure oxygen, or steam) is intentionally introduced.
This limited oxygen is not enough for full combustion but is sufficient to convert the vast majority of the biomass into a gaseous product through a series of chemical reactions.
The Primary Output: Syngas
The main product of gasification is syngas, a combustible gas mixture composed primarily of hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), and methane (CH₄).
This gas can be burned directly in a turbine to generate electricity, used to produce heat, or further refined to create liquid fuels or valuable chemicals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Pyrolysis: The Bio-Oil Challenge
While fast pyrolysis is effective at producing liquid bio-oil, this liquid is not a drop-in replacement for gasoline or diesel. It is acidic, unstable, and contains impurities and tars that must be removed through a significant and costly upgrading process before it can be used as a transportation fuel.
Gasification: The Efficiency Advantage
Gasification is generally considered a highly efficient conversion method, particularly for power generation. The process results in high heat efficiency and minimal pollutant emissions compared to direct combustion, producing a clean, combustible gas as its main output.
Product Focus Dictates the Process
Your desired end product is the most critical factor in choosing a technology. If you need a liquid intermediate to refine into fuels, pyrolysis is the starting point. If you need a combustible gas for immediate power generation, gasification is the more direct and efficient route.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision between pyrolysis and gasification is driven entirely by the intended outcome.
- If your primary focus is producing a liquid fuel (bio-oil): Pyrolysis is the necessary pathway, but you must account for the significant downstream upgrading and refining required.
- If your primary focus is generating a combustible gas (syngas) for power or heat: Gasification is the more direct and efficient method, delivering a clean gaseous fuel as its main product.
- If your primary focus is creating solid bio-char for soil amendment or carbon sequestration: Pyrolysis is the process that yields bio-char as a major co-product alongside bio-oil.
Ultimately, both are powerful tools for converting biomass into value, but they are engineered to achieve fundamentally different results.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Condition | Primary Product(s) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pyrolysis | Heating in the absence of oxygen | Bio-oil, Bio-char, Syngas | Producing liquid fuel intermediates or solid bio-char |
| Gasification | Heating with a limited oxygen supply | Syngas (H₂, CO, CH₄) | Generating combustible gas for power/heat |
Ready to transform your biomass into valuable energy?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced laboratory equipment for biomass conversion research and development. Whether you are developing pyrolysis processes for bio-oil or optimizing gasification for syngas production, our reactors and analytical systems provide the precision and reliability you need.
We help you:
- Test and optimize conversion parameters for your specific biomass feedstock.
- Analyze product yields and quality with high accuracy.
- Scale your process from lab to pilot with confidence.
Let's discuss your project and how our expertise in lab equipment can accelerate your biomass conversion goals.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Double Layer Five-Port Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave in rGO/TiO2 synthesis? Key Role in Nanocomposites
- How does a high-pressure reactor facilitate the solvothermal synthesis? Master Supercritical Material Engineering
- Why is a high-pressure hydrothermal autoclave preferred for the synthesis of high-crystallinity nanocatalysts?
- How does a high-pressure hydrothermal autoclave facilitate the synthesis of BiVO4@PANI nanocomposites? Unlock Precision.
- What is the role of a high-pressure hydrothermal autoclave in the synthesis of MgAlCe-LDH? Optimize Crystal Growth



















