Yes, a range of machines exists specifically to test and verify diamonds. These devices vary significantly in complexity, from simple handheld probes that test for thermal and electrical conductivity to highly sophisticated laboratory instruments. Their primary purpose is to differentiate genuine diamonds from common simulants and, more importantly, to distinguish natural diamonds from lab-grown synthetics.
The central challenge in diamond testing today is not just identifying fakes, but distinguishing between natural diamonds and lab-grown diamonds. Because they are chemically and physically identical, this requires advanced technology that goes far beyond the simple testers available to the public.

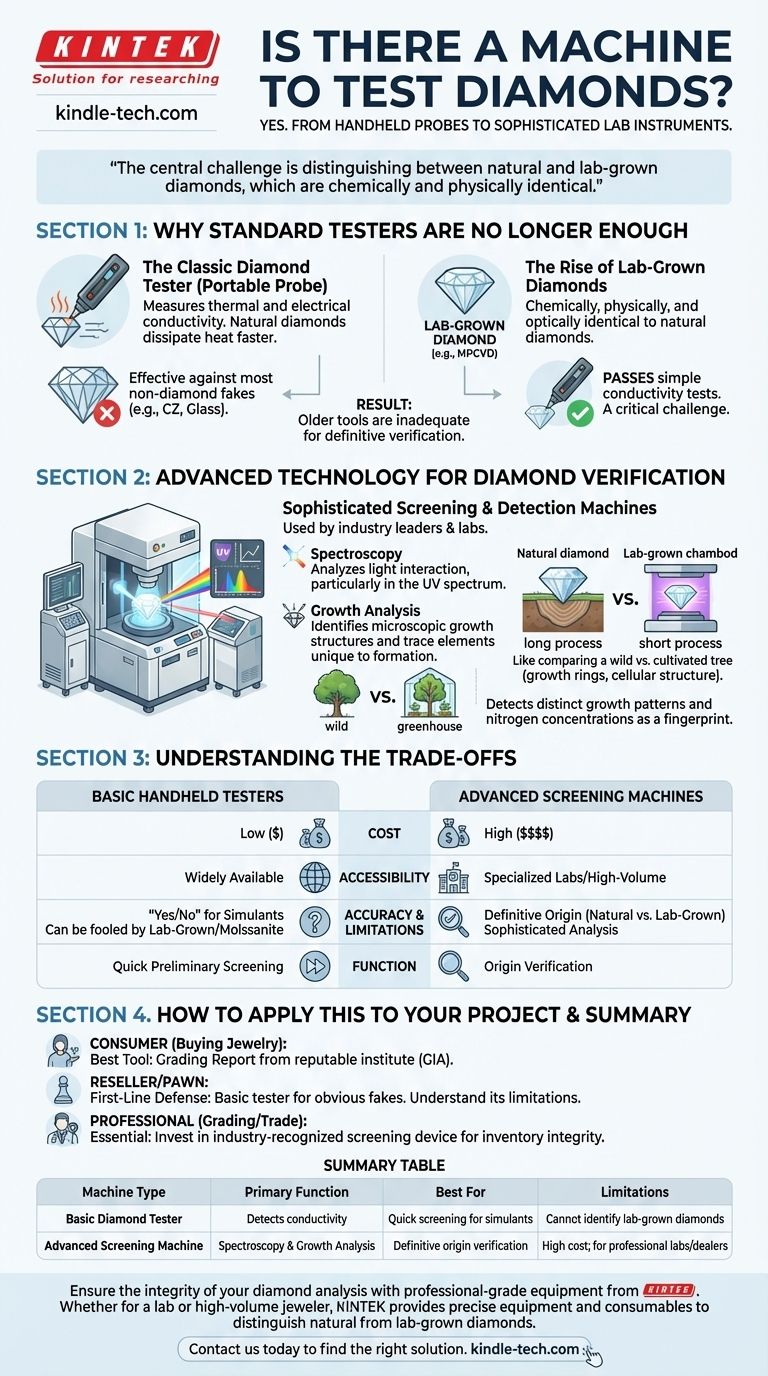
Why Standard Testers Are No Longer Enough
For decades, simple testers were sufficient for most needs. However, the mass production of high-quality lab-grown diamonds has fundamentally changed the landscape, rendering these older tools inadequate for definitive verification.
