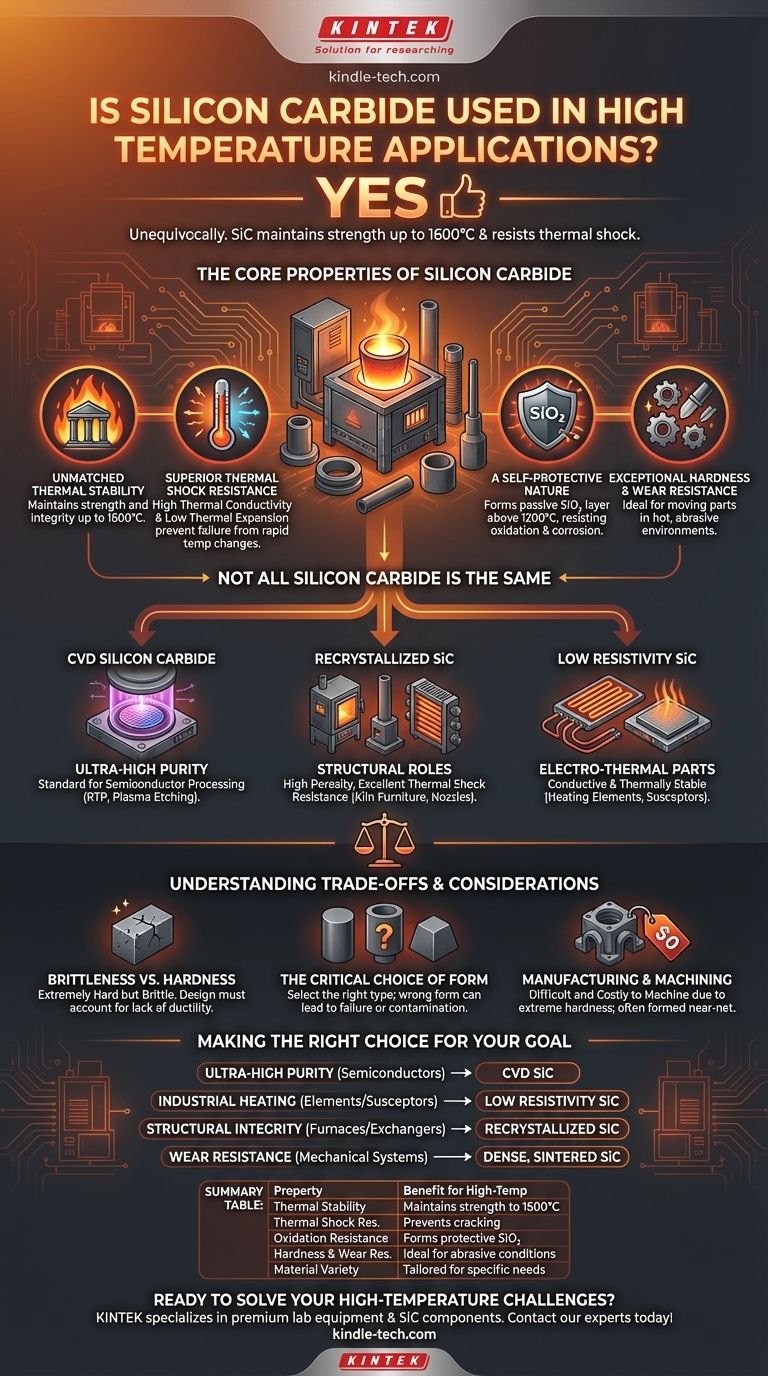
Unequivocally, yes. Silicon carbide is a premier material for high-temperature applications. It stands out because it maintains its mechanical strength at temperatures up to 1600°C and possesses an exceptional ability to resist thermal shock—the failure that occurs from rapid temperature changes. This resilience is due to its unique combination of high thermal conductivity, low thermal expansion, and inherent strength.
Silicon carbide's value is not just in withstanding high heat, but in its ability to maintain structural and mechanical integrity under extreme thermal cycling and chemically aggressive conditions where most metals would fail.

The Core Properties of Silicon Carbide
To understand why silicon carbide is so effective, we must look at its fundamental physical properties. These characteristics work in concert to create a uniquely robust material.
Unmatched Thermal Stability
Silicon carbide does not lose strength at elevated temperatures like metals do. It maintains its structural integrity and mechanical strength up to 1600°C.
This makes it an ideal candidate for components inside industrial furnaces, engines, and other environments defined by extreme, sustained heat.
Superior Thermal Shock Resistance
Thermal shock happens when a material expands or contracts too quickly due to a rapid temperature change, causing it to crack.
