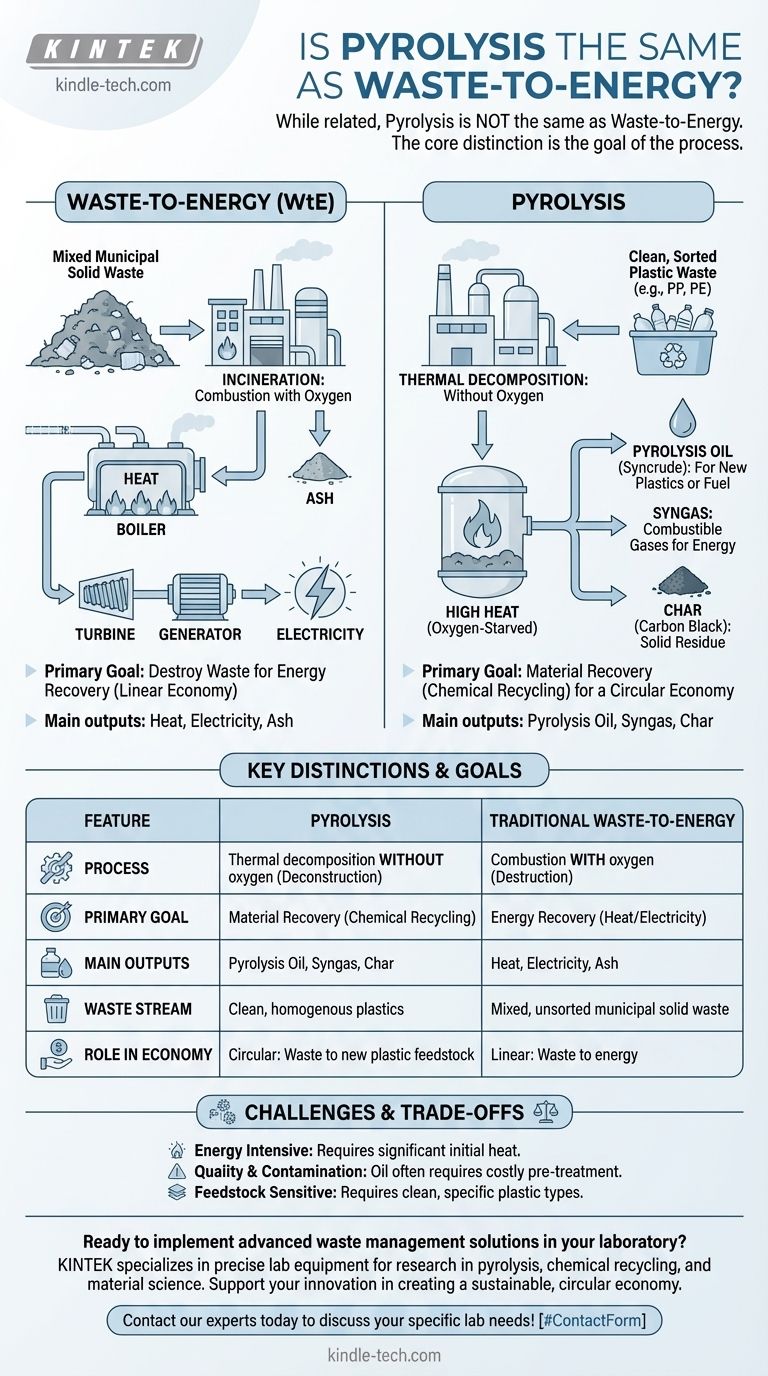
While related, pyrolysis is not the same as waste-to-energy. Pyrolysis is a specific thermal process that breaks down materials like plastic in the absence of oxygen. "Waste-to-energy" is a much broader category of technologies whose primary goal is to produce heat and electricity from waste, most commonly through incineration (burning). Pyrolysis can be used to create fuels for energy, but its unique potential lies in creating feedstocks for new materials.
The core distinction is the goal of the process. Traditional waste-to-energy aims to destroy waste for energy recovery. Pyrolysis aims to deconstruct waste into valuable chemical components for material recovery, a process often called chemical recycling.

What is Waste-to-Energy?