The Classic Diamond Tester
A basic diamond tester is a portable electronic probe. It works by measuring how quickly heat or electricity moves through a stone.
Because natural diamonds are exceptional thermal conductors, they dissipate heat from the probe's tip much faster than common imitations like glass or cubic zirconia. This simple test is effective at weeding out most non-diamond fakes.
The Rise of Lab-Grown Diamonds
The problem is that lab-grown diamonds—often created using methods like Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition (MPCVD)—are not fakes. They are chemically, physically, and optically identical to natural diamonds.
Consequently, a lab-grown diamond will pass a simple thermal or electrical conductivity test with ease. This has created a critical need for more advanced detection methods to ensure transparency in the supply chain.
The Advanced Technology for Diamond Verification
To solve the problem of identifying lab-grown diamonds, industry leaders like De Beers and major gemological labs have developed sophisticated screening and detection machines. These instruments look for subtle markers left behind during the diamond's formation.
Spectroscopy and Growth Analysis
These advanced machines use techniques like spectroscopy to analyze how a diamond interacts with light, particularly in the ultraviolet spectrum.
They are designed to identify the microscopic growth structures and trace elements unique to each formation process. A diamond that grew over billions of years deep within the Earth has a different internal structure than one grown in a laboratory over a few weeks.
How These Machines Work
Think of it like comparing a wild tree from an ancient forest to a cultivated tree from a greenhouse. Both are real trees, but a botanist can identify differences in their growth rings, cellular structure, and the minerals they absorbed.
Similarly, these machines detect the distinct growth patterns and nitrogen concentrations that act as a fingerprint, revealing whether a diamond is of natural or laboratory origin.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The right tool for testing a diamond depends entirely on your goal, budget, and the level of certainty you require.
Cost and Accessibility
Basic handheld diamond testers are relatively inexpensive and widely available. They are useful for a quick, preliminary screening.
The advanced screening and detection machines, however, are highly specialized laboratory equipment. Their cost can run into many thousands of dollars, making them accessible only to gemological labs, large wholesalers, and high-volume jewelers.
Accuracy and Limitations
A simple tester provides a "Yes/No" answer for identifying common simulants. However, it can be easily fooled by lab-grown diamonds and even moissanite, which also has high thermal conductivity.
An advanced detection machine provides a definitive conclusion about a diamond's origin. It is not a simple pass/fail device but a sophisticated analytical instrument for professionals.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Ultimately, verifying a diamond is about managing risk and ensuring trust. The right approach depends on your role in the industry.
- If your primary focus is buying jewelry as a consumer: Your best tool is not a machine, but a grading report from a reputable gemological institute like the GIA, which uses this advanced equipment.
- If your primary focus is reselling or pawn: A basic tester is a valuable first-line defense against obvious fakes, but you must understand its inability to identify lab-grown diamonds.
- If your primary focus is professional grading or high-volume trade: Investing in an industry-recognized screening device is now an essential cost of doing business to maintain inventory integrity.
Choosing the correct method of verification is the key to navigating the modern diamond market with confidence.
Summary Table:
| Machine Type | Primary Function | Best For | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Diamond Tester | Detects thermal/electrical conductivity | Quick screening for common simulants | Cannot identify lab-grown diamonds |
| Advanced Screening Machine | Uses spectroscopy to analyze growth patterns | Definitive origin verification (natural vs. lab-grown) | High cost; for professional labs and large dealers |
Ensure the integrity of your diamond analysis with professional-grade equipment from KINTEK.
Whether you're a gemological lab requiring advanced spectroscopy tools or a jeweler needing reliable initial screening devices, KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables to meet your verification needs. Our solutions help you accurately distinguish natural diamonds from lab-grown ones, protecting your business and building trust with your clients.
Contact us today to find the right diamond testing solution for your laboratory. Get in touch via our contact form to speak with an expert!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a mechanical sieve shaker for biomass analysis? Optimize Particle Size Distribution
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- What is the function of sieving equipment in CuAlMn alloys? Master Pore Size Precision



















