At its core, plastic pyrolysis is an industrial process with inherent hazards. Its safety is not guaranteed by the technology itself but is entirely dependent on the rigor of the engineering design, the quality of automated control systems, and the discipline of its human operators. While it can be operated safely, it is fundamentally unforgiving of negligence or design flaws.
The central issue is managing a high-temperature process that deliberately creates flammable gases and liquids inside a sealed, pressurized vessel. Safety, therefore, is not a feature to be added but the foundational principle around which the entire system must be built.

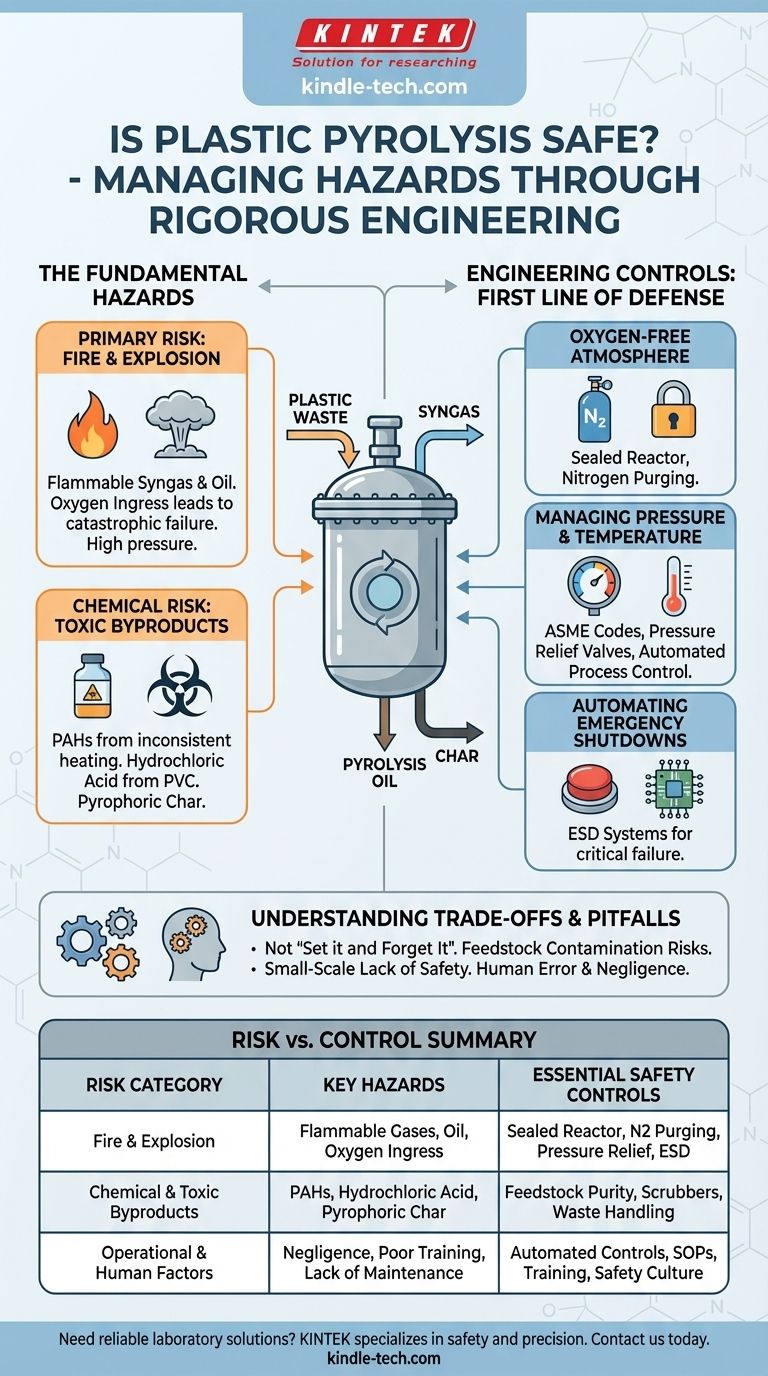
The Fundamental Hazards of Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis deconstructs plastics by heating them in an oxygen-free environment. This simple description hides a complex interplay of thermal, chemical, and pressure-related risks that must be actively managed.
The Primary Risk: Fire and Explosion
The process generates syngas, a mixture of flammable gases like hydrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide. This gas is a valuable fuel but also a significant explosion hazard if mixed with air.
Likewise, the liquid pyrolysis oil produced is a flammable, fuel-like substance that requires careful handling and storage protocols similar to those for diesel or gasoline.
