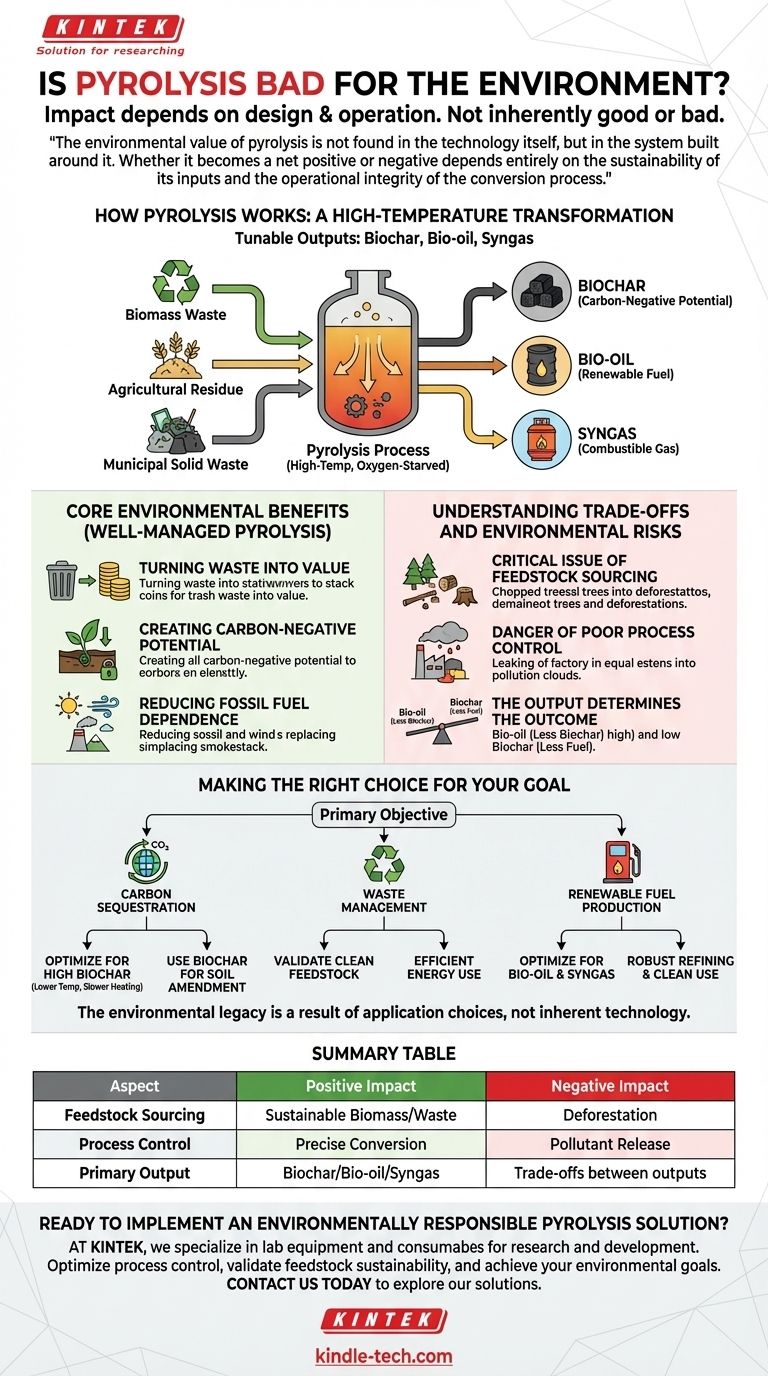
To be clear, pyrolysis is not inherently good or bad for the environment. Its impact is a direct consequence of how it is designed and operated, turning what could be a powerful environmental solution into a potential liability if managed poorly. The key determining factors are the sustainability of the biomass source and the precision of the process control.
The environmental value of pyrolysis is not found in the technology itself, but in the system built around it. Whether it becomes a net positive or negative depends entirely on the sustainability of its inputs and the operational integrity of the conversion process.

