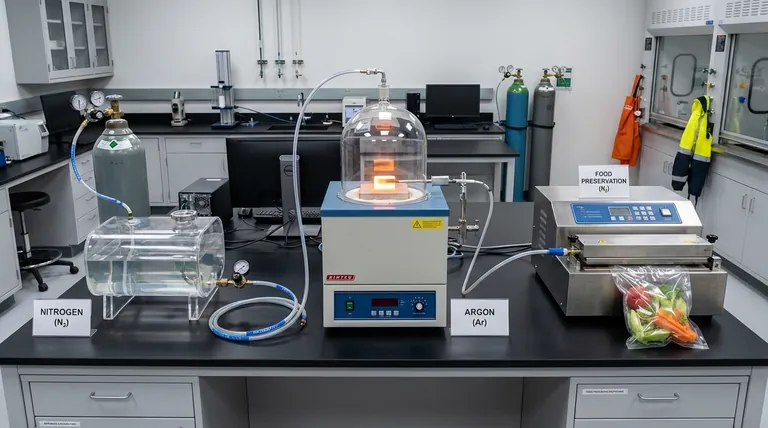
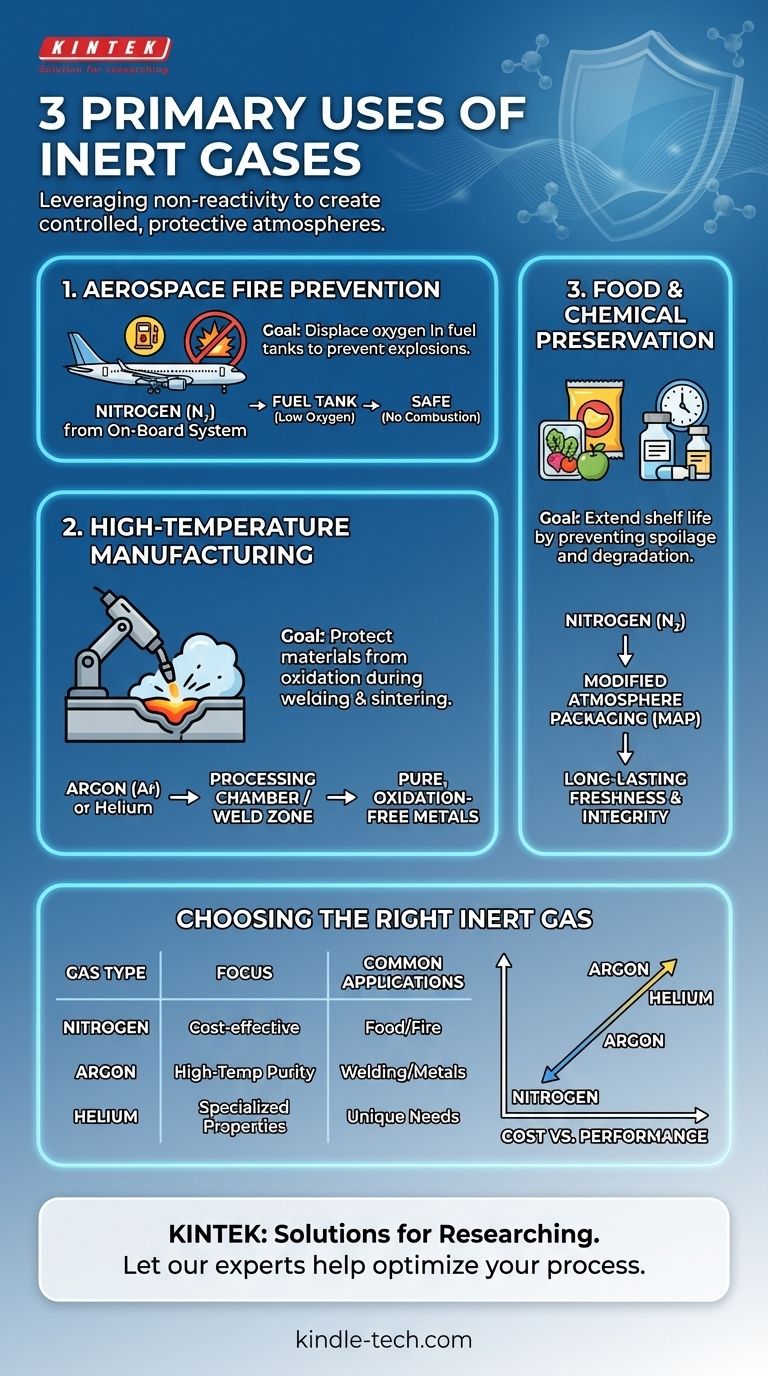
Three primary uses of inert gases are preventing fires and explosions in aerospace, protecting materials during high-temperature manufacturing like welding and sintering, and preserving the quality of food and sensitive chemicals. These applications all leverage the core property of inert gases: their chemical inability to react with other substances, which allows them to displace reactive gases like oxygen.
The fundamental purpose of using an inert gas is to create a controlled, non-reactive atmosphere. This protective shield prevents undesirable chemical processes such as oxidation, combustion, and degradation that would otherwise compromise the safety, quality, or integrity of a product or process.

