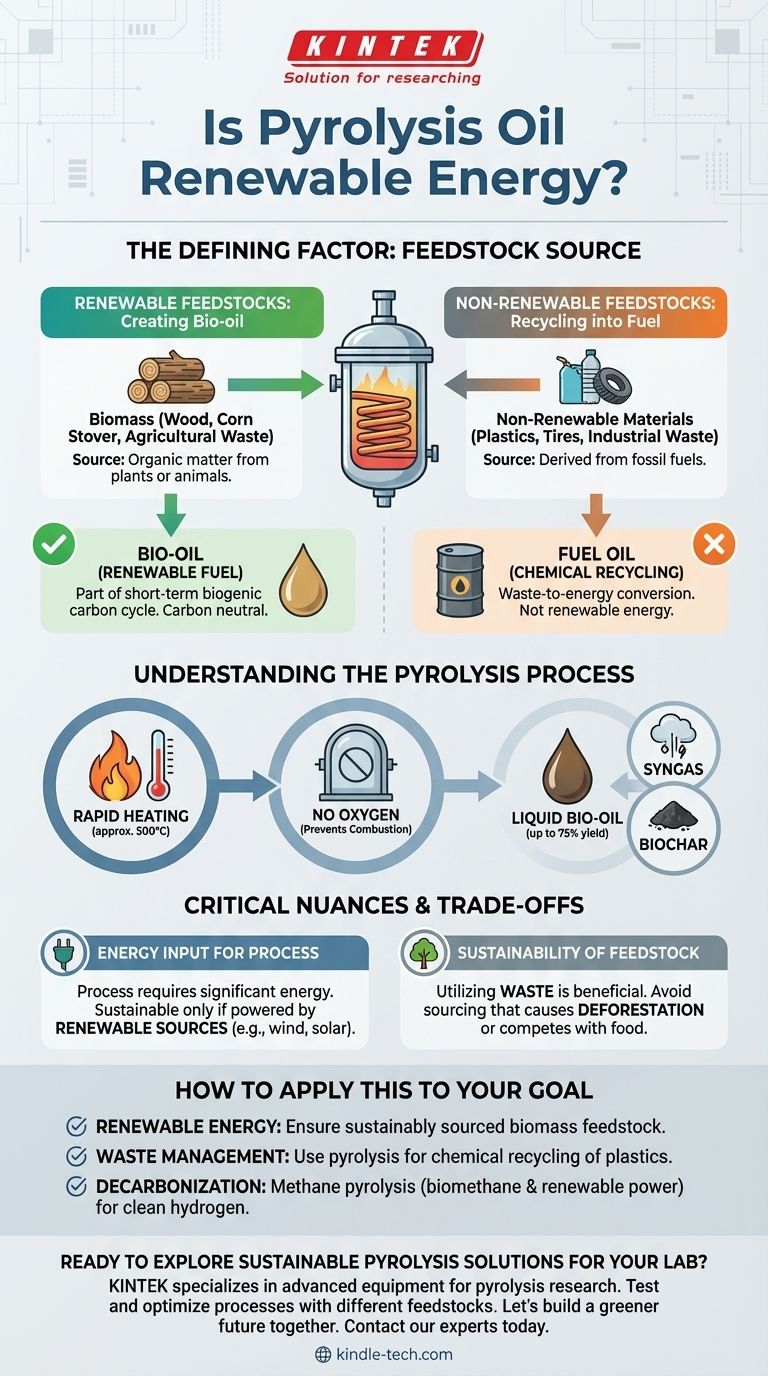
Yes, in the right context. Pyrolysis oil is considered a renewable energy source when it is produced from renewable organic materials, known as biomass. This process, called fast pyrolysis, converts materials like wood, corn stover, or perennial grasses into a liquid biofuel. However, the term "pyrolysis" describes a process, and its renewability is entirely dependent on the material being heated.
The critical factor determining if pyrolysis oil is renewable is not the process itself, but the feedstock used. If the feedstock is renewable (like plant biomass), the resulting oil is a renewable fuel. If the feedstock is non-renewable (like plastic waste), the oil is not.
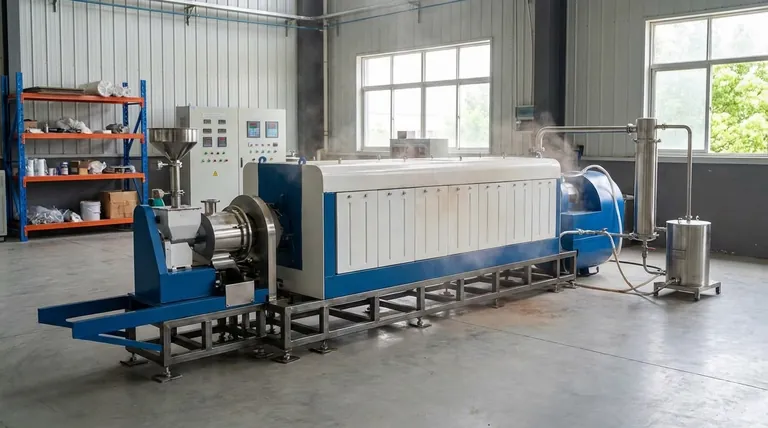

The Defining Factor: Feedstock Source
The source of the material put into a pyrolysis reactor is the single most important variable for determining its environmental classification.
