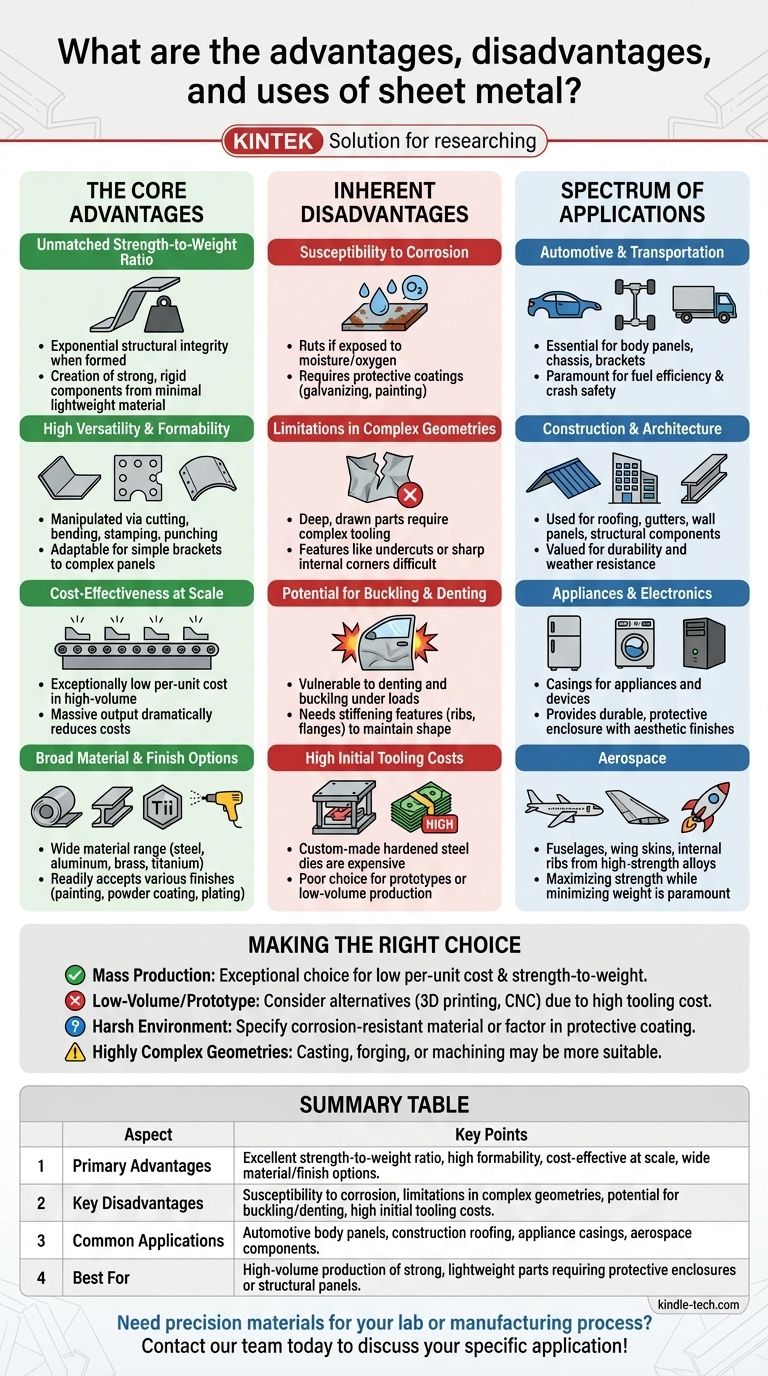
At its core, sheet metal is one of the most versatile and foundational materials in modern engineering and manufacturing. It refers to metal that has been formed into thin, flat pieces, available in a wide range of materials like steel, aluminum, brass, and titanium. Its primary advantages lie in an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, high formability, and cost-effectiveness at scale, though it requires careful design to mitigate its susceptibility to corrosion and buckling.
Sheet metal's fundamental trade-off is its incredible efficiency in creating strong, lightweight structures against the design and tooling complexities required to achieve that strength. Understanding this balance is the key to using it effectively.
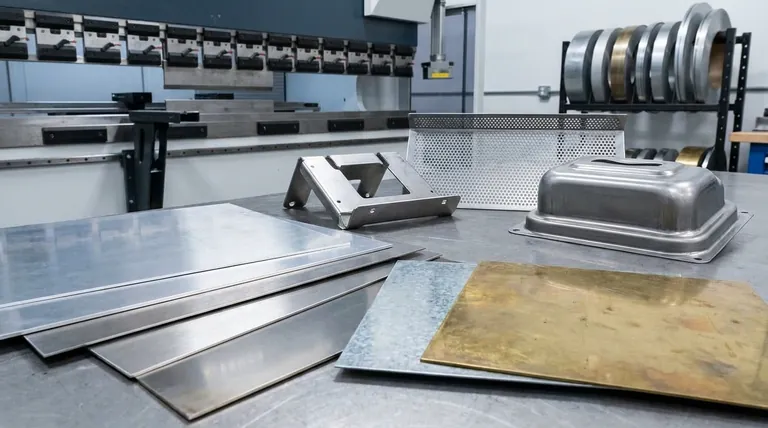

The Core Advantages of Sheet Metal
The widespread use of sheet metal is a direct result of several key physical and economic properties. When leveraged correctly, these advantages make it the optimal choice for an enormous range of applications.
