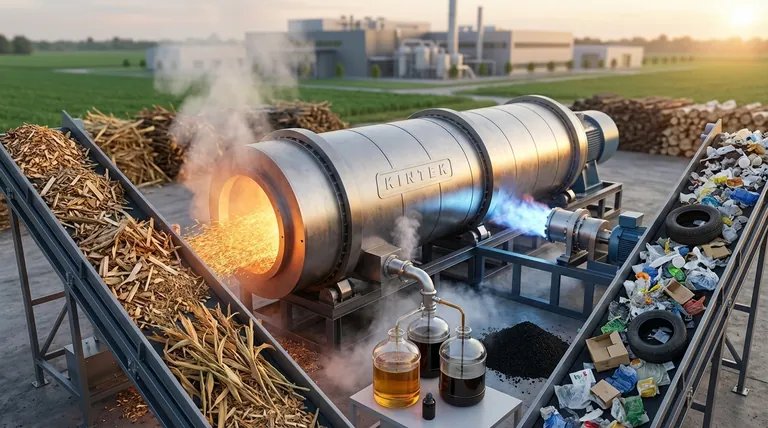
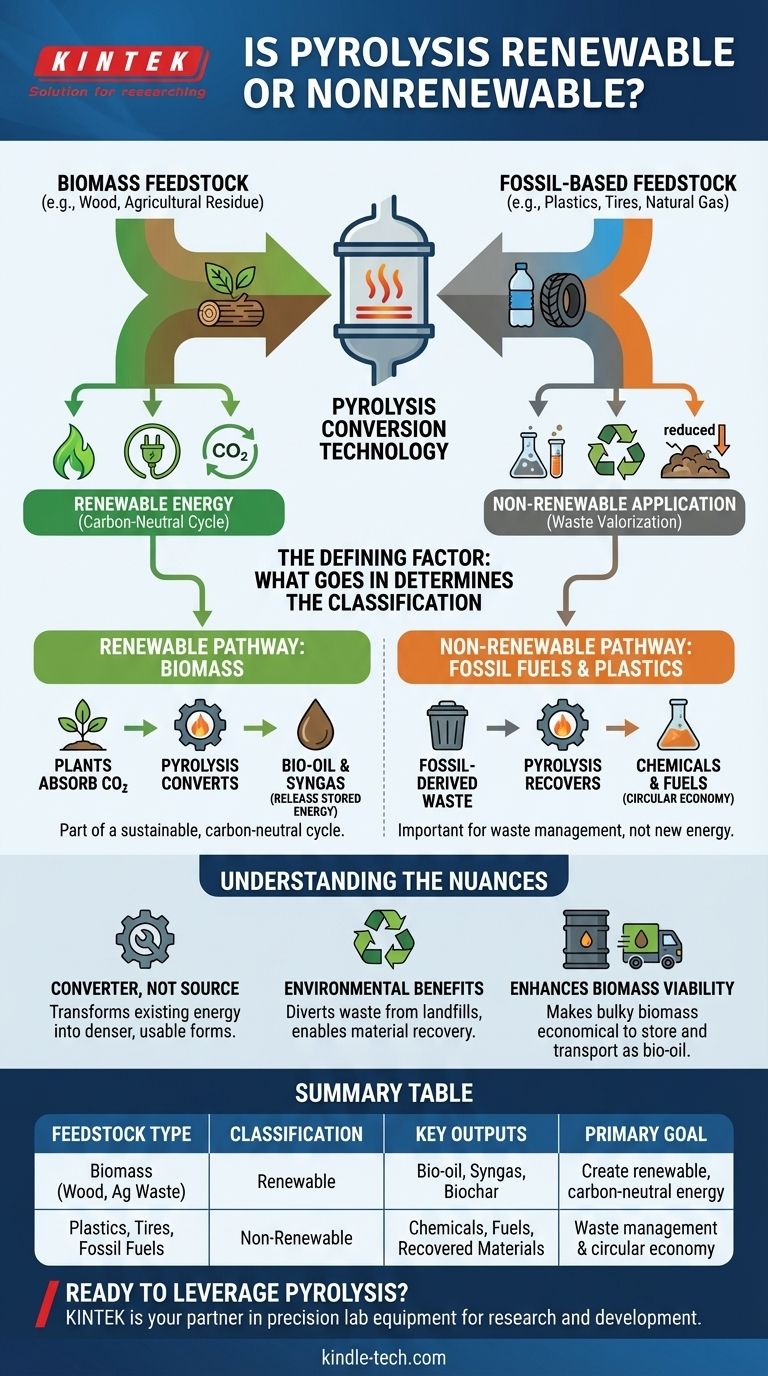
The renewability of pyrolysis is determined entirely by its input material, or "feedstock." When pyrolysis processes renewable biomass like wood, agricultural residue, or organic waste, the resulting energy is classified as renewable. However, if the process uses fossil-fuel-derived materials such as plastics, tires, or natural gas, it is considered a non-renewable application, even though it can provide significant environmental benefits.
