In essence, a mold is a specialized tool used to shape raw materials into a desired, finished form. Molds are hollow blocks, typically made of steel, that are filled with a liquid or pliable material like molten plastic, metal, or glass. Once the material hardens or sets inside the mold, it takes on the mold's shape, creating a consistent and repeatable part.
Molds are the backbone of modern mass production. They solve the fundamental manufacturing challenge of creating a high volume of identical parts with precision, speed, and cost-effectiveness that would be impossible to achieve manually.

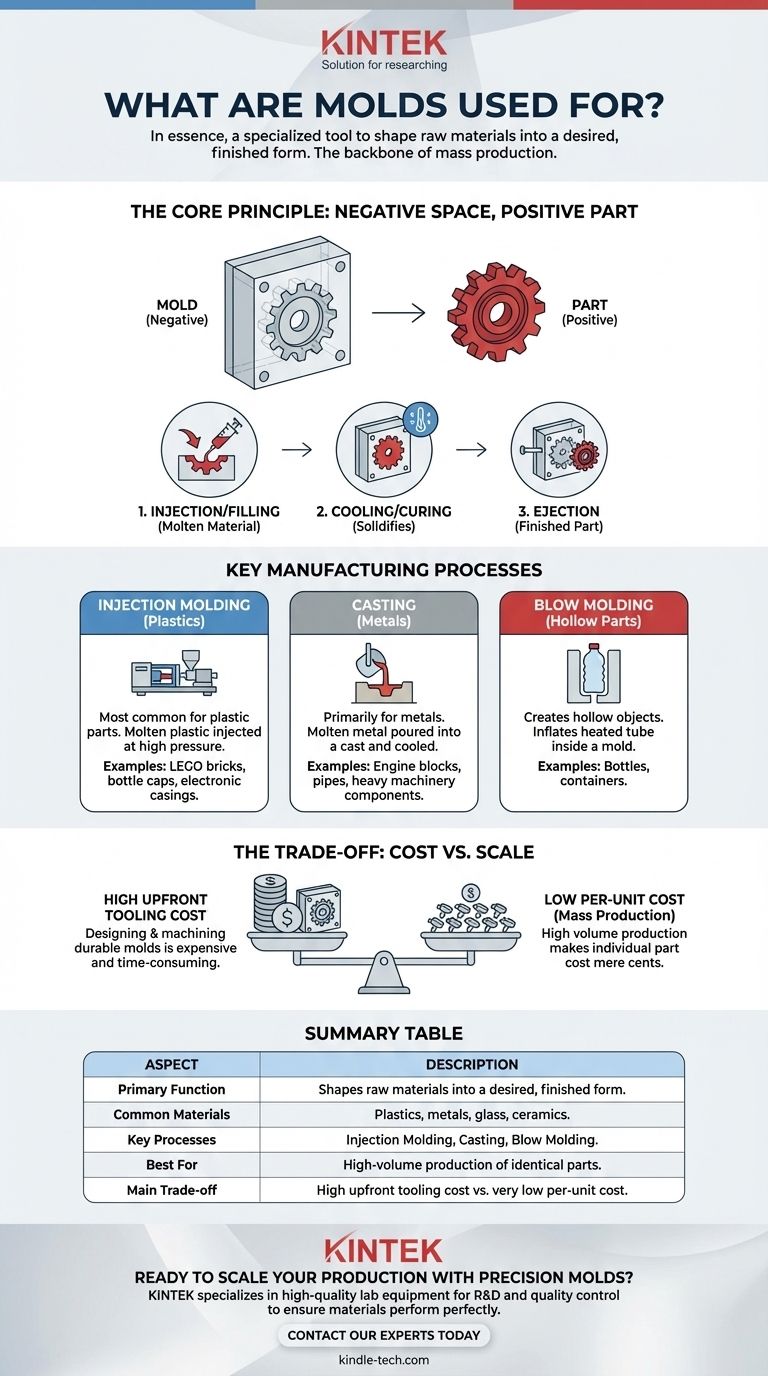
The Core Principle: A Negative Space for a Positive Part
The concept behind a mold is elegantly simple. It is the "negative" or inverse shape of the object you want to create.
