The primary advantages of PVD lie in its lower temperature application and wear resistance, while CVD excels at creating highly uniform, pure coatings on complex shapes. Both are thin-film deposition techniques used to enhance a material's surface, but they achieve this through fundamentally different mechanisms—one physical, one chemical—which dictates their ideal use cases.
Choosing between PVD and CVD is not about which is 'better,' but about aligning the process with your specific needs. CVD offers unmatched conformity on intricate designs through a chemical reaction, while PVD provides a robust, line-of-sight physical process ideal for creating tough surfaces on more temperature-sensitive materials.
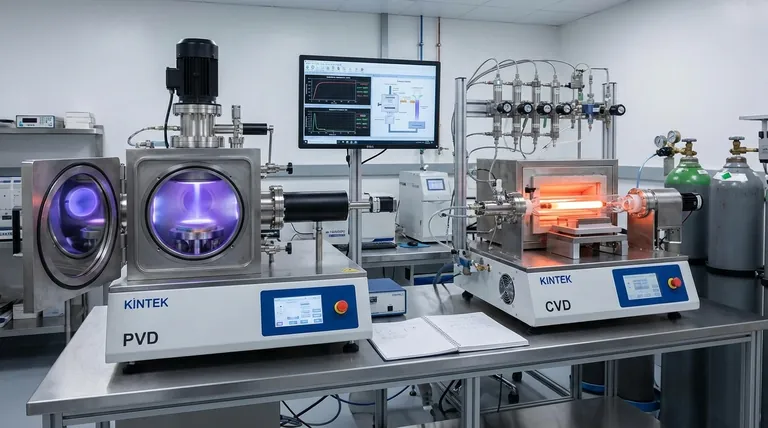

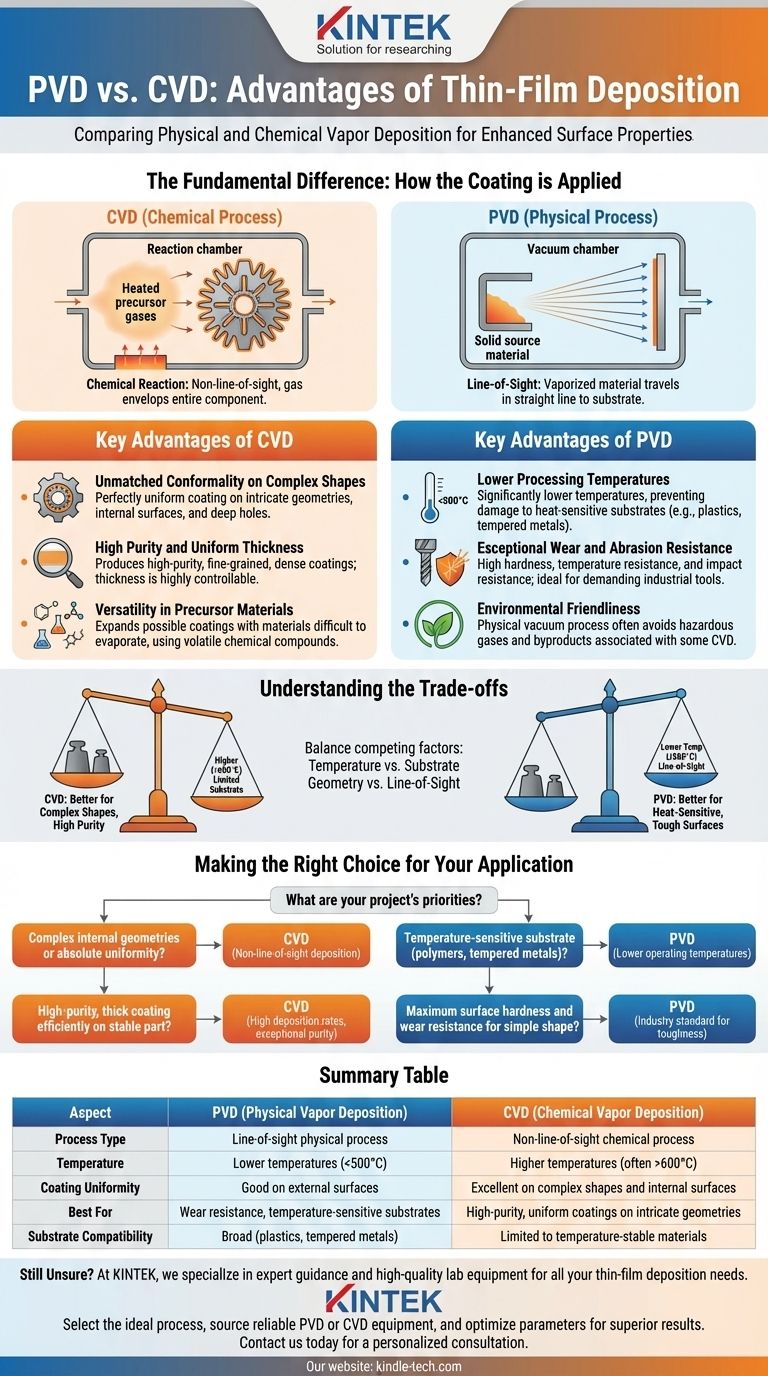
The Fundamental Difference: How the Coating is Applied
The advantages of each method are a direct result of their core processes. Understanding this distinction is key to making the right choice.
