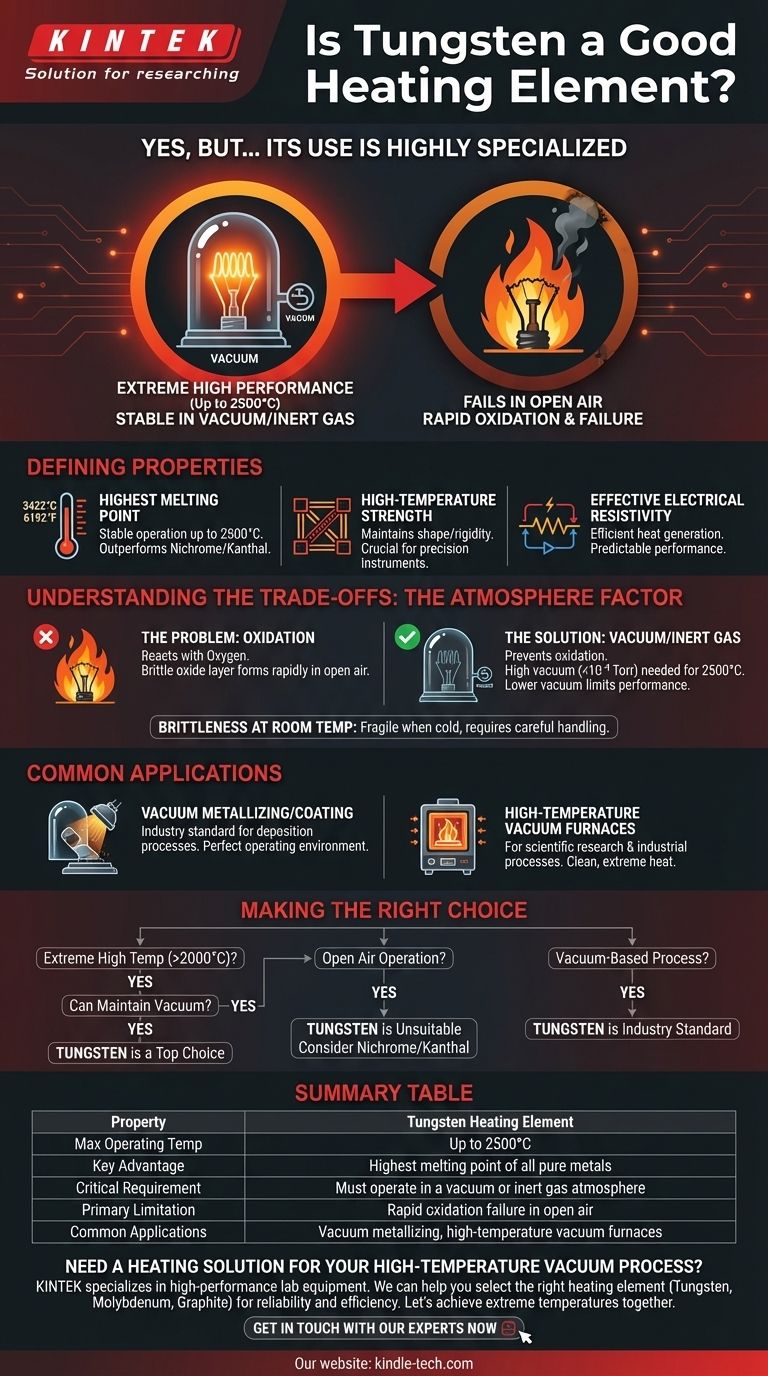
Yes, tungsten is an exceptional heating element, but its use is highly specialized. Its primary advantage is the highest melting point of any pure metal (3422 °C), allowing it to reach extreme operating temperatures that other materials cannot. However, this capability is only unlocked when tungsten is used in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere, as it oxidizes and fails very quickly in open air at high temperatures.
The decision to use tungsten is not about its absolute quality, but its suitability for a specific environment. Its unparalleled high-temperature performance is directly tied to its greatest weakness: a vulnerability to oxidation that requires operation in a vacuum.

The Defining Properties of Tungsten Heaters
Tungsten's unique physical characteristics make it a powerful but demanding choice for heating applications. Its value comes from a combination of factors that set it apart from more common heating element alloys.
The Highest Melting Point of All Metals
Tungsten's melting point of 3422 °C (6192 °F) is its defining feature. This allows for stable and reliable operation at temperatures up to 2500 °C, far beyond the limits of materials like nichrome or Kanthal.