Unmatched Strength-to-Weight Ratio
A flat sheet of metal is flimsy, but once it is bent, stamped, or formed into shapes like channels or ribs, its structural integrity increases exponentially. This principle allows for the creation of very strong and rigid components from a minimal amount of lightweight material, a critical factor in the automotive and aerospace industries.
High Versatility and Formability
Sheet metal can be manipulated through a variety of processes—including cutting, bending, stamping, punching, and drawing—to create nearly any geometric shape. This adaptability makes it suitable for everything from simple brackets to complex automotive body panels.
Cost-Effectiveness at Scale
While the initial investment in tooling, such as dies for stamping, can be substantial, the per-unit production cost for sheet metal parts is exceptionally low in high-volume manufacturing. The speed of processes like stamping allows for massive output, dramatically reducing costs for consumer goods and automotive components.
Broad Material and Finish Options
Sheet metal is available in a vast array of materials, from inexpensive carbon steel to lightweight aluminum, corrosion-resistant stainless steel, and high-performance titanium alloys. Furthermore, it readily accepts a wide range of finishes, including painting, powder coating, and plating, for both protective and aesthetic purposes.
Understanding the Inherent Disadvantages and Limitations
No material is perfect. The same thinness that gives sheet metal its advantages also introduces specific constraints that must be addressed during the design phase.
Susceptibility to Corrosion
Many common sheet metals, particularly carbon steel, will rust if exposed to moisture and oxygen. This necessitates the use of protective coatings like galvanizing (a zinc coating), painting, or powder coating, which add cost and processing steps.
Limitations in Complex Geometries
While formable, sheet metal has its limits. Creating deep, drawn parts without tearing or wrinkling requires significant engineering and complex tooling. Features like undercuts or sharp internal corners are often impossible to form and require secondary assembly operations.
Potential for Buckling and Denting
The thin nature of sheet metal makes it vulnerable to denting from impacts and buckling under compressive loads. Effective design requires incorporating stiffening features like ribs, flanges, or compound curves to maintain shape and resist deformation.
High Initial Tooling Costs
For processes like stamping, the custom-made hardened steel dies are expensive and time-consuming to produce. This makes sheet metal fabrication a poor choice for one-off prototypes or very low-volume production runs, where methods like CNC machining or 3D printing are more economical.
A Spectrum of Applications: Where Sheet Metal Excels
The properties of sheet metal make it the backbone of numerous industries, each leveraging its unique advantages.
Automotive and Transportation
From the car body panels and chassis that protect you to the brackets holding components in place, sheet metal is essential. Its strength-to-weight ratio is paramount for achieving both fuel efficiency and crash safety.
Construction and Architecture
Sheet metal is used for roofing, gutters, wall panels, and structural components like steel studs. Here, its durability, weather resistance (when coated), and cost-effectiveness for covering large areas are the primary drivers.
Appliances and Electronics
The cases of your refrigerator, washing machine, computer, and other devices are almost always made from sheet metal. It provides a durable and protective enclosure that is inexpensive to produce in high volumes and can be finished to a high aesthetic standard.
Aerospace
Aircraft fuselages, wing skins, and internal ribs are fabricated from high-strength aluminum and titanium sheet metal alloys. In this field, maximizing strength while minimizing weight is the single most important objective, making sheet metal the ideal material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, selecting sheet metal depends entirely on the goals and constraints of your project. Balancing performance, cost, and production volume is the key to making an informed decision.
- If your primary focus is mass production of strong, lightweight parts: Sheet metal is an exceptional choice due to its low per-unit cost and high strength-to-weight ratio.
- If your primary focus is a low-volume or one-off prototype: Consider alternatives like 3D printing or CNC machining, as the high tooling cost of sheet metal fabrication will likely be prohibitive.
- If your primary focus is durability in a harsh environment: You must specify either a naturally corrosion-resistant material like aluminum or stainless steel, or factor in the cost of a robust protective coating.
- If your design involves highly complex or thick geometries: A process like casting, forging, or machining from a solid block may be a more suitable manufacturing method.
By understanding its fundamental properties and trade-offs, you can effectively determine when sheet metal is the right material to bring your design to life.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Primary Advantages | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio, high formability, cost-effective at scale, wide material/finish options |
| Key Disadvantages | Susceptibility to corrosion, limitations in complex geometries, potential for buckling/denting, high initial tooling costs |
| Common Applications | Automotive body panels, construction roofing, appliance casings, aerospace components |
| Best For | High-volume production of strong, lightweight parts requiring protective enclosures or structural panels |
Need precision materials for your lab or manufacturing process? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, serving diverse laboratory needs. Whether your project involves material testing, prototyping, or production, our expertise can help you achieve superior results. Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your specific application and material requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Gold Platinum Copper Iron Metal Sheets
- Carbon Graphite Plate Manufactured by Isostatic Pressing Method
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Flat Corrugated Heat Sink for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Battery Lab Applications
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How thick is gold sputtering? Achieve Precise Coatings from Ångstroms to Microns
- How hot can a metal surface get in the sun? The Surprising Science Behind Extreme Heat
- What is the purity of the gold and platinum sheets used for experiments? Ensuring 99.99% Purity for Reliable Results
- Why is platinum unreactive? The Atomic Secrets Behind Its Remarkable Stability
- Where is soldering commonly used? From Everyday Electronics to Industrial Applications












