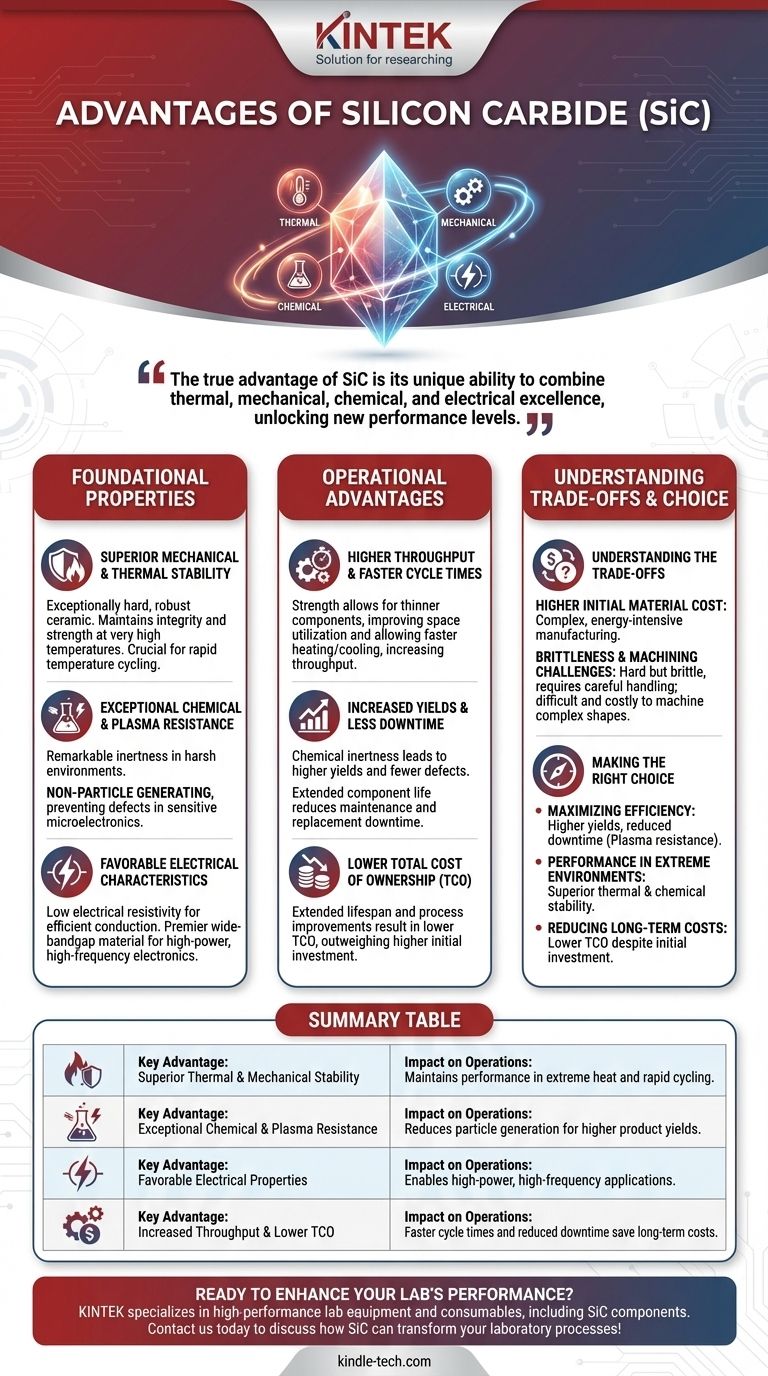
At its core, Silicon Carbide (SiC) provides a powerful combination of physical toughness, chemical stability, and advanced electrical properties. It consistently outperforms traditional materials, especially in harsh chemical and plasma environments. This superiority translates directly into tangible operational benefits like higher manufacturing yields, faster throughput, and a lower total cost of ownership.
The true advantage of SiC is not just one superior property, but its unique ability to combine thermal, mechanical, chemical, and electrical excellence. This synergy unlocks new levels of performance in demanding applications where conventional materials have reached their limits.

The Foundational Properties of SiC
Silicon Carbide's value stems from a set of intrinsic characteristics that make it uniquely suited for high-performance applications, from semiconductor manufacturing to aerospace technology.
### Superior Mechanical and Thermal Stability
SiC is an exceptionally hard and robust ceramic material. It maintains its structural integrity and strength at very high temperatures where other materials would warp, melt, or degrade.