High-Temperature Strength and Stability
Beyond simply not melting, tungsten remains physically strong and rigid at extreme temperatures. This structural integrity is crucial in applications where the heating element must maintain a precise shape, such as in scientific instruments or vacuum furnaces.
Effective Electrical Resistivity
To function as a heater, a material must resist the flow of electricity, converting electrical energy into heat. Tungsten possesses sufficient electrical resistivity to generate heat efficiently and predictably when a current is applied.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Critical Role of Atmosphere
The primary limitation of tungsten is not its performance at temperature, but its interaction with its surrounding environment. This is the most important factor to consider when evaluating it for your application.
The Problem: Rapid Oxidation
Despite having good corrosion resistance in certain conditions, tungsten reacts readily with oxygen at high temperatures. When heated in open air, it rapidly forms a brittle tungsten oxide layer and the element fails, making it completely unsuitable for such applications.
The Solution: Vacuum or Inert Gas
To prevent oxidation, tungsten heaters must be operated in a controlled atmosphere. High performance up to 2500 °C requires a high vacuum (less than 10⁻⁴ Torr).
Even in a lower-quality vacuum, its performance is severely limited. At a vacuum level below 10⁻² Torr, its maximum recommended operating temperature drops to just 1200 °C. The classic example of this principle is the incandescent light bulb, which encases a thin tungsten filament in a vacuum or an inert gas to prevent it from instantly burning out.
Brittleness at Room Temperature
While strong at high temperatures, tungsten can become very brittle after being heated and cooled. This makes the elements fragile to handle and susceptible to mechanical shock during maintenance or installation.
Common Applications Driven by Its Properties
Tungsten's specific requirements mean it is the default choice in several advanced industrial and scientific fields where its strengths align perfectly with the process environment.
Vacuum Metallizing and Coating
Tungsten filaments are the industry standard for vacuum deposition processes like aluminizing or chrome plating. In these applications, a high vacuum is already a core requirement of the process itself, creating the perfect operating environment for a tungsten heater to thrive.
High-Temperature Vacuum Furnaces
For scientific research or industrial processes that require extremely high temperatures within a vacuum, tungsten mesh or wire heaters are one of the few viable options. They provide the necessary heat without contaminating the vacuum environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the correct heating element requires matching the material's properties to your specific operational environment and temperature goals.
- If your primary focus is extreme high-temperature operation (above 2000 °C): Tungsten is one of the few viable options, provided you can maintain a high-vacuum environment.
- If your application operates in open air: Tungsten is unsuitable; you should consider alternatives like nichrome (NiCr) or Kanthal (FeCrAl) alloys, which are designed to form a protective oxide layer.
- If your project involves a vacuum-based process: Tungsten is an industry-standard choice due to its high-temperature capability and perfect compatibility with the required environment.
Ultimately, understanding a material's environmental limitations is just as important as knowing its strengths.
Summary Table:
| Property | Tungsten Heating Element |
|---|---|
| Max Operating Temp | Up to 2500°C |
| Key Advantage | Highest melting point of all pure metals |
| Critical Requirement | Must operate in a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere |
| Primary Limitation | Rapid oxidation failure in open air |
| Common Applications | Vacuum metallizing, high-temperature vacuum furnaces |
Need a heating solution for your high-temperature vacuum process?
Tungsten heating elements are engineered for peak performance in extreme environments. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including vacuum furnace systems that leverage the superior capabilities of tungsten. Our experts can help you select the right heating element material—whether it's tungsten, molybdenum, or graphite—to ensure reliability, efficiency, and longevity for your specific application.
Contact us today to discuss how our heating solutions can enhance your process. Let's achieve extreme temperatures together.
Get in touch with our experts now
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Are heating elements safe? Ensuring Reliable and Secure Thermal Processing
- Why tungsten is not used in heating devices? The Critical Role of Oxidation Resistance
- What is SiC elements? The Ultimate High-Temperature Heating Solution
- What is the difference between induction and resistance heating? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heat Source
- What are the high temperature furnace elements to be used in oxidizing environments? Select the Right Element for Your Lab
- Do heating elements lose power over time? The science behind inevitable performance decline
- At what temperature does molybdenum disilicide undergo sintering? Unlock the Key Variables for Optimal Performance
- What are silicon carbide heating elements used for? Reliable High-Temp Heating for Industrial Processes



