An Umbrella Term for Energy Recovery
"Waste-to-energy" (WtE) is not a single technology but a category of processes that convert non-recyclable waste into usable energy in the form of electricity, heat, or fuel.
The most established and common form of WtE is incineration.
The Incineration Model
Incineration is the controlled combustion of waste with oxygen. This process burns the waste at high temperatures, releasing a tremendous amount of heat.
This heat is used to boil water, creating high-pressure steam. The steam then drives a turbine to generate electricity, making it a method for energy recovery from materials that would otherwise go to a landfill. The primary solid byproduct is ash.
How Pyrolysis is Different
Thermal Decomposition Without Oxygen
Pyrolysis is fundamentally different from incineration because it heats materials, typically plastic waste, to very high temperatures in an oxygen-starved environment.
Because there is no oxygen, the material does not combust or burn. Instead, the long polymer chains that make up plastics break down into smaller molecules.
The Primary Outputs: Oil, Gas, and Char
Instead of just producing heat and ash, pyrolysis creates three distinct products:
- Pyrolysis Oil (Syncrude): A liquid mixture of hydrocarbons that can be refined into diesel fuel or, more importantly, processed into a feedstock to create new plastics.
- Syngas: A mixture of combustible gases (like hydrogen and methane) that is often used to provide the energy needed to power the pyrolysis process itself, making it partially self-sustaining.
- Char (Carbon Black): A solid, carbon-rich residue that can be used in applications like filtration, soil amendment, or as a pigment.
The Goal: Chemical Recycling
The ability to turn pyrolysis oil back into the building blocks for new plastics is the key differentiator. This positions pyrolysis as a form of chemical recycling or "advanced recycling."
Instead of a one-way path from waste to energy, pyrolysis offers a potential pathway to a circular economy, where plastic waste is turned back into plastic.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Energy Input vs. Output
Pyrolysis is an energy-intensive process that requires a significant initial heat input. A key point of technical and economic viability is whether the energy value of the resulting oil and gas is greater than the energy required to run the process.
Quality and Contamination of Pyrolysis Oil
The liquid produced is not a "drop-in" replacement for crude oil. It is often acidic and contaminated with chlorine, nitrogen, and other elements from the original plastic waste.
This oil requires significant, costly, and energy-intensive pre-treatment and upgrading before it can be used by a conventional refinery or plastics plant.
Environmental and Feedstock Limitations
Pyrolysis is highly sensitive to the type of waste it processes. To produce a high-quality oil, it requires a very clean and homogenous stream of specific types of plastic. Contaminants can create toxic byproducts and degrade the quality of the outputs.
While it avoids the direct emissions of incineration, the overall environmental footprint, including the energy for pre-sorting waste and upgrading the oil, must be carefully assessed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The choice between these technologies depends entirely on the desired outcome for a given waste stream.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy generation from mixed, unsorted municipal waste: Conventional waste-to-energy (incineration) is the more direct, established, and scalable pathway for energy recovery.
- If your primary focus is recovering material value from specific, clean plastic waste streams: Pyrolysis offers a potential route for chemical recycling, turning that waste back into a feedstock for new materials and contributing to a circular economy.
Understanding the distinction between simple energy recovery and complex material recovery is the key to evaluating modern waste solutions effectively.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Pyrolysis | Traditional Waste-to-Energy (Incineration) |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Thermal decomposition WITHOUT oxygen | Combustion WITH oxygen |
| Primary Goal | Material Recovery (Chemical Recycling) | Energy Recovery (Heat/Electricity) |
| Main Outputs | Pyrolysis Oil, Syngas, Char | Heat, Electricity, Ash |
| Waste Stream | Clean, homogenous plastics (e.g., PP, PE) | Mixed, unsorted municipal solid waste |
| Role in Economy | Circular: Waste to new plastic feedstock | Linear: Waste to energy |
Ready to implement advanced waste management solutions in your laboratory?
KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for research and development in pyrolysis, chemical recycling, and material science. Whether you are exploring new feedstocks, optimizing processes, or analyzing outputs, our reliable tools help you achieve accurate and reproducible results.
Let us support your innovation in creating a sustainable, circular economy.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific lab needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products



