Pyrolysis is a conversion technology, not a source of energy in itself. Its classification as renewable or non-renewable depends entirely on the feedstock it processes—biomass makes it renewable, while fossil-based materials like plastic or natural gas make it non-renewable.

The Defining Factor: What Goes In
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that uses high heat in an oxygen-free environment to decompose materials. Think of it not as burning, but as intensely "cooking" a substance until it breaks down into valuable new components. The nature of those original materials is what matters.
The Renewable Pathway: Biomass
When the feedstock is biomass—organic matter like wood, corn stover, or perennial grasses—the process is part of a renewable cycle.
Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere as they grow. Pyrolysis converts this biomass into bio-oil, releasing the stored energy. This is considered carbon-neutral because the carbon released originated from the atmosphere, not from ancient fossil reserves.
The Non-Renewable Pathway: Plastics and Fossil Fuels
When pyrolysis processes materials like plastics, car tires, or natural gas (methane), the feedstock is derived from fossil fuels.
While this is not a renewable process, it serves a different but equally important purpose: waste valorization. It turns landfill-bound waste into valuable chemicals or energy, recovering resources that would otherwise be lost and reducing the need to extract virgin raw materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
Viewing pyrolysis as simply "renewable" or "non-renewable" overlooks its flexibility. The context of its application is critical.
It's a Converter, Not a Source
Pyrolysis does not create energy from nothing. It transforms the chemical energy already stored in the feedstock into a more usable and energy-dense form, such as liquid bio-oil.
The process can be highly efficient, with the energy value of the outputs often exceeding the external energy required to power the reactor.
Environmental Benefits Beyond Renewability
Even when using a non-renewable feedstock like plastic, pyrolysis offers significant environmental advantages.
It diverts massive amounts of waste from landfills, reduces pollution, and enables a circular economy by recovering raw materials. For example, breaking down plastics back into chemical building blocks reduces our reliance on new oil extraction.
Enhancing the Viability of Biomass
A major challenge for biomass energy is that the raw material is bulky, wet, and costly to transport.
Pyrolysis solves this by converting solid biomass into a dense, stable liquid bio-oil. This makes it far more practical and economical to store and transport energy from remote agricultural or forested areas.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply pyrolysis effectively, you must first define your primary objective. The "best" feedstock depends entirely on the problem you are trying to solve.
- If your primary focus is creating truly renewable fuel: Concentrate on pyrolysis systems that use certified sustainable biomass or organic waste streams.
- If your primary focus is waste management and circular economy: Pyrolysis of plastics and tires is a valid and powerful tool, even though the feedstock itself is non-renewable.
- If your primary focus is grid stability and hydrogen production: Methane pyrolysis, especially when powered by renewable electricity, offers a pathway to produce low-carbon hydrogen from existing natural gas infrastructure.
Ultimately, viewing pyrolysis as a flexible conversion tool, rather than a fixed energy source, is the key to leveraging its true potential.
Summary Table:
| Feedstock Type | Classification | Key Outputs | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biomass (Wood, Agricultural Waste) | Renewable | Bio-oil, Syngas, Biochar | Create renewable, carbon-neutral energy |
| Plastics, Tires, Fossil Fuels | Non-Renewable | Chemicals, Fuels, Recovered Materials | Waste management & circular economy |
Ready to leverage pyrolysis technology for your specific goals?
Whether your primary focus is developing sustainable, renewable energy from biomass or implementing advanced waste valorization solutions, KINTEK is your partner in precision. We specialize in supplying high-quality lab equipment and consumables essential for pyrolysis research, development, and quality control.
Our expertise helps you accurately analyze feedstocks, optimize process parameters, and characterize outputs like bio-oil and biochar. By choosing KINTEK, you gain a reliable partner dedicated to supporting your innovation in renewable energy and circular economy projects.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our laboratory solutions can accelerate your pyrolysis research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions



















