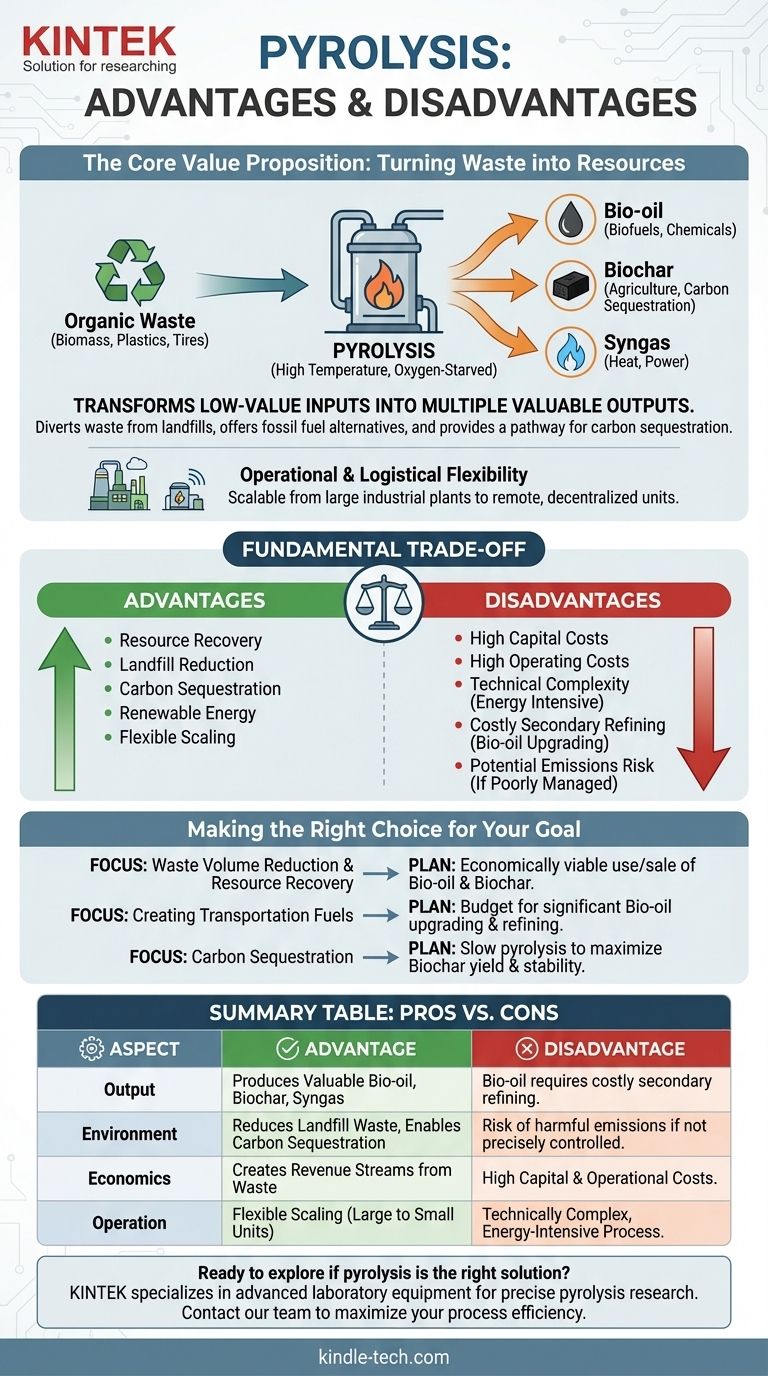
In short, the primary advantage of pyrolysis is its unique ability to transform organic waste into valuable products like bio-oil, biochar, and syngas, reducing landfill burdens and offering alternatives to fossil fuels. However, this powerful capability is balanced by significant disadvantages, including high capital and operational costs, technical complexity, and the potential for harmful emissions if not managed with precision.
Pyrolysis presents a fundamental trade-off: it offers a compelling path to a circular economy by valorizing waste, but its economic viability and environmental friendliness are not guaranteed. Success hinges entirely on careful engineering, feedstock selection, and a clear strategy for the end-products.

