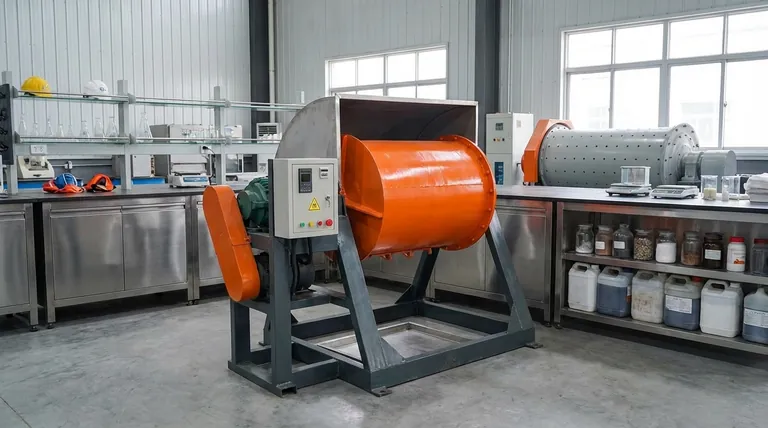
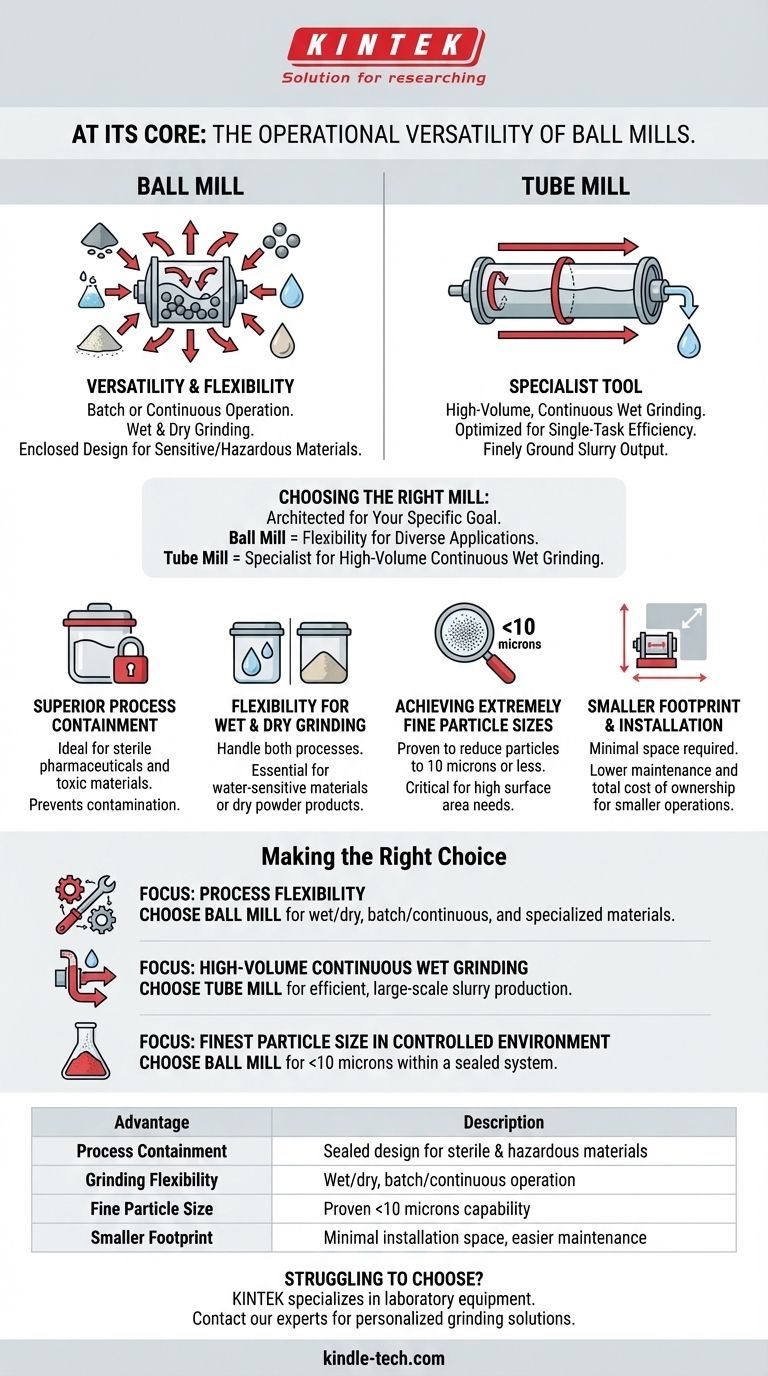
At its core, the primary advantage of a ball mill over a tube mill is its operational versatility. While both use tumbling media to grind materials, a ball mill is uniquely suited for a wider range of processes. It can perform both wet and dry grinding, operate in either batch or continuous modes, and its enclosed design makes it ideal for handling sensitive or hazardous materials where containment is critical.