The most critical failure mode is the accidental ingress of oxygen into the hot reactor. This can create an explosive atmosphere, which, when combined with the high temperatures, can lead to catastrophic failure of the vessel.
The Chemical Risk: Toxic Byproducts
While the goal is to create fuel, side reactions and feedstock contamination can produce hazardous materials. Inconsistent heating or poor process control can increase the formation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs).
Feedstock that contains chlorine, such as PVC plastics, will produce corrosive and toxic hydrochloric acid, which can damage equipment and pose a severe health risk.
The solid residue, or char, can sometimes be pyrophoric, meaning it can spontaneously ignite when exposed to oxygen in the air.
Engineering Controls: The First Line of Defense
A safe pyrolysis plant is a testament to robust engineering. Safety is built directly into the hardware and software that runs the process.
Maintaining an Oxygen-Free Atmosphere
The core of process safety is the sealed reactor. This system must be designed to prevent any air from leaking in. Industrial plants use nitrogen purging systems to flush out all oxygen before heating begins and to maintain a positive pressure of inert gas during operation.
Managing Pressure and Temperature
Reactors are built to strict industrial codes (like the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code) to withstand high operational pressures.
They are equipped with redundant pressure relief valves and rupture discs as mechanical failsafes. Sophisticated process control systems constantly monitor temperature and pressure, automatically adjusting heating to prevent dangerous excursions.
Automating Emergency Shutdowns
Modern plants rely on Emergency Shutdown (ESD) systems. These are automated safety protocols that can shut down the heaters, isolate the reactor, and vent pressure to a flare or scrubber in the event of a critical failure, often without human intervention.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
The gap between the theoretical promise of pyrolysis and its real-world execution is where safety is most often compromised. Understanding these pitfalls is crucial for any evaluation.
The Myth of "Set it and Forget It"
Pyrolysis systems are not simple appliances. They are complex chemical plants that demand constant monitoring, skilled operation, and a rigorous preventative maintenance schedule. Underestimating the operational complexity is a common and dangerous mistake.
The Danger of Feedstock Contamination
The safety and efficiency of pyrolysis are directly tied to the purity of the plastic feedstock. Mixed, dirty, or unverified plastic waste can introduce contaminants that create toxic outputs, corrode equipment, and disrupt the process, leading to unsafe conditions.
Small-Scale vs. Industrial-Scale Systems
Large, industrial-grade facilities often have the capital to invest in the sophisticated controls, redundancies, and automation required for safe operation.
Conversely, smaller or "backyard" scale units frequently lack these essential safety systems. They are far more susceptible to oxygen leaks, over-pressurization, and operator error, making them significantly more hazardous.
The Human Factor
Even the best-engineered plant can be rendered unsafe by poor operational discipline. Comprehensive operator training, strict adherence to Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), and a strong organizational safety culture are non-negotiable requirements. As the reference material notes, negligence is a primary cause of accidents.
Evaluating the Safety of a Pyrolysis Project
Your approach to verifying the safety of a pyrolysis operation should depend on your role and your objective.
- If your primary focus is investment or policy: Demand third-party verification of the plant's engineering standards (e.g., ASME, ATEX), the robustness of its automated safety systems, and the operator certification program.
- If your primary focus is plant operation or management: Prioritize the quality of the process control system, the clarity of the operational and emergency procedures, and the depth of the hands-on training provided.
- If your primary focus is community oversight: Insist on transparency regarding continuous emissions monitoring data, the facility's safety record, and its publicly available emergency response plan.
A truly safe pyrolysis operation is defined not by its promise, but by its demonstrable commitment to rigorous engineering and unwavering operational discipline.
Summary Table:
| Risk Category | Key Hazards | Essential Safety Controls |
|---|---|---|
| Fire & Explosion | Flammable syngas, pyrolysis oil, oxygen ingress | Sealed reactor, nitrogen purging, pressure relief valves, ESD systems |
| Chemical & Toxic Byproducts | PAHs, hydrochloric acid (from PVC), pyrophoric char | Feedstock purity, temperature control, scrubbers, proper waste handling |
| Operational & Human Factors | Negligence, poor training, lack of maintenance | Automated controls, SOPs, rigorous operator training, safety culture |
Need reliable, safe solutions for your laboratory processes? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables designed with safety and precision in mind. Whether you're managing thermal processes or handling complex materials, our products are engineered to meet rigorous standards. Contact us today to learn how we can support your laboratory's safety and efficiency goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success


















