In short, the primary limitations of powder metallurgy (PM) are constraints on part size, challenges with producing highly complex geometries, and mechanical properties—specifically strength and ductility—that are generally lower than those achieved through forging or casting. These limitations are a direct result of the physics of compacting and bonding metal powders rather than casting molten metal or deforming a solid billet.
The core challenge of powder metallurgy is achieving uniform density. The limitations on part size, complexity, and strength all originate from the difficulty of uniformly compacting a dry powder and then sintering it into a fully dense, homogenous final part.

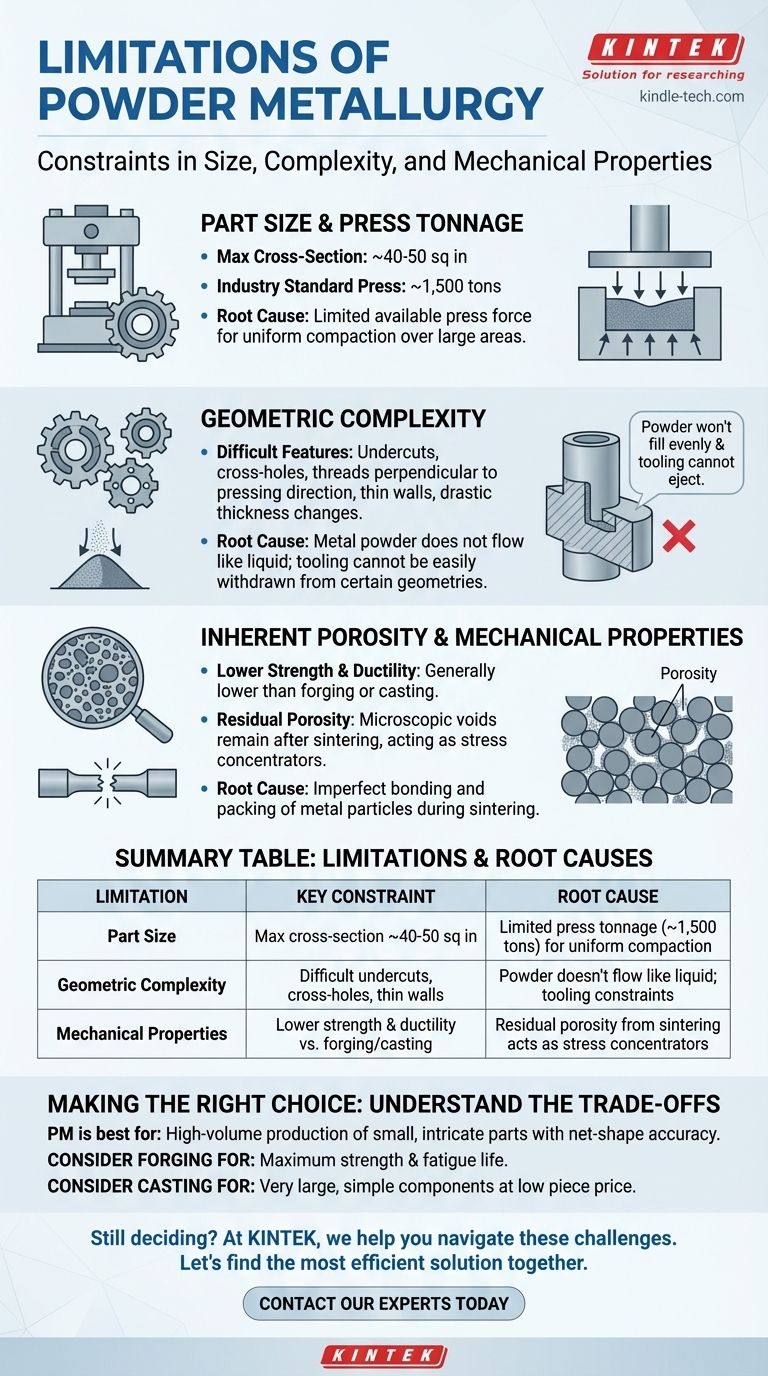
The Physics Behind the Limitations
To understand if PM is right for your application, it's essential to understand why these constraints exist. They are not arbitrary rules but fundamental consequences of the process itself.
Part Size and Press Tonnage
The size of a PM part is directly limited by the available press force. The industry standard for large presses is around 1,500 tons.