This thermal stability is critical for processes that involve rapid temperature cycling, ensuring components remain dimensionally stable and reliable over time.
### Exceptional Chemical and Plasma Resistance
In the aggressive environments found inside semiconductor processing chambers, SiC demonstrates remarkable inertness. It resists corrosion and erosion from harsh chemicals and high-energy plasmas.
A key benefit of this resistance is that SiC is non-particle generating. By not shedding particles, it helps maintain a pristine processing environment, which is crucial for preventing defects in sensitive microelectronics.
### Favorable Electrical Characteristics
SiC possesses low electrical resistivity, allowing for efficient current conduction in applications like electrodes. Its properties also make it a premier wide-bandgap semiconductor material.
This electrical performance is fundamental to its growing role in high-power, high-frequency electronics, enabling devices that are smaller, faster, and more efficient than their silicon-based counterparts.
Translating Properties into Operational Advantages
The physical characteristics of SiC create direct and measurable benefits in industrial and high-tech settings, improving both efficiency and a company's bottom line.
### Higher Throughput and Faster Cycle Times
Because of its strength and stability, components made from SiC can be designed with thinner sections. This improves space utilization in crowded tools and allows for faster heating and cooling, which shortens process cycle times and increases overall throughput.
### Increased Yields and Less Downtime
The chemical inertness and non-particle generating nature of SiC directly lead to higher manufacturing yields. A cleaner process chamber means fewer defects on each wafer or product.
Furthermore, its durability means components last significantly longer, leading to less equipment downtime for maintenance and replacement.
### Lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
While SiC components may have a higher initial purchase price, their extended lifespan and the process improvements they enable result in a lower total cost of ownership. The savings from reduced downtime and increased yield quickly outweigh the upfront investment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every situation. Acknowledging the practical considerations of SiC is key to making an informed decision.
### Higher Initial Material Cost
The manufacturing process for high-purity Silicon Carbide is complex and energy-intensive. This results in a higher upfront cost compared to traditional materials like alumina, quartz, or standard silicon.
### Brittleness and Machining Challenges
Like many advanced ceramics, SiC is hard but also brittle. It can be susceptible to fracture from sharp impacts or high tensile stress, requiring careful design and handling protocols.
Its extreme hardness also makes it more difficult and costly to machine into complex shapes compared to metals or softer materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting SiC is a strategic decision that should align with your primary operational goals.
- If your primary focus is maximizing manufacturing efficiency: SiC's resistance to plasma and its non-particle generating nature directly lead to higher product yields and reduced downtime.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme environments: SiC's unparalleled thermal and chemical stability make it the superior choice for components in high-temperature or corrosive settings.
- If your primary focus is reducing long-term operational costs: The extended component lifetime and improved process reliability of SiC deliver a lower total cost of ownership, despite a higher initial investment.
Ultimately, adopting Silicon Carbide is an investment in stability, efficiency, and performance at the edge of what is technologically possible.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Impact on Your Operations |
|---|---|
| Superior Thermal & Mechanical Stability | Maintains performance in extreme heat and rapid cycling. |
| Exceptional Chemical & Plasma Resistance | Reduces particle generation for higher product yields. |
| Favorable Electrical Properties | Enables high-power, high-frequency applications. |
| Increased Throughput & Lower TCO | Faster cycle times and reduced downtime save long-term costs. |
Ready to enhance your lab's performance with the superior material science of Silicon Carbide? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including SiC components designed for demanding environments. Our solutions help you achieve higher manufacturing yields, faster throughput, and a lower total cost of ownership. Contact us today to discuss how SiC can transform your laboratory processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
People Also Ask
- Why is it necessary to use high-temperature and corrosion-resistant ceramics for H2SO4 decomposers in the IS process?
- What are the different types of silicon carbide? A Guide to Polytypes, Manufacturing, and Applications
- What is the specific heat of alumina? It's a range from 451 to 955 J/kg·K
- How do you prepare silicon carbide in the laboratory? Master High-Temperature Synthesis Methods
- How is sintering done to ceramics? Master the Process for High-Performance Materials
- What is the use of SiC semiconductor? Unlock Higher Efficiency for EVs and Power Systems
- Which ceramic materials are most widely used? A Guide to Alumina, Zirconia, SiC, and Si3N4
- What is the strongest zirconia phase? Tetragonal Zirconia Offers Unmatched Toughness



















