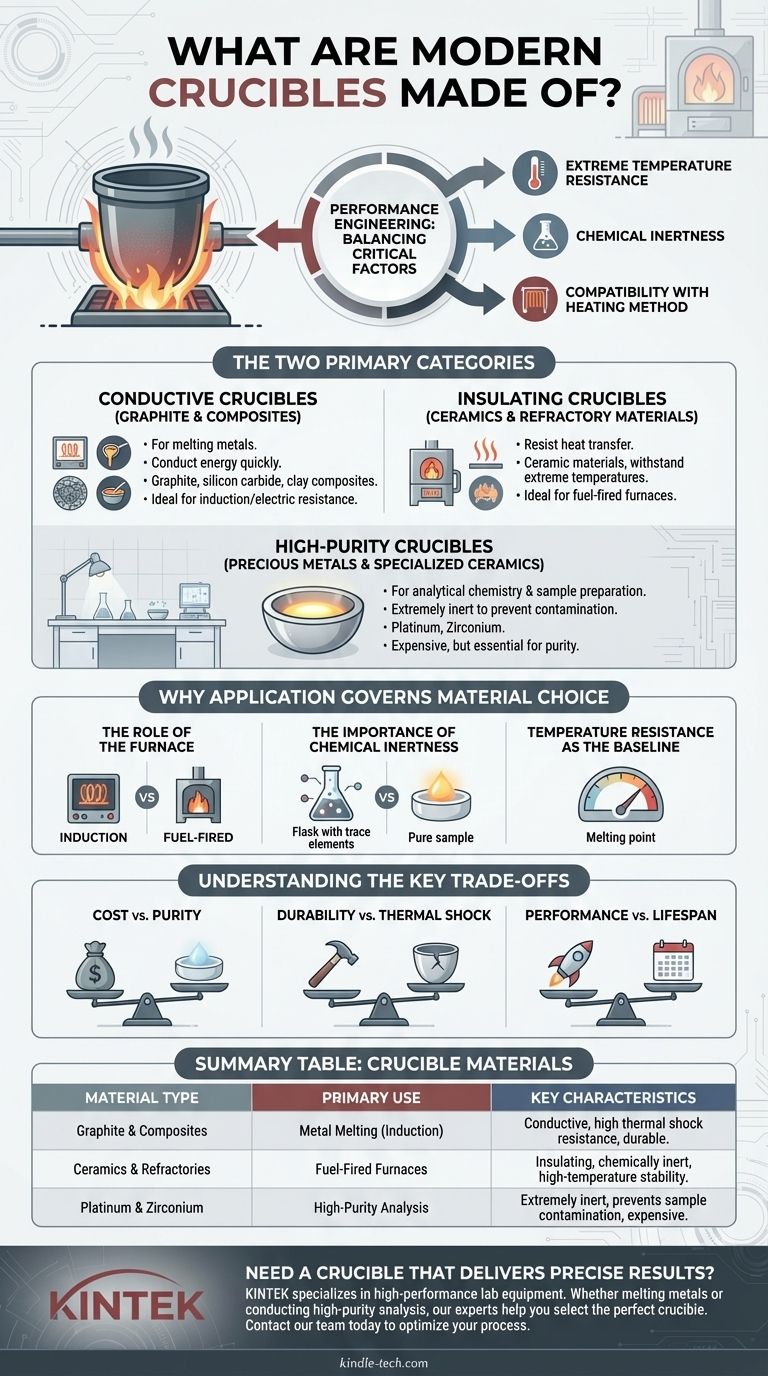
To be direct, modern crucibles are not made from a single material but from a range of highly specialized substances tailored to specific tasks. The most common materials for industrial applications are graphite-based composites, while laboratory settings often rely on inert ceramics or precious metals like platinum to ensure sample purity. The material choice is dictated entirely by the required temperature, the substance being heated, and the type of furnace used.
The core principle to understand is that a modern crucible is a piece of performance engineering. Its material is strategically chosen to balance three critical factors: extreme temperature resistance, chemical inertness with its contents, and compatibility with the heating method.

The Two Primary Categories of Modern Crucibles
Modern crucible materials can be broadly classified into two functional groups: those that conduct energy and those that insulate. This distinction is fundamental because it determines how the crucible interacts with the furnace and the material it holds.
Conductive Crucibles: Graphite and Composites
Most crucibles used for melting metals are conductive. These are engineered to absorb energy quickly and transfer it efficiently to the contents.