Renewable Feedstocks: Creating Bio-oil
Pyrolysis of biomass produces a renewable fuel often called bio-oil. Biomass includes any organic matter derived from plants or animals, such as agricultural waste, forest residue, or dedicated energy crops.
This process is a key component of a renewable energy system because the carbon released when the bio-oil is burned is part of the natural, short-term biogenic carbon cycle. It is simply returning carbon that the plants absorbed from the atmosphere.
Non-Renewable Feedstocks: Recycling into Fuel
Pyrolysis can also be used to break down non-renewable materials like plastics, tires, and other industrial wastes. These materials are derived from fossil fuels.
While this is an effective method for waste management and creates a useful fuel oil, it is not a form of renewable energy. It is more accurately described as a form of chemical recycling or waste-to-energy conversion.
Understanding the Pyrolysis Process
To understand the context, it's helpful to know what happens inside a reactor.
The Core Mechanism
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that involves rapidly heating a material to high temperatures (around 500°C) in an environment without oxygen.
The absence of oxygen is crucial. It prevents the material from combusting (burning) and instead causes it to break down into smaller molecules, which are then rapidly cooled and condensed.
Primary Products
The main output of biomass pyrolysis is a liquid bio-oil, which can be refined into transportation fuels or used for heat and power. The process is highly efficient, capable of converting up to 75% of the initial biomass into oil.
Other products include syngas (a combustible gas mixture) and biochar (a form of solid carbon that can be used as a soil amendment).
Critical Nuances and Trade-offs
Labeling pyrolysis oil as "renewable" requires looking at the entire lifecycle, not just the final product.
Energy Input for the Process
The pyrolysis process itself requires a significant energy input to reach its high operating temperatures. For the entire system to be truly sustainable, this energy should come from a renewable source.
For example, some modern systems use microwaves powered by intermittent renewables (like wind or solar) to drive the reaction, which greatly improves the overall environmental profile.
Sustainability of the Feedstock
Even when using biomass, the sustainability of its sourcing is a critical factor. Using agricultural or forestry waste is highly beneficial.
However, if biomass sourcing leads to deforestation or competes with land used for food production, it can have significant negative environmental consequences that undermine its "renewable" credentials.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your evaluation of pyrolysis oil depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is generating truly renewable energy: You must ensure the pyrolysis process uses a sustainably sourced biomass feedstock, like agricultural residue or non-food energy crops.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Pyrolysis is an excellent technology for converting hard-to-recycle materials like plastics into a usable fuel, but this should be categorized as chemical recycling, not renewable energy.
- If your primary focus is decarbonization via hydrogen: Methane pyrolysis can produce clean hydrogen and solid carbon, but it is only a green solution if the feedstock is biomethane (from renewable sources) and the process is powered by renewable electricity.
Ultimately, pyrolysis is a powerful and flexible conversion technology whose environmental benefit is defined by the choices made about what goes in and how it is powered.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Determines Renewable Status |
|---|---|
| Feedstock Source | Biomass (e.g., wood waste, crops) = Renewable. Plastic/fossil-fuel waste = Not renewable. |
| Process Energy | Powered by renewables (solar, wind) = More sustainable. |
| Carbon Cycle | Biomass oil uses short-term biogenic carbon, making it carbon-neutral. |
Ready to explore sustainable pyrolysis solutions for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment for pyrolysis research and development. Whether your goal is to produce renewable bio-oil from biomass or to advance chemical recycling processes, our reactors and systems are designed for precision, efficiency, and scalability.
We help you:
- Test and optimize processes with different feedstocks.
- Achieve high conversion efficiencies for your specific application.
- Integrate sustainable energy sources into your workflow.
Let's build a greener future together. Contact our experts today to discuss how our pyrolysis solutions can meet your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the temperature control of a laboratory oven affect bimetallic catalysts? Ensure Optimal Metal Dispersion
- What are the defects that occur during heat treatment of steel? Prevent Cracking, Warping & Soft Spots
- What is the role of thin films in devices? The Invisible Engine of Modern Technology
- What is the future scope of pyrolysis? Unlocking Circular Economy Potential with Waste-to-Resource Tech
- What is chemical sputtering? Create Advanced Ceramic & Nitride Films with Reactive Sputtering
- What does a heat treatment do? Unlock Your Material's Full Potential
- How do you measure ash content? Choose the Right Method for Accurate Results
- How does heat treatment affect metal microstructure? Unlock Desired Hardness, Toughness, and Ductility



















