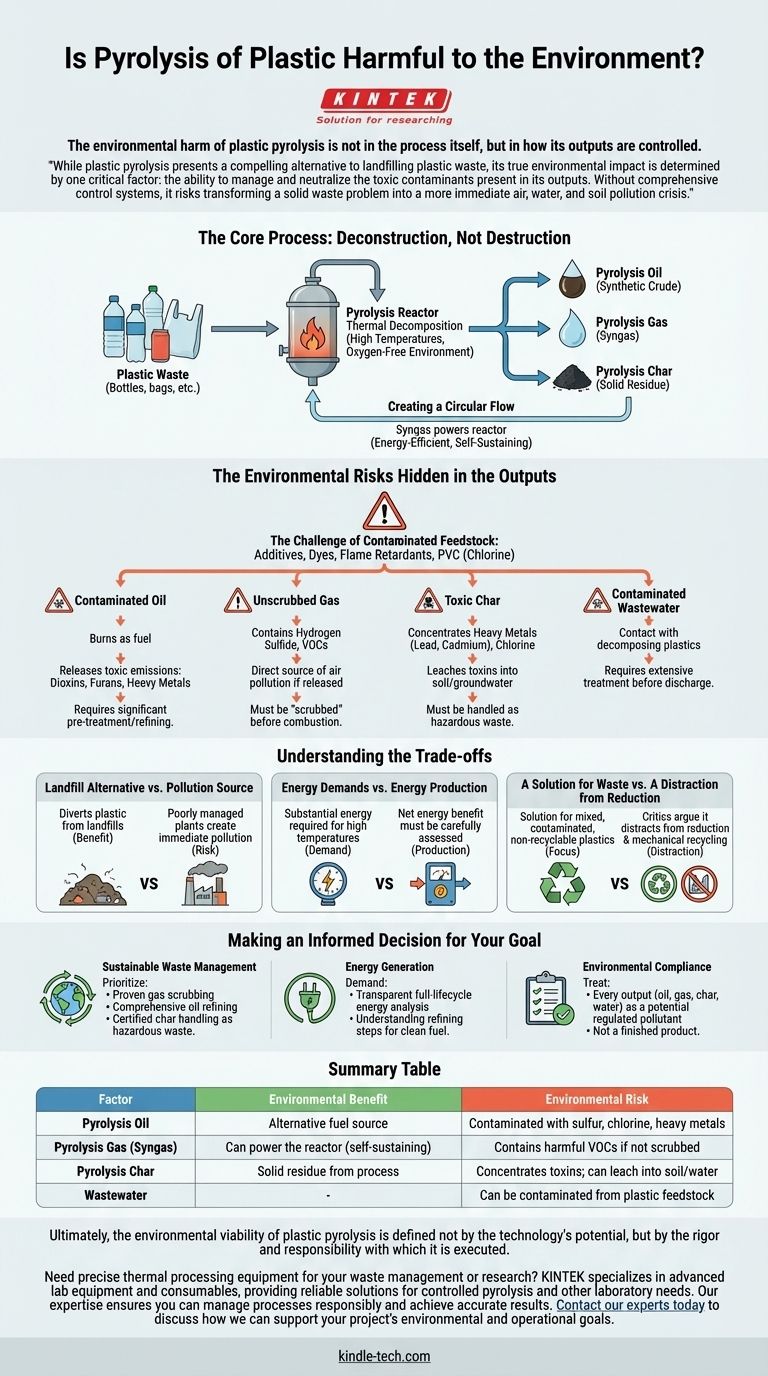
The environmental harm of plastic pyrolysis is not in the process itself, but in how its outputs are controlled. It is a technology with a dual nature: it can be a valuable tool for managing plastic waste that would otherwise go to a landfill, or it can be a significant source of pollution. The outcome depends entirely on the sophistication of the technology, the rigor of its operation, and the management of its byproducts.
While plastic pyrolysis presents a compelling alternative to landfilling plastic waste, its true environmental impact is determined by one critical factor: the ability to manage and neutralize the toxic contaminants present in its outputs. Without comprehensive control systems, it risks transforming a solid waste problem into a more immediate air, water, and soil pollution crisis.

The Core Process: Deconstruction, Not Destruction
Pyrolysis is a method of thermal decomposition, breaking down materials at high temperatures in an oxygen-free or low-oxygen environment. Unlike incineration, which burns waste, pyrolysis essentially "melts" and vaporizes long-chain plastic polymers into simpler, smaller molecules.
The Intended Outputs
The ideal goal of plastic pyrolysis is to create valuable commodities from waste. The primary outputs generated are pyrolysis oil (also called "Tire Pyrolysis Oil" or TPO when from tires), pyrolysis gas (syngas), and a solid carbon residue known as pyrolysis char.
Creating a Circular Flow
In a well-designed system, the syngas produced is often used to power the pyrolysis reactor itself. This creates a more energy-efficient, self-sustaining operation, reducing the need for external fossil fuels to power the process.
