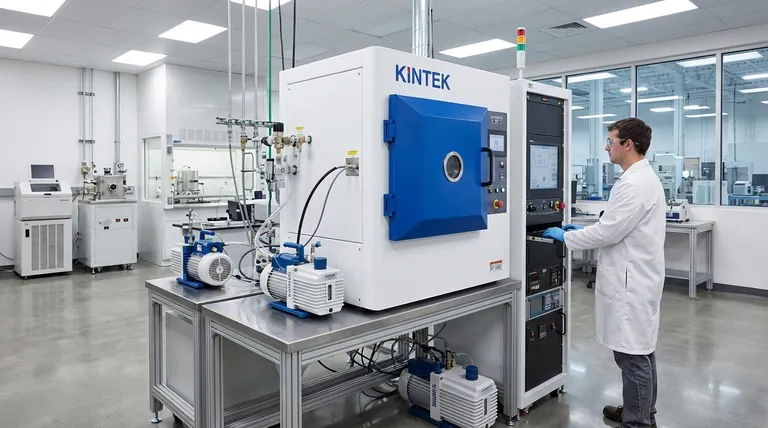
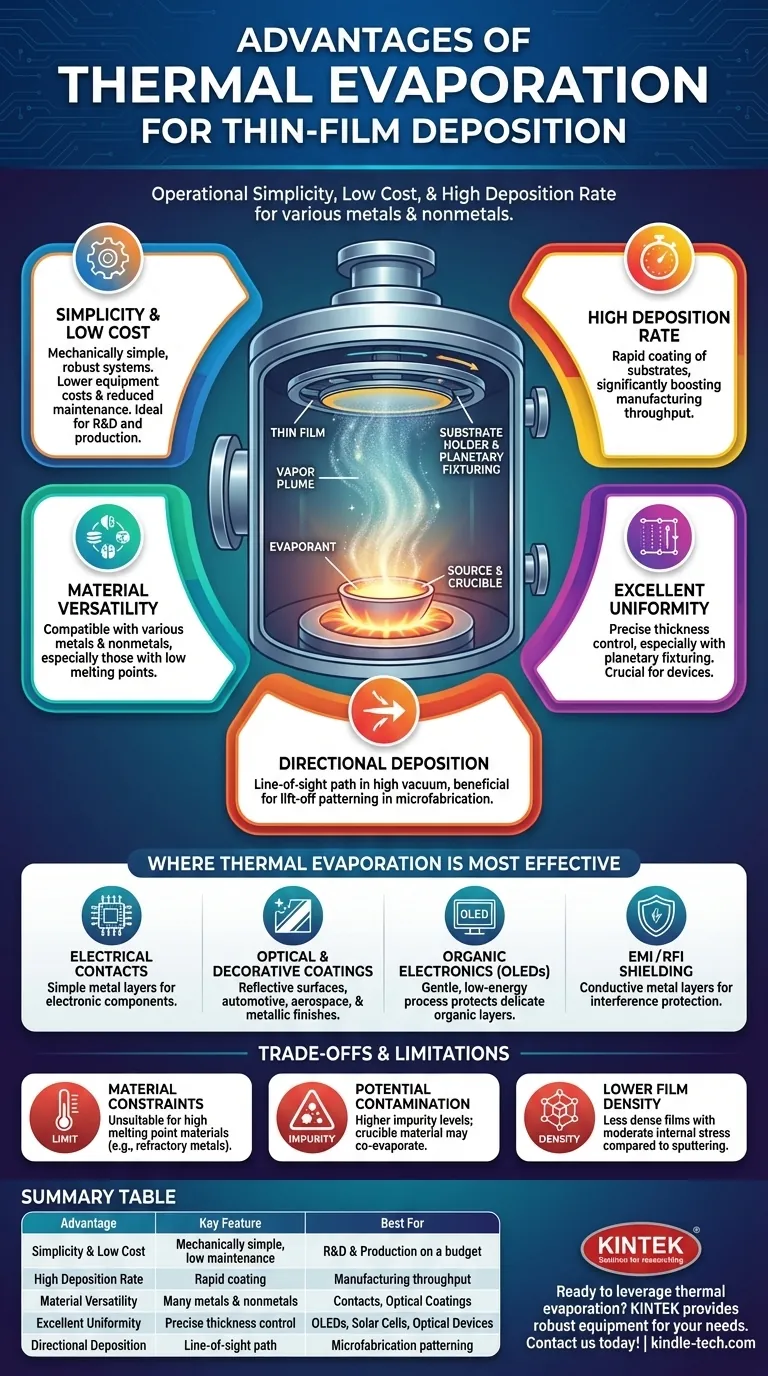
In the world of thin-film deposition, the primary advantages of the thermal evaporation method are its operational simplicity, low cost, and high deposition rate. It is particularly well-suited for depositing a range of materials, including metals and nonmetals, that have relatively low melting points, making it a highly accessible and efficient technique for many applications.