How Pyrolysis Works: A High-Temperature Transformation
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that decomposes organic material at elevated temperatures in the absence of oxygen. Think of it not as burning, but as a form of high-temperature, oxygen-starved cooking.
The Core Mechanism
Instead of combusting and releasing energy haphazardly, the process breaks down complex materials like wood waste, agricultural residue, or municipal solid waste into simpler, more stable products.
The Three Key Outputs
The final products depend on temperature and heating speed. By tuning the process, operators can prioritize the creation of biochar (a charcoal-like solid), bio-oil (a liquid fuel), or syngas (a combustible gas mixture).
The Core Environmental Benefits of Well-Managed Pyrolysis
When executed responsibly, pyrolysis offers significant environmental advantages by transforming waste streams into valuable, eco-friendly resources.
Turning Waste into Value
Pyrolysis provides a highly effective method for processing materials that might otherwise end up in a landfill. This includes agricultural residues, wood processing waste, and even certain components of municipal solid waste.
Creating Carbon-Negative Potential
The process can be a powerful tool for carbon sequestration. When biomass (which pulls CO2 from the atmosphere as it grows) is converted into biochar and that biochar is added to soil, the carbon is locked away for hundreds or even thousands of years, effectively removing it from the atmosphere.
Reducing Fossil Fuel Dependence
The bio-oil and syngas produced can be used as renewable energy sources. This displaces the need for fossil fuels, reducing the associated pollution and greenhouse gas emissions from conventional energy production.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Environmental Risks
The potential benefits of pyrolysis are matched by significant risks. An improperly managed operation can cause more harm than good.
The Critical Issue of Feedstock Sourcing
This is the single most important factor. If pyrolysis relies on biomass from unsustainable logging, it will lead directly to deforestation and habitat destruction. A pyrolysis plant is only as green as the material it consumes.
The Danger of Poor Process Control
A poorly designed or operated pyrolysis unit can be inefficient and release harmful pollutants. The process must be precisely controlled to ensure complete conversion and capture of all valuable products without fugitive emissions.
The Output Determines the Outcome
Maximizing one output often comes at the expense of another. A process optimized for bio-oil production (at high temperatures) will produce less biochar, reducing the system's carbon sequestration potential. The intended environmental goal must align with the operational parameters.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To evaluate the environmental impact of a pyrolysis project, you must first define its primary objective.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration: You must prioritize a process optimized for high biochar yield (lower temperatures, slower heating rates) and ensure the biochar is used for soil amendment.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Pyrolysis is an excellent option, but you must validate that the waste feedstock is clean and the energy produced is utilized efficiently.
- If your primary focus is renewable fuel production: The process should be optimized for bio-oil and syngas, but this comes with a lower carbon sequestration benefit and requires robust systems to refine and use the fuel cleanly.
Ultimately, the environmental legacy of pyrolysis is not inherent in the technology but is a direct result of the choices we make in its application.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Positive Impact | Negative Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Feedstock Sourcing | Uses sustainable biomass or waste | Causes deforestation if unsustainable |
| Process Control | Precise, efficient conversion | Releases pollutants if poorly managed |
| Primary Output | Biochar (carbon sequestration), bio-oil/syngas (renewable energy) | Trade-offs between outputs (e.g., less biochar for more fuel) |
Ready to implement an environmentally responsible pyrolysis solution? At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Our precision instruments help you optimize process control, validate feedstock sustainability, and achieve your environmental goals—whether carbon sequestration, waste management, or renewable fuel production. Contact us today to explore how our solutions can support your project's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the meaning of rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- What are the equipment for pyrolysis laboratory? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Research
- How does a rotary extractor work? Master Continuous High-Volume Solid Processing
- How does precision temperature control impact TiAl alloy sintering? Master Microstructure Development
- What is the drying zone in a rotary kiln? Boost Efficiency with Modern Drying Solutions



















