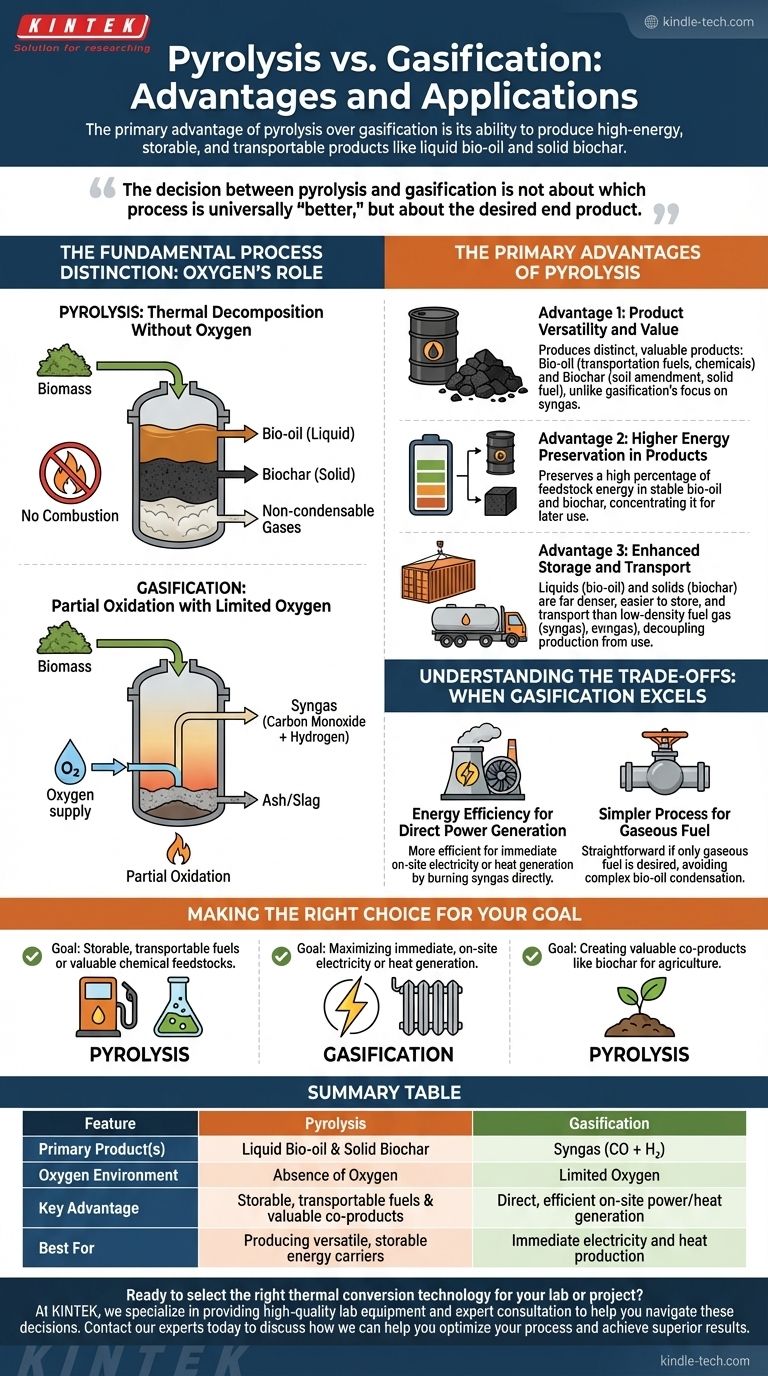
At its core, the primary advantage of pyrolysis over gasification is its ability to produce high-energy, storable, and transportable products like liquid bio-oil and solid biochar. Unlike gasification, which immediately converts biomass into a gaseous fuel, pyrolysis preserves the chemical energy from the feedstock in more versatile liquid and solid forms.
The decision between pyrolysis and gasification is not about which process is universally "better," but about the desired end product. Gasification is optimized for the immediate production of gaseous fuel (syngas) for power and heat, while pyrolysis is designed to create storable liquid fuel and solid co-products.
The Fundamental Process Distinction: Oxygen's Role
To understand the advantages of each, we must first look at the defining difference in their chemical environments. The presence or absence of oxygen dictates the entire outcome.
Pyrolysis: Thermal Decomposition Without Oxygen
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of organic material at high temperatures in the complete absence of oxygen.
This oxygen-free environment prevents combustion. Instead of burning, the material breaks down into smaller molecules, which can be captured as a liquid (bio-oil), a solid (biochar), and non-condensable gases.
