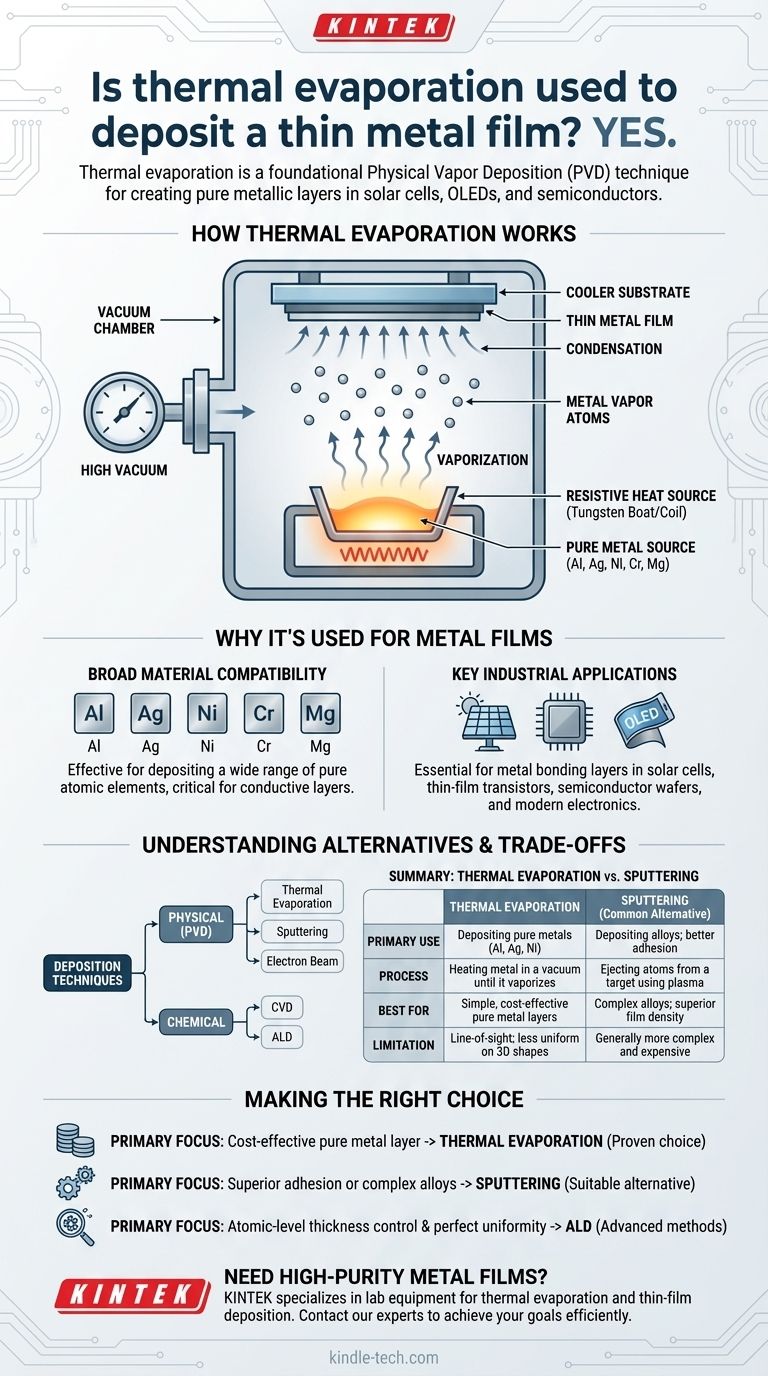
Yes, thermal evaporation is a foundational and widely used technique for depositing thin metal films. It is a form of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) that effectively creates pure metallic layers for applications ranging from solar cells and OLED displays to semiconductor manufacturing.
The core principle of thermal evaporation is straightforward: a metal is heated in a high vacuum until it vaporizes, and this vapor then condenses onto a cooler surface (the substrate), forming a solid, thin film.

How Thermal Evaporation Works
The Core Principle: Heating in a Vacuum
Thermal evaporation relies on a simple physical process. The source material, such as a pure metal like aluminum or silver, is placed inside a high-vacuum chamber.
The material is then heated using a resistive heat source, such as a tungsten "boat," "basket," or "coil," until its temperature rises to the point of evaporation.
The Deposition Process
Once the metal turns into a vapor, its atoms travel in a straight line through the vacuum chamber.
These gaseous atoms eventually strike the cooler substrate (the material being coated), where they condense back into a solid state. This condensation builds up layer by layer, creating a thin, uniform film.
Why It's Used for Metal Films
Broad Material Compatibility
This method is highly effective for depositing a wide range of pure atomic elements.
Commonly deposited metals include Aluminum, Silver, Nickel, Chromium, and Magnesium, which are critical for creating electrically conductive layers.
Key Industrial Applications
Thermal evaporation is a workhorse in many industries. It's used to create metal bonding layers in solar cells, thin-film transistors, and semiconductor wafers.
It is also essential in manufacturing modern electronics like carbon-based organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs).
Understanding the Alternatives and Trade-offs
The Broader Deposition Landscape
Thermal evaporation is just one of many ways to create a thin film. Deposition techniques are broadly divided into two categories: Physical and Chemical.
Thermal evaporation, sputtering, and electron beam evaporation are all physical methods. Chemical methods include techniques like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD).
The Rise of Sputtering
While effective, thermal evaporation is not the only option. For many modern applications, a different PVD technique called sputtering is used.
Sputtering can offer superior film adhesion and density, which may be critical depending on the specific goal.
Key Limitations
The line-of-sight nature of thermal evaporation can sometimes make it difficult to coat complex, three-dimensional shapes uniformly.
Furthermore, while it excels at depositing pure metals, creating films from complex alloys or compounds can be more challenging compared to other techniques.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition method requires understanding the goal of the final film.
- If your primary focus is depositing a pure metal layer simply and cost-effectively: Thermal evaporation is an excellent and highly proven choice.
- If your primary focus is superior film adhesion or depositing complex metal alloys: You should investigate sputtering as a more suitable alternative.
- If your primary focus is achieving atomic-level thickness control and perfect uniformity: Advanced methods like Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) are likely required.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental principles of each technique empowers you to select the ideal tool for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Thermal Evaporation | Common Alternative (Sputtering) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Depositing pure metals (Al, Ag, Ni) | Depositing alloys; better adhesion |
| Process | Heating metal in a vacuum until it vaporizes | Ejecting atoms from a target using plasma |
| Best For | Simple, cost-effective pure metal layers | Complex alloys; superior film density |
| Limitation | Line-of-sight; less uniform on 3D shapes | Generally more complex and expensive |
Need to deposit a high-purity metal film for your research or production?
KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables you need for thermal evaporation and other thin-film deposition techniques. Our experts can help you select the right tools to achieve your project goals efficiently and cost-effectively.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- Is pyrolysis a carbon negative process? Only with the right feedstock and sequestration strategy.
- What is the principle of rotavap? Efficient, Gentle Solvent Removal for Sensitive Compounds
- Are biomass fuels sustainable? Uncover the truth behind carbon neutrality and lifecycle impacts.
- What are the different types of heat treatment furnaces? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Material's Success
- How much does XRF cost per sample? Budgeting for Precision in Material Analysis
- What is the best material for end mills? A Guide to Hardness vs. Toughness for Your Application
- Can brazing be used to join two different base metals? Unlock Strong, Reliable Dissimilar Metal Joints
- Why are SEM samples coated with carbon? For Accurate Elemental Analysis Without Interference



