How a Mold Works
A mold functions as a container or cavity. The manufacturing process generally involves three steps:
- Injection/Filling: A liquid material (like molten plastic or metal) is poured or injected under pressure into the mold's cavity.
- Cooling/Curing: The material is allowed to cool and solidify, taking on the precise shape and surface texture of the cavity.
- Ejection: The mold opens, and the finished, solid part is pushed out.
From Plastic to Metal
Molds are incredibly versatile and are used to shape a wide range of materials. The process and mold design are adapted to the material's properties, but the principle remains the same for plastics (resins), molten metals, glass, and even ceramics.
Key Manufacturing Processes Using Molds
Molds are not a single technology but a foundational tool used across several critical manufacturing methods.
Injection Molding
This is the most common process for producing plastic parts. It involves injecting molten plastic into a precision-machined mold at high pressure. This method is responsible for creating everything from LEGO bricks and bottle caps to car bumpers and electronic casings.
Casting
Casting is primarily used for metals. Molten metal is poured into a mold, known as a cast, and allowed to cool. This is how heavy-duty parts like engine blocks, pipes, and machinery components are often made.
Blow Molding
This process is used to create hollow plastic parts, most notably bottles and containers. It works by inflating a heated plastic tube inside a mold, forcing it to take the shape of the mold's interior.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Scale
While powerful, mold-based manufacturing is not the right choice for every situation. The decision to use a mold is governed by a clear economic trade-off.
High Upfront Tooling Cost
The primary drawback is the cost and time required to create the mold itself—a process known as tooling. Designing and machining a high-quality, durable steel mold can cost tens or even hundreds of thousands of dollars and take weeks or months.
Extremely Low Per-Unit Cost
The high initial investment is offset by an exceptionally low cost per part. Once the mold is running, it can produce thousands or millions of parts very quickly, making the cost of each individual item mere cents.
Design Inflexibility
A mold is built for one specific design. If you need to change the part's shape after the mold has been made, it often requires extensive and expensive re-machining or creating an entirely new mold. This makes molds unsuitable for prototyping or products that require frequent design updates.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a mold-based process depends entirely on your project's scale, budget, and design maturity.
- If your primary focus is mass production and consistency: Mold-based manufacturing is the unparalleled standard for producing high volumes of identical parts at a low unit cost.
- If your primary focus is prototyping or low-volume production: The high tooling cost and inflexibility of molds make alternative methods, such as 3D printing or CNC machining, far more practical.
- If your primary focus is creating a hollow object: A specialized process like blow molding is the most efficient and effective solution.
By enabling the rapid and repeatable creation of complex shapes, molds form the invisible foundation of nearly every product we use today.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Shapes raw materials into a desired, finished form. |
| Common Materials | Plastics, metals, glass, ceramics. |
| Key Processes | Injection Molding, Casting, Blow Molding. |
| Best For | High-volume production of identical parts. |
| Main Trade-off | High upfront tooling cost vs. very low per-unit cost. |
Ready to scale your production with precision molds?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables essential for developing and testing materials for mold-based manufacturing. Whether you're in R&D or quality control, our solutions help ensure your materials perform perfectly in the molding process.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory needs and help you achieve manufacturing excellence.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
- XRF & KBR steel ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- Assemble Square Lab Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- No Demolding Lab Infrared Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
People Also Ask
- What is mould in manufacturing? Unlock Mass Production with Precision Tooling
- What is a pressing die? The Precision Tool for Shaping Powder into Solid Pellets
- How do high-precision molds contribute to Li6PS5Cl electrolyte membrane formation? Achieve Perfect Density and Thickness
- Why is a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP) Required for NaSICON? Achieve Maximum Green Density and Ionic Conductivity
- How does a Hot Isostatic Press (HIP) machine improve AlFeTiCrZnCu alloys? Achieving 10 GPa Hardness and Maximum Density



