How PVD Works (A Physical Process)
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a line-of-sight process that takes place in a vacuum. A solid source material is physically vaporized (e.g., through sputtering or evaporation) and travels in a straight line to condense on the substrate. Think of it like spray painting, where the paint can only coat surfaces it can directly see.
How CVD Works (A Chemical Process)
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) uses a chemical reaction to build the coating. Volatile precursor gases are introduced into a reaction chamber, where they decompose on the heated substrate's surface, leaving behind the desired material as a solid film. Because the gas envelops the entire component, the process is not limited by line-of-sight.
Key Advantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD's strengths are rooted in its ability to "grow" a film from a reactive gas, leading to superior coverage and purity.
Unmatched Conformality on Complex Shapes
This is CVD's most significant advantage. Since it is not a line-of-sight process, it can deposit a perfectly uniform coating over complex geometries, including deep holes, sharp corners, and internal surfaces that are impossible to coat with PVD.
High Purity and Uniform Thickness
The chemical reaction process results in extremely high-purity, fine-grained, and dense coatings. The thickness of the coating is highly controllable by simply adjusting the process temperature and duration, ensuring consistent results.
Versatility in Precursor Materials
CVD can be used with elements that are very difficult to evaporate for PVD processes. As long as a volatile chemical compound of the material exists, it can likely be used as a precursor gas in a CVD process, expanding the range of possible coatings.
Key Advantages of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
PVD is a highly refined physical process valued for its versatility with different substrates and the exceptional toughness of its coatings.
Lower Processing Temperatures
PVD generally operates at significantly lower temperatures than CVD. This is a critical advantage, as it allows for coating heat-sensitive substrates (like plastics, certain alloys, or tempered metals) that would be damaged or destroyed by the high temperatures required for many CVD reactions.
Exceptional Wear and Abrasion Resistance
PVD coatings are renowned for their high hardness, temperature resistance, and impact resistance. This makes PVD a standard choice in demanding industries like automotive, manufacturing, and construction for tools and components that require a highly durable surface.
Environmental Friendliness
As a purely physical process that occurs in a vacuum, PVD often avoids the use of the hazardous precursor gases and byproducts associated with some CVD processes, making it a more environmentally friendly option.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between these two methods always involves balancing competing factors.
Temperature vs. Substrate Compatibility
The high heat of CVD (often >600°C) produces excellent, dense coatings but limits the types of materials you can use. PVD's lower temperature range (<500°C) makes it compatible with a much broader array of substrates.
Geometry vs. Line-of-Sight
This is the most critical trade-off. For any part with complex surfaces, internal channels, or a need for absolute uniformity, CVD is the only option. For simpler, externally facing surfaces, PVD's line-of-sight nature is perfectly sufficient.
Coating Properties vs. Process
CVD often yields coatings with higher purity and better crystalline structure. However, PVD can produce exceptionally hard and wear-resistant coatings that are ideal for extending the life of tools and high-wear components.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your application's specific requirements will point you to the correct technology.
- If your component has complex internal geometries or requires absolute coating uniformity: CVD is the superior choice due to its non-line-of-sight deposition process.
- If your substrate is temperature-sensitive (like certain polymers or tempered metals): PVD's lower operating temperatures make it the safer and often only viable option.
- If your primary goal is maximum surface hardness and wear resistance for a relatively simple shape: PVD coatings are an industry standard for their toughness and are ideal for this purpose.
- If you need to deposit a high-purity, thick coating efficiently on a temperature-stable part: CVD often has high deposition rates and can produce films with exceptional purity.
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently select the coating technology that best aligns with your material, design, and performance goals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Line-of-sight physical process | Non-line-of-sight chemical process |
| Temperature | Lower temperatures (<500°C) | Higher temperatures (often >600°C) |
| Coating Uniformity | Good on external surfaces | Excellent on complex shapes and internal surfaces |
| Best For | Wear resistance, temperature-sensitive substrates | High-purity, uniform coatings on intricate geometries |
| Substrate Compatibility | Broad (plastics, tempered metals) | Limited to temperature-stable materials |
Still Unsure Which Coating Technology is Right for Your Project?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing expert guidance and high-quality lab equipment for all your thin-film deposition needs. Whether you're working with temperature-sensitive materials requiring PVD or complex components that need the uniform coverage of CVD, our team is here to help.
We can help you:
- Select the ideal coating process for your specific application
- Source reliable PVD or CVD equipment tailored to your requirements
- Optimize your coating parameters for superior results
Contact us today for a personalized consultation and let our experts guide you to the perfect solution for enhancing your material's performance. Get in touch with our team now →
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- How is PECVD different from CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the examples of CVD method? Discover the Versatile Applications of Chemical Vapor Deposition
- What is the difference between CVD and PVD process? A Guide to Choosing the Right Coating Method
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- How plasma is generated in PECVD? A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process



