Choosing between these mills is not about which is universally "better," but which is architected for your specific goal. A ball mill provides flexibility for diverse or specialized applications, whereas a tube mill is a specialist tool built for high-volume, continuous wet grinding.

Fundamental Differences in Mill Design
The Principle of Grinding: Tumbling Media
Both ball mills and tube mills operate on the same fundamental principle. A cylindrical shell rotates, causing grinding media (such as steel balls) inside to cascade and tumble, crushing and grinding material through impact and attrition.
Ball Mills: Versatility in Process Type
A ball mill's key design feature is its adaptability. It can be loaded with material for a batch process, where the entire grinding cycle is completed within a sealed container. This is crucial for applications requiring sterility or the handling of toxic substances.
They can also be configured for continuous operation and are capable of performing both wet and dry grinding, making them a flexible tool for many industries.
Tube Mills: High-Throughput Continuous Flow
A tube mill is essentially a longer, larger version of a ball mill, designed almost exclusively for continuous, high-volume work. Material is fed into one end and slowly passes through the long chamber, exiting the other end as a finely ground slurry.
This design is optimized for a single task: processing large quantities of material in a continuous, wet grinding circuit.
Key Advantages of the Ball Mill
Superior Process Containment
The ability to operate a ball mill as a sealed, closed container is a significant advantage. This makes it the default choice for manufacturing pharmaceutical products (parenteral and ophthalmic) where sterility must be maintained.
This same feature allows for the safe grinding of toxic or hazardous materials, preventing contamination of the work environment.
Flexibility for Wet and Dry Grinding
A ball mill's ability to handle both wet and dry processes gives operators more control. Some materials cannot be exposed to water or require a dry powder as the final product, making a ball mill the only viable option.
Achieving Extremely Fine Particle Sizes
Ball mills are proven to produce exceptionally fine powders, with documented performance of reducing particle sizes to 10 microns or less. This level of pulverization is critical for applications requiring high surface area or specific material properties.
Smaller Footprint and Installation
Compared to the larger, high-capacity tube mills, ball mills generally require minimal space for installation. Their design often leads to lower maintenance costs and easier cleaning, reducing the total cost of ownership for smaller-scale or intermittent operations.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When a Tube Mill Excels
The Throughput Limitation of Batch Processing
While a ball mill's batch capability is an advantage for containment, it is a bottleneck for production volume. If your goal is to process tons of material per hour without interruption, the stop-and-start nature of batch grinding is inefficient.
The Case for High-Volume Slurry Production
A tube mill is the undisputed specialist for large-scale industrial processes that require a continuous stream of finely ground slurry. Industries like mineral processing or cement manufacturing rely on the constant, high-throughput nature of tube mills.
In these scenarios, the tube mill's singular focus on continuous wet grinding delivers an economy of scale that a more versatile ball mill cannot match.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision must be driven by your operational needs for scale, material handling, and the desired final product.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility and specialized materials: A ball mill is the correct choice for its ability to handle wet/dry grinding, batch processing of toxic or sterile substances, and its smaller footprint.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous wet grinding: A tube mill is the more efficient solution, as it is designed specifically for producing a constant slurry output at a large industrial scale.
- If your primary focus is achieving the finest particle size in a controlled environment: The proven capability of a ball mill to produce powders down to 10 microns within a sealed system makes it the superior option.
By matching the mill's core design to your specific production goals, you ensure maximum efficiency and return on your investment.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Containment | Sealed design ideal for sterile pharmaceuticals and hazardous materials. |
| Grinding Flexibility | Capable of both wet and dry grinding, and batch or continuous operation. |
| Fine Particle Size | Proven to reduce particles to 10 microns or less. |
| Smaller Footprint | Requires minimal installation space and offers easier maintenance. |
Struggling to choose the right mill for your specific materials and process? KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables, providing expert solutions for your grinding needs. Whether you require the versatility of a ball mill for specialized applications or high-throughput equipment, our team can help you select the perfect tool to enhance your lab's efficiency and ensure a strong return on investment. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the product size of a ball mill? Achieve Micron-Level Precision for Your Materials
- Why is a laboratory ball mill used in Co-Ni catalyst research? Optimize CO2 Conversion with Precise Milling
- What is the function of ball milling equipment in NZSSP electrolyte preparation? Optimize NASICON Solid-State Synthesis
- What are the disadvantages of a ball mill? High Energy Use, Noise, and Contamination Risks
- Why use ball milling for NMC cathode materials? Achieve Precision Particle Sizing for Composite Cathodes



