Silicon carbide mitigates this risk through two key properties: high thermal conductivity (it dissipates heat quickly) and low thermal expansion (it doesn't change size dramatically when heated).
A Self-Protective Nature
When heated above 1200°C, silicon carbide forms a protective, passive layer of silicon oxide (SiO₂). This coating acts as a barrier, significantly increasing its resistance to oxidation and chemical corrosion at high temperatures.
Exceptional Hardness and Wear Resistance
Historically used for abrasives and cutting tools, silicon carbide's inherent hardness translates directly to its performance in high-temperature applications. This makes it suitable for moving parts like pump components, sealing rings, and sliding bearings that must operate in hot, abrasive environments.
Not All Silicon Carbide Is the Same
The term "silicon carbide" refers to a family of materials, each tailored for specific needs. Choosing the right type is critical for success.
CVD Silicon Carbide for Purity
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) silicon carbide is exceptionally pure. This makes it the standard for semiconductor processing equipment, such as chamber components for rapid thermal processing (RTP) and plasma etching.
Its purity and resistance to erosion from high-energy plasmas ensure that the semiconductor manufacturing process is not contaminated.
Recrystallized SiC for Structural Roles
This form of SiC has high porosity but excellent thermal conductivity and shock resistance. Its structure makes it perfect for applications like high-temperature kiln furniture, heat exchangers, and combustion nozzles where thermal performance is more important than absolute density.
Low Resistivity SiC for Electro-Thermal Parts
Some applications require a material that is not only thermally stable but also electrically conductive. Low resistivity silicon carbide is engineered for this purpose.
It is used for heating elements, susceptors in processing chambers, and electrostatic chucks, where its ability to conduct electricity is as important as its ability to withstand heat and wear.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While silicon carbide's properties are impressive, it is not a universal solution. As an advanced ceramic, its primary trade-off is its inherent brittleness compared to ductile metals.
Brittleness vs. Hardness
Like most ceramics, silicon carbide is extremely hard but can be brittle. It does not deform plastically before failure. This means part design and engineering must account for its lack of ductility, avoiding sharp corners or features that could concentrate stress.
The Critical Choice of Form
The biggest potential pitfall is using the wrong type of silicon carbide. Using porous, recrystallized SiC in a high-purity semiconductor application would lead to contamination. Conversely, using dense CVD SiC for kiln furniture might be unnecessarily expensive and not offer the ideal thermal performance of its recrystallized counterpart.
Manufacturing and Machining
Silicon carbide's extreme hardness makes it difficult and costly to machine into complex shapes compared to metals. Parts are often formed into their near-net shape during initial production through processes like sintering or deposition.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective determines which form of silicon carbide is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high purity for semiconductor processing: Choose CVD silicon carbide for its resistance to plasma erosion and minimal contamination.
- If your primary focus is industrial heating elements or susceptors: Choose low resistivity silicon carbide for its combination of electrical conductivity and thermal stability.
- If your primary focus is structural components inside furnaces or heat exchangers: Choose recrystallized silicon carbide for its superior thermal shock resistance and structural integrity at extreme temperatures.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance in high-heat mechanical systems: Choose a dense, sintered silicon carbide for components like seals, bearings, or pump parts.
Ultimately, understanding the specific form of silicon carbide is the key to unlocking its exceptional performance in the most demanding high-temperature environments.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for High-Temperature Applications |
|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | Maintains strength up to 1600°C, unlike metals. |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | High thermal conductivity & low expansion prevent cracking. |
| Oxidation Resistance | Forms protective SiO₂ layer above 1200°C. |
| Hardness & Wear Resistance | Ideal for mechanical parts in abrasive, hot environments. |
| Material Variety | Different types (CVD, Recrystallized) for specific needs. |
Ready to solve your high-temperature challenges?
KINTEK specializes in premium lab equipment and consumables, including silicon carbide components for furnaces, semiconductor processing, and more. Our expertise ensures you select the right SiC material—whether for ultra-high purity, structural integrity, or electro-thermal performance—to enhance your laboratory's efficiency and results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover the perfect silicon carbide solution for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Precision Machined Yttria Stabilized Zirconia Ceramic Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Precision Machined Silicon Nitride (SiN) Ceramic Sheet for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- Is silicon carbide heat resistant? Unlock Superior Performance in Extreme Temperatures
- What are the characteristics of SiC? Unlock High-Temp, Hard, and Chemically Inert Performance
- Which is harder silicon carbide or tungsten carbide? Discover the Key to Material Selection
- Is silicon carbide better than ceramic? Discover the Superior Technical Ceramic for Your Application
- What is the resistivity of silicon carbide? It's a tunable property from <0.1 ohm-cm to highly resistive.



