Thermal evaporation stands out as a simple, fast, and cost-effective method for creating thin films. Its value is best understood in applications where extreme purity and film density are secondary to speed and budget, making it a workhorse for specific industrial and research tasks.

The Core Advantages of Thermal Evaporation
Thermal evaporation operates on a straightforward principle: a source material is heated in a high-vacuum environment until it evaporates, and the resulting vapor travels in a straight line to condense on a cooler substrate, forming a thin film. This simplicity is the source of its key benefits.
### Simplicity and Low Cost
Thermal evaporation systems are mechanically simple and robust compared to other physical vapor deposition (PVD) methods. This translates directly to lower initial equipment costs and reduced maintenance, making it an attractive option for both R&D and production environments.
### High Deposition Rate
The process can achieve very high deposition rates, allowing for the rapid coating of substrates. This speed is a significant advantage in manufacturing settings where throughput is a critical performance metric.
### Material Versatility (Within Limits)
The method is compatible with a wide variety of materials, including both metals (like aluminum and silver) and nonmetals. It is especially effective for elemental materials with a uniform, low melting point that can be easily evaporated from a crucible or boat.
### Excellent Uniformity Control
Achieving a highly uniform film thickness across a substrate is critical for many devices. Thermal evaporation can produce excellent uniformity, especially when paired with planetary substrate fixturing, which rotates the substrates to ensure even coating.
### Directional Deposition
The high-vacuum environment (typically 0.0013 Pa or lower) ensures that evaporated atoms travel in an essentially collisionless, line-of-sight path from the source to the substrate. This good directionality is beneficial for "lift-off" patterning processes used in microfabrication.
Where Thermal Evaporation is Most Effective
The unique combination of advantages makes thermal evaporation the preferred method for a number of well-established applications.
### Electrical Contacts and Simple Metal Layers
Its most common use is for depositing single-metal layers for electrical contacts. The ability to quickly lay down conductive films of aluminum or silver on electronic components is a perfect match for the technique's strengths.
### Optical and Decorative Coatings
Thermal evaporation is widely used to create reflective surfaces. This includes light reflectors for the automotive and aerospace industries, as well as decorative metallic finishes on items like cosmetic packaging and sporting goods.
### Organic Electronics and Thin-Film Devices
The process is a cornerstone in manufacturing OLED displays and some types of solar cells. The relatively low energy of the evaporated particles is gentle on the underlying delicate organic layers, which could be damaged by more energetic deposition methods.
### EMI/RFI Shielding
A thin, conductive metal layer deposited via thermal evaporation can provide effective shielding against electromagnetic and radio-frequency interference for sensitive electronic enclosures.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
To use thermal evaporation effectively, one must be aware of its inherent limitations. Its simplicity comes at the cost of control and film quality compared to more advanced techniques.
### Material Constraints
The primary limitation is temperature. The process is unsuitable for materials with very high melting points, such as refractory metals like tungsten or molybdenum. The heating element (crucible or boat) itself can melt or react with the source material at extreme temperatures.
### Potential for Contamination
Thermal evaporation typically produces films with the highest impurity levels among PVD methods. Contamination can arise from the heated crucible material itself, which may co-evaporate along with the desired source material.
### Lower Film Density
Films deposited by thermal evaporation are often less dense and have more moderate internal stress compared to those created by sputtering. While this quality can be improved with ion-assist sources, it is a key consideration for applications requiring highly durable or hermetic coatings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct deposition method depends entirely on your project's specific requirements for film quality, material, and budget.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective metal deposition for contacts or coatings: Thermal evaporation offers an unmatched combination of simplicity, speed, and low operational cost.
- If your primary focus is high-purity or dense films for advanced applications: You should consider alternative methods like electron-beam evaporation or sputtering to avoid contamination and achieve superior film quality.
- If your primary focus is depositing organic materials for devices like OLEDs: Thermal evaporation is a standard and highly effective technique due to the low-energy deposition that protects sensitive underlying layers.
By understanding both its strengths and its inherent limitations, you can leverage thermal evaporation as a powerful and efficient tool for the right application.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Simplicity & Low Cost | Mechanically simple systems, low maintenance | R&D and production on a budget |
| High Deposition Rate | Rapid coating of substrates | Manufacturing with high throughput needs |
| Material Versatility | Compatible with many metals and nonmetals | Electrical contacts, optical coatings |
| Excellent Uniformity | Precise thickness control with planetary fixturing | OLEDs, solar cells, and optical devices |
| Directional Deposition | Line-of-sight path for lift-off patterning | Microfabrication and precise patterning |
Ready to leverage thermal evaporation for your thin-film projects? KINTEK specializes in providing robust and cost-effective lab equipment, including thermal evaporation systems, to meet your specific research and production needs. Whether you're depositing metals for electrical contacts or delicate layers for OLED displays, our expertise ensures you get the right solution for superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Managing the Trade-offs of Low-Temperature Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Coating Solution for Sensitive Materials



