This force must be distributed across the part's planar area to compact the powder. As a result, the practical limit for a component's cross-section is typically around 40 to 50 square inches. Exceeding this makes it impossible to achieve the necessary pressure for adequate "green" (pre-sintered) density.
The Challenge of Geometric Complexity
Metal powders do not flow like a liquid. This simple fact creates significant design constraints.
Features like undercuts, cross-holes, or threads perpendicular to the pressing direction are often impossible to mold directly. The tooling cannot be easily withdrawn, and the powder will not fill these features evenly under pressure, leading to critical weak points.
Thin walls and drastic changes in section thickness also pose problems. They can prevent uniform pressure transmission, resulting in density variations and a structurally unsound part. While skilled design can mitigate some issues, PM is best suited for parts with relatively uniform thickness along the pressing axis.
Inherent Porosity and Mechanical Properties
Unlike casting or forging which produce fully dense materials, standard PM parts contain a small amount of residual porosity.
During sintering, the compacted particles bond metallurgically, but microscopic voids often remain. These pores act as stress concentrators, which is the primary reason PM parts typically exhibit lower tensile strength and ductility compared to their wrought or cast counterparts.
While post-processing steps like Hot-Isostatic Pressing (HIP) can be used to close this porosity, it adds significant cost and complexity to the process.
Understanding the Trade-offs: PM vs. Other Methods
No manufacturing process is perfect. The limitations of PM must be weighed against its significant advantages in specific contexts.
Strength vs. Net Shape
Forging produces parts with superior strength and fatigue resistance due to its ability to align the material's grain structure. However, it often requires extensive secondary machining to achieve final dimensions, adding cost and waste.
Powder metallurgy excels at producing parts to net-shape or near-net-shape, minimizing or eliminating the need for machining. This is a massive advantage for complex geometries where machining would be difficult or expensive.
Material Utilization vs. Component Scale
PM offers outstanding material utilization, with waste often below 3%. This is a significant cost and sustainability advantage over subtractive methods like machining.
Casting, on the other hand, is far more scalable for producing very large components. The tooling is often less expensive for simpler geometries, making it a cost-effective choice where the extreme precision of PM is not required.
Cost Profile
The high cost of PM tooling (the die and punches) makes it most economical for high-volume production runs, typically in the tens of thousands of parts or more. This allows the tooling cost to be amortized effectively.
For low-volume or prototype work, the tooling cost can be prohibitive, making machining from bar stock or even 3D printing a more logical choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct manufacturing process depends entirely on your project's key engineering and business drivers.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and fatigue life: Forging is almost always the superior choice, especially for critical structural components.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of small, intricate parts with excellent dimensional accuracy: Powder metallurgy is an outstanding and often unbeatable option.
- If your primary focus is producing very large, relatively simple components at a low piece price: Casting is likely the most economical and practical method.
- If your primary focus is achieving near-full density and strength in a complex PM part: Consider advanced processes like Metal Injection Molding (MIM) or adding a post-sinter Hot-Isostatic Pressing (HIP) step.
Ultimately, understanding these limitations empowers you to leverage powder metallurgy for what it does best: efficiently creating complex, precise components at scale.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Key Constraint | Root Cause |
|---|---|---|
| Part Size | Max cross-section ~40-50 sq in | Limited press tonnage (~1,500 tons) for uniform compaction |
| Geometric Complexity | Difficult undercuts, cross-holes, thin walls | Powder doesn't flow like liquid; tooling constraints |
| Mechanical Properties | Lower strength & ductility vs. forging/casting | Residual porosity from sintering acts as stress concentrators |
Still deciding if powder metallurgy is right for your project?
At KINTEK, we specialize in helping manufacturers navigate these exact challenges. Our expertise in lab equipment and consumables for material testing and process development can help you validate your design, optimize your sintering process, and ensure you select the right manufacturing method for your specific needs—whether it's PM, forging, or casting.
Let's discuss your application requirements and find the most efficient solution together. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
People Also Ask
- What is cold isostatic pressing mold material? Essential Elastomers for Uniform Density
- What is the process of isostatic graphite? A Guide to High-Performance, Uniform Material Creation
- How much does an isostatic press cost? A Guide to Lab vs. Industrial Pricing
- How big is the isostatic pressing market? A Deep Dive into the $1.2B+ Advanced Manufacturing Enabler
- What are the disadvantages of powder metallurgy? Key Limitations in Strength and Size



