The Core Value Proposition: Turning Waste into Resources
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that decomposes organic material at high temperatures in an oxygen-starved environment. Unlike incineration (burning), this process breaks down complex materials into simpler, more valuable components.
From Waste Stream to Value Stream
The most significant benefit of pyrolysis is its ability to create multiple valuable outputs from a single low-value input, such as biomass, plastics, or tires.
The primary products are bio-oil, a dense liquid that can be refined into biofuels and chemicals; biochar, a stable, carbon-rich solid with applications in agriculture and filtration; and syngas, a mixture of combustible gases that can be used to generate heat and power for the process itself.
This conversion diverts enormous volumes of waste from landfills, directly addressing a major environmental and logistical challenge for municipalities and industries.
Environmental and Climate Benefits
By providing an alternative to fossil fuels, pyrolysis can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The energy generated from its products is often considered renewable, especially when using biomass feedstock.
Furthermore, the production of biochar offers a direct pathway for carbon sequestration. When returned to the soil, biochar can lock away carbon for centuries, improving soil health while actively removing CO2 from the atmosphere.
Operational and Logistical Flexibility
Pyrolysis systems can be designed for a wide range of scales, from large industrial plants to smaller, decentralized units.
This flexibility allows them to be deployed in remote locations, processing local biomass and converting it into an energy-dense liquid (bio-oil) that is far cheaper to transport than the original raw material.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
The potential of pyrolysis is clear, but its practical implementation is constrained by several critical economic and technical hurdles. Mistaking it for a simple "plug-and-play" solution is a common and costly error.
The Economic Hurdles: High Costs
Pyrolysis plants require significant upfront capital investment. The high-temperature, oxygen-free reactor and sophisticated control systems are expensive to build and install.
Operating costs are also substantial. The process is energy-intensive, requiring a constant supply of heat to maintain high temperatures, and ongoing maintenance is critical for safety and efficiency.
The Technical Complexity: Energy and Refinement
While syngas can offset some energy needs, the process often requires a net energy input, especially during startup. Achieving and maintaining precise temperature control is a constant technical challenge.
Crucially, the raw bio-oil is not a drop-in fuel. It is acidic, unstable, and contains high levels of oxygen and water. It requires significant and costly secondary refining (upgrading) before it can be used as a transportation fuel or chemical feedstock.
The Environmental Risk: Managing Emissions
Although pyrolysis is not direct combustion, it can produce harmful emissions if the system is poorly designed or operated. Volatile organic compounds and other pollutants can be released if the process is not perfectly sealed and managed.
Ensuring the process is truly environmentally friendly requires robust furnace design, precise operational control, and effective gas cleanup systems, all of which add to the overall cost and complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Pyrolysis is not a one-size-fits-all technology. Its suitability depends entirely on your specific objective, available feedstock, and capacity for managing its outputs and costs.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction and resource recovery: Pyrolysis is a powerful option, but you must have a clear and economically viable plan for using or selling the resulting bio-oil and biochar.
- If your primary focus is creating transportation fuels: Be prepared for a two-stage process. The pyrolysis unit is just the first step, and you must budget for significant downstream investment in bio-oil upgrading and refining technology.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration: Slow pyrolysis systems designed to maximize the yield and stability of biochar are the most direct and effective approach.
Ultimately, harnessing the benefits of pyrolysis requires a holistic understanding of its costs, complexities, and trade-offs from start to finish.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| Output | Produces valuable bio-oil, biochar, and syngas | Bio-oil requires costly secondary refining |
| Environment | Reduces landfill waste & enables carbon sequestration | Risk of harmful emissions if not precisely controlled |
| Economics | Creates revenue streams from waste | High capital investment and operational costs |
| Operation | Flexible scaling from large plants to small units | Technically complex, energy-intensive process |
Ready to explore if pyrolysis is the right solution for your waste or energy needs? The experts at KINTEK specialize in providing the advanced laboratory equipment and consumables necessary for precise pyrolysis research and development. We can help you navigate the technical complexities to maximize your process efficiency and product yield. Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and how we can support your project's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs



