What Defines an Inert Gas?
The Principle of Non-Reactivity
An inert gas is defined by its chemical stability. These gases have a full outer shell of electrons, making them extremely reluctant to form chemical bonds with other elements.
The noble gases on the periodic table—like helium, neon, and argon—are the truest examples of inert elements. However, for most industrial purposes, unreactive diatomic gases like nitrogen are also considered and used as inert gases.
Common Industrial Inert Gases
Nitrogen (N₂) is the most widely used inert gas due to its abundance (making up over 78% of the air) and low cost. It is effective for many general-purpose applications.
Argon (Ar) is also extremely common. While more expensive than nitrogen, it is denser than air and provides a higher degree of inertness, especially at the high temperatures found in welding and metallurgy.
Helium (He) is used in specialized applications where its unique properties, like high thermal conductivity and low density, are required. It is generally the most expensive option.
Key Industrial Applications
Metallurgy and High-Temperature Processing
In processes like vacuum sintering or welding, metals are heated to extreme temperatures where they become highly reactive with atmospheric oxygen and moisture. This reaction, oxidation, can create impurities and weaken the final product.
By flooding the processing chamber or weld zone with an inert gas like argon, reactive oxygen is physically displaced. This prevents the depletion of key alloying elements, controls the final carbon content, and ensures the structural integrity and purity of the metal part.
Aerospace and Fire Prevention
Aircraft fuel tanks contain a dangerous mixture of fuel vapor and air. An electrical spark in this environment could be catastrophic. To mitigate this risk, modern aircraft use an On-Board Inert Gas Generation System (OBIGGS).
These systems use a membrane to separate nitrogen from engine bleed air. This nearly pure nitrogen is then pumped into the fuel tanks, displacing the oxygen. By keeping the oxygen concentration below the flammability limit (around 10-12%), the risk of an explosion is virtually eliminated.
Chemical and Food Preservation
Oxygen is the primary enemy of freshness in packaged foods, causing staleness, spoilage, and loss of flavor through oxidation. Similarly, many pharmaceuticals and sensitive chemicals degrade when exposed to air.
In a process called modified atmosphere packaging (MAP), food packagers replace the oxygen inside a package with nitrogen. This dramatically extends shelf life without the need for chemical preservatives. The same principle is used to blanket sensitive chemicals during storage and transport.
Understanding the Trade-offs
"Inertness" is Relative
A gas that is inert in one scenario may be reactive in another. The effectiveness of an inert gas depends on temperature, pressure, and the specific materials involved.
For example, while nitrogen is inert to most steels at moderate temperatures, it can react to form metal nitrides at the higher temperatures used to process certain alloys. In those cases, a more truly inert gas like argon is required.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct trade-off between the cost of an inert gas and its level of performance.
Nitrogen is the workhorse for its low cost, ideal for large-volume applications like food packaging. Argon and helium offer superior inertness but come at a significant price premium, reserving them for high-value processes where purity is non-negotiable.
Sourcing and Purity
Inert gases can be supplied in high-pressure cylinders, as a cryogenic liquid in dewar flasks, or generated on-site. For continuous, high-volume use, on-site nitrogen generators can be the most economical solution. The required purity of the gas will also impact the cost and choice of supply.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing an inert gas requires matching the gas's properties to the specific goals of your process.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, large-scale displacement: Nitrogen is almost always the optimal choice for applications like fire suppression and food preservation.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature metallurgical purity: Argon is the industry standard for welding and metal processing to prevent oxidation and ensure material integrity.
- If your primary focus is a specialized application requiring unique physical properties: Helium is used when characteristics like its high thermal conductivity or low molecular weight are critical.
Ultimately, selecting the right inert gas is a strategic decision that balances precise chemical requirements against operational costs.
Summary Table:
| Use Case | Key Goal | Common Gases |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace Fire Prevention | Displace oxygen in fuel tanks to prevent explosions. | Nitrogen |
| High-Temperature Manufacturing | Protect metals from oxidation during welding & sintering. | Argon |
| Food & Chemical Preservation | Extend shelf life by preventing spoilage and degradation. | Nitrogen |
Need to select the right inert gas for your lab or production process?
The choice between nitrogen, argon, and helium is critical for safety, purity, and cost-effectiveness. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance and solutions for all your inert gas needs—from high-purity gas supply to integrated systems for welding, sintering, and sample preservation.
Let our experts help you optimize your process. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application and ensure material integrity and safety.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 10L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the key performance characteristics and applications of platinum sheets? Unmatched Reliability for Demanding Applications
- How should a platinum sheet electrode be operated during an experiment? Ensure Accurate and Reproducible Results
- What precautions should be taken when using a platinum sheet electrode? Ensure Accurate & Reproducible Electrochemical Data
- What is the most critical guideline for immersing a platinum sheet electrode in an electrolyte? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- What are the available specifications for platinum sheet electrodes? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Electrochemical Needs



