The Environmental Risks Hidden in the Outputs
The core environmental challenge stems from the fact that plastic waste is not a clean, homogenous feedstock. It contains additives, dyes, flame retardants, and contaminants like chlorine (from PVC plastics) which are concentrated and transformed during pyrolysis.
The Challenge of Contaminated Pyrolysis Oil
The liquid oil produced is often marketed as a synthetic crude oil. However, it can be laden with sulfur, chlorine, heavy metals, and other contaminants from the original plastic. Burning this oil as fuel without significant pre-treatment and refining can release toxic emissions like dioxins, furans, and heavy metals into the atmosphere.
The Hazard of Unscrubbed Pyrolysis Gas
The syngas, while useful as fuel, is not pure. It can contain harmful compounds like hydrogen sulfide and other volatile organic compounds (VOCs). If this gas is not properly "scrubbed" or cleaned before being combusted or released, it becomes a direct source of air pollution.
The Problem of Toxic Pyrolysis Char
The solid residue, or char, is not benign biochar. It acts like a sponge for heavy metals (such as lead and cadmium), chlorine, and other toxic substances present in the plastic waste. If this char is simply sent to a landfill, these toxins can leach into the soil and groundwater. It often must be handled as hazardous waste.
The Impact of Contaminated Wastewater
If the plastic feedstock contains moisture, the process will generate wastewater. This water comes into direct contact with the decomposing plastics and can become a contaminated stream that requires extensive treatment before it can be safely discharged.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Evaluating plastic pyrolysis requires an objective look at its place in the broader waste management landscape. It is not a perfect solution, but a complex tool with specific applications and drawbacks.
Landfill Alternative vs. Pollution Source
The primary argument for pyrolysis is that it diverts plastic from landfills, where it would sit for centuries. This is a significant benefit, but only if the pyrolysis plant itself does not create a more immediate pollution problem through its air emissions and hazardous byproducts. A poorly managed plant is arguably worse than a well-managed modern landfill.
Energy Demands vs. Energy Production
Pyrolysis requires a substantial amount of energy to reach and maintain its high operating temperatures. The net energy benefit—the energy value of the oil and gas produced minus the energy required to run the plant—must be carefully assessed. Inefficient systems may end up being net energy consumers.
A Solution for Waste vs. A Distraction from Reduction
Critics argue that focusing on "end-of-pipe" solutions like pyrolysis can distract from more fundamental goals: reducing plastic production, increasing reuse, and improving mechanical recycling for clean plastic streams. Pyrolysis is best positioned as a solution for mixed, contaminated, or non-recyclable plastics that have no other destination.
Making an Informed Decision for Your Goal
To determine if pyrolysis is an environmentally sound choice, you must look past the simple promise and scrutinize the operational details of a specific facility.
- If your primary focus is sustainable waste management: Prioritize facilities that have proven, state-of-the-art gas scrubbing technology, comprehensive plans for treating and refining the pyrolysis oil, and a certified process for handling the char as hazardous waste.
- If your primary focus is energy generation: Demand a transparent, full-lifecycle energy analysis. The value of the fuel produced is directly tied to its purity, so understand the refining steps required to make it a clean and usable energy source.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance: Treat every output—oil, gas, char, and water—as a potential regulated pollutant, not a finished product. The environmental integrity of the entire operation depends on managing these streams responsibly.
Ultimately, the environmental viability of plastic pyrolysis is defined not by the technology's potential, but by the rigor and responsibility with which it is executed.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Environmental Benefit | Environmental Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Pyrolysis Oil | Alternative fuel source | Contaminated with sulfur, chlorine, heavy metals |
| Pyrolysis Gas (Syngas) | Can power the reactor (self-sustaining) | Contains harmful VOCs if not scrubbed |
| Pyrolysis Char | Solid residue from process | Concentrates toxins; can leach into soil/water |
| Wastewater | - | Can be contaminated from plastic feedstock |
Need precise thermal processing equipment for your waste management or research? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable solutions for controlled pyrolysis and other laboratory needs. Our expertise ensures you can manage processes responsibly and achieve accurate results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your project's environmental and operational goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Does melting require increase in temperature? Understanding Latent Heat and Phase Changes
- What is the pressureless sintering process? A Guide to Simpler, Cost-Effective Material Consolidation
- How does Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) optimize additive manufactured Inconel 718? Achieve 100% Density and Integrity
- Why are anaerobic glove boxes and nitrogen purging systems required for SRB experiments? Ensure Optimal Oxygen Exclusion
- What is the process of thin film formation? A Guide to Atomic-Level Surface Engineering
- What are the ceramic materials applicable to sintering? A Guide to Choosing the Right Material
- What is the principle of wiped film molecular still? Preserve and Purify Heat-Sensitive Compounds
- How does temperature affect melting? Master Precise Control for Material Integrity



