The primary material here is graphite, often mixed with other substances like silicon carbide and clay to form a robust composite. The specific composition and the structural alignment of the graphite are critical to the crucible's performance and durability. These are the go-to choice for induction and electric resistance furnaces.
Insulating Crucibles: Ceramics and Refractory Materials
Insulating crucibles are made from ceramic materials designed to resist heat transfer. They act as a container that can withstand extreme temperatures while the heat is applied directly to the contents from an external source, such as in a fuel-fired furnace.
Materials in this category have evolved from traditional clay to advanced ceramics. They are chosen when the crucible itself should not be part of the electrical or inductive circuit.
High-Purity Crucibles: Precious Metals and Specialized Ceramics
For analytical chemistry and sample preparation, preventing contamination is the highest priority. In these cases, crucibles are made from extremely inert materials.
Platinum and, to a lesser extent, zirconium are common choices. While expensive, their extreme resistance to chemical reactions ensures that the analysis reflects the sample itself, not a reaction with the container.
Why Application Governs Material Choice
You cannot select a crucible without first defining its purpose. The environment it will be used in places strict demands on its material properties.
The Role of the Furnace
The heating method is a primary deciding factor. An induction furnace requires a conductive crucible (like graphite) to generate heat directly within the material. Using a ceramic crucible in an induction furnace would be ineffective.
Conversely, a fuel-fired furnace heats the crucible from the outside, making a durable, insulating ceramic a more suitable choice.
The Importance of Chemical Inertness
The crucible must not react with the molten metal or chemical solution it contains. A graphite crucible, for example, could introduce carbon into a steel melt, which may or may not be desirable.
For high-stakes laboratory analysis, even trace amounts of leaching from the crucible wall can invalidate results, mandating the use of ultra-pure materials like platinum.
Temperature Resistance as the Baseline
The most fundamental requirement is that the crucible's melting point must be significantly higher than the working temperature. Every material choice—from clay to graphite to platinum—is first filtered by its ability to remain solid and structurally sound under extreme heat.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing a crucible material is an exercise in balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" material, only the most appropriate one for a specific job.
Cost vs. Purity
A high-purity platinum crucible offers unmatched chemical inertness but is exceptionally expensive. A clay-graphite composite is far more economical for melting tons of bronze but is completely unsuitable for sensitive chemical analysis.
Durability vs. Thermal Shock
Some materials can withstand enormous sustained heat but will crack if their temperature changes too rapidly—a phenomenon known as thermal shock. Modern composite crucibles are often engineered specifically to improve their resistance to the stresses of repeated heating and cooling cycles.
Performance vs. Lifespan
A crucible is a consumable item. Aggressive chemical fluxes or extremely high temperatures will degrade the crucible over time. The material choice often involves a trade-off between peak performance and the operational lifespan before the crucible must be replaced.
Selecting the Right Crucible for Your Task
Your final decision must be guided by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is large-scale metal melting: You will almost certainly require a graphite or silicon carbide composite crucible designed for your specific furnace type.
- If your primary focus is high-purity chemical analysis: An inert crucible made of platinum, zirconium, or a specialized high-purity ceramic is essential to prevent sample contamination.
- If your primary focus is general workshop or hobbyist casting: A versatile and cost-effective clay-graphite or silicon carbide crucible offers the best balance of performance and durability.
Ultimately, understanding the material science behind your crucible empowers you to achieve more consistent and reliable results.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Primary Use | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Graphite & Composites | Metal Melting (Induction Furnaces) | Conductive, high thermal shock resistance, durable |
| Ceramics & Refractories | Fuel-Fired Furnaces | Insulating, chemically inert, high-temperature stability |
| Platinum & Zirconium | High-Purity Analysis | Extremely inert, prevents sample contamination, expensive |
Need a crucible that delivers precise results? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including a full range of crucibles for every application. Whether you're melting metals or conducting high-purity analysis, our experts will help you select the perfect crucible material for your specific temperature, chemical, and furnace requirements. Contact our team today to optimize your process and ensure reliable, contamination-free results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range of alumina crucibles? Key Factors for Safe High-Temp Use
- What is the function of an alumina crucible in NaSICON synthesis? Ensure Purity in High-Temperature Reactions
- Why are alumina crucibles or baskets essential for Boudouard reaction studies? Ensure Pure Data & Chemical Inertness
- Why are high-alumina crucibles selected for Cs-zeolite heat treatment? Ensure Sample Purity at 1100 °C
- How does the use of corrosion-resistant ceramic crucibles ensure the chemical purity of materials? | KINTEK



