Gasification: Partial Oxidation with Limited Oxygen
Gasification exposes organic material to very high temperatures (>700°C) in a controlled, oxygen-limited environment.
This process of partial oxidation provides just enough oxygen to convert the feedstock primarily into a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen known as synthesis gas, or syngas.
The Primary Advantages of Pyrolysis
The oxygen-free nature of pyrolysis directly leads to its key advantages, which center on the types of products it creates.
Advantage 1: Product Versatility and Value
Pyrolysis produces a slate of distinct, valuable products. Bio-oil can be refined into transportation fuels or used as a chemical feedstock. Biochar is a stable, carbon-rich solid that can be used for soil amendment, filtration, or as a solid fuel.
Gasification, by contrast, is singularly focused on producing syngas, whose primary use is immediate combustion for heat and power.
Advantage 2: Higher Energy Preservation in Products
Because no oxidation occurs, pyrolysis is primarily an endothermic process that preserves a very high percentage of the feedstock's original energy content within the resulting bio-oil and biochar.
The energy is effectively concentrated and locked into these stable forms, ready for later use.
Advantage 3: Enhanced Storage and Transport
This is a critical logistical advantage. Liquids (bio-oil) and solids (biochar) are far denser and easier to store and transport than a hot, low-density fuel gas like syngas.
This decouples the initial processing of the feedstock from its final use. A facility can produce bio-oil and ship it to a refinery or power plant hundreds of miles away, a feat that is not practical with syngas.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When Gasification Excels
To make an objective decision, you must recognize the scenarios where gasification is the superior choice. The advantages of pyrolysis are not without their corresponding trade-offs.
Energy Efficiency for Direct Power Generation
For the specific goal of producing on-site electricity or heat, gasification is often more efficient.
The process of converting feedstock directly to syngas and then immediately burning that gas in a turbine or engine is a more direct and established pathway for power generation than producing, collecting, and then burning bio-oil.
Simpler Process for Gaseous Fuel
If a gaseous fuel is the only desired output, gasification is the more straightforward process. Pyrolysis requires an additional, complex step of rapidly cooling and condensing the vapors to capture the liquid bio-oil fraction, which adds equipment and operational complexity.
Feedstock Flexibility for Gas Production
While both processes are sensitive to feedstock characteristics, gasification's goal of breaking everything down into simple gas molecules (CO and H2) can sometimes make it more tolerant of diverse or less-than-ideal feedstocks compared to producing a high-quality, stable bio-oil.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal technology is dictated entirely by your project's primary objective. Use these points as a clear guide for your decision.
- If your primary focus is producing storable, transportable fuels or valuable chemical feedstocks: Pyrolysis is the superior choice due to its production of energy-dense bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is maximizing immediate, on-site electricity or heat generation: Gasification is typically the more direct and efficient pathway.
- If your primary focus is creating valuable co-products like biochar for agriculture or sequestration: Pyrolysis is the only process of the two that generates biochar in significant quantities.
Ultimately, choosing the right thermal conversion technology depends on a clear understanding of your desired outcome and the logistical chain that follows.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Pyrolysis | Gasification |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Product(s) | Liquid Bio-oil & Solid Biochar | Syngas (CO + H₂) |
| Oxygen Environment | Absence of Oxygen | Limited Oxygen |
| Key Advantage | Storable, transportable fuels & valuable co-products | Direct, efficient on-site power/heat generation |
| Best For | Producing versatile, storable energy carriers | Immediate electricity and heat production |
Ready to select the right thermal conversion technology for your lab or project? The choice between pyrolysis and gasification is critical for achieving your specific energy and product goals. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and expert consultation to help you navigate these decisions. Whether you're researching bio-oil refinement, biochar applications, or syngas utilization, our team is here to support your laboratory's needs. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you optimize your process and achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
People Also Ask
- What are the factors affecting pyrolysis yield? Mastering the Control of Char, Oil, and Gas Production
- What plastics can be used in pyrolysis? A Guide to Ideal Feedstocks for Waste-to-Energy
- What are the products of pyrolysis of rubber? Transforming Waste into Valuable Resources
- What are the safety concerns of pyrolysis? Managing Fire, Toxicity, and Process Control Risks
- Does pyrolysis produce gas? Unlocking the Potential of Syngas, Bio-oil, and Biochar
- What are the products of calcination? A Guide to Thermal Decomposition Outputs
- What is the pyrolysis method for plastic waste? Convert Non-Recyclable Plastics into Fuel
- Does pyrolysis use a lot of energy? Achieve Net Energy Positive Waste Conversion


















