Fundamentally, thermal evaporation is a highly effective physical vapor deposition (PVD) technique due to its relative simplicity, low cost, and high deposition rate. It excels at depositing thin films of materials with lower melting points, including both metals and non-metals, making it a versatile tool for a wide range of applications from electronics to decorative coatings.
Thermal evaporation's primary advantage is its balance of speed and cost-effectiveness. However, this simplicity comes with inherent trade-offs in film purity and density, making it ideal for specific applications where ultimate film quality is not the single most critical parameter.

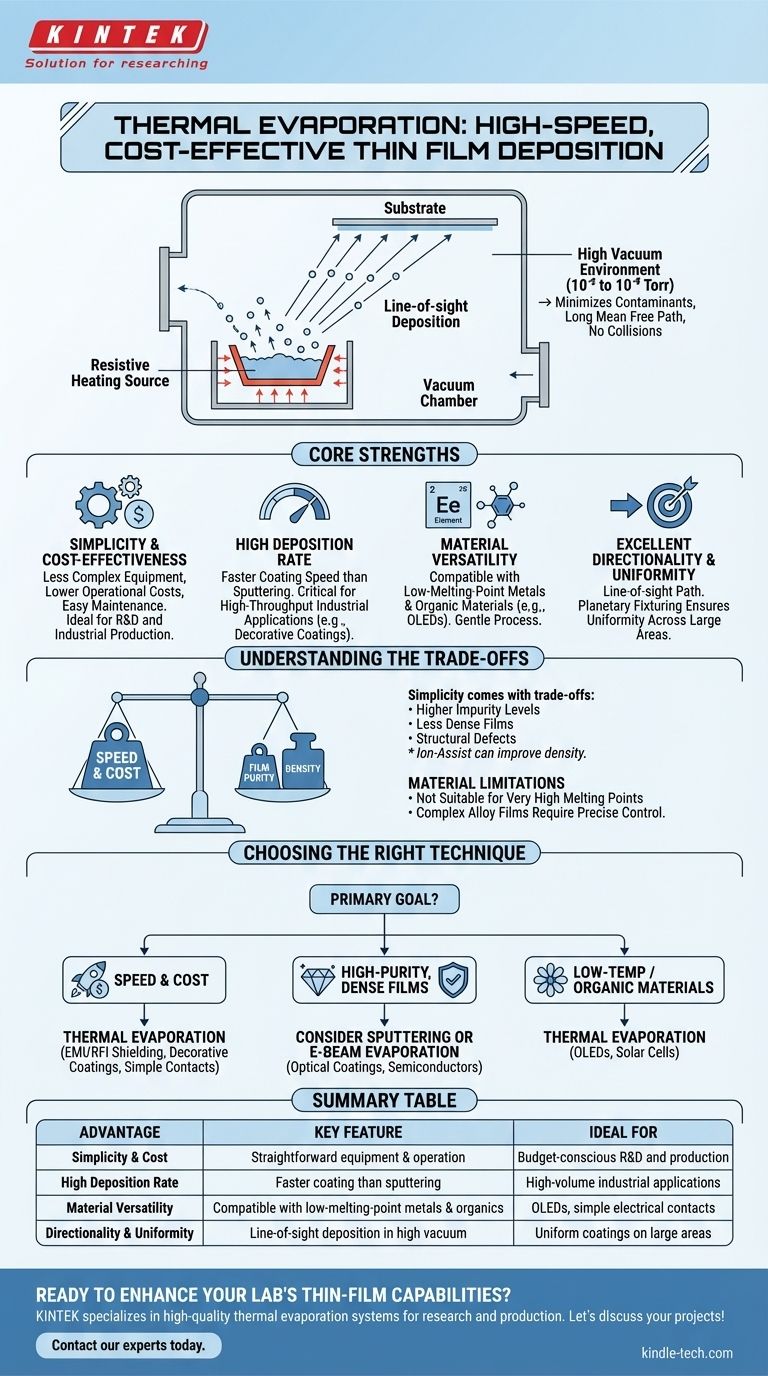
The Core Strengths of Thermal Evaporation
Thermal evaporation's popularity stems from a few key operational strengths that make it a go-to choice for many thin-film applications.
Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness
Resistive thermal evaporation is one of the most straightforward PVD methods. The equipment is less complex and therefore more affordable than systems for sputtering or electron-beam evaporation.
This simplicity translates to lower operational costs and easier maintenance, making it highly accessible for both research and industrial production.
High Deposition Rate
A significant advantage of thermal evaporation is its speed. It can deposit material onto a substrate at a much higher rate than other common techniques like sputtering.
This high throughput is critical for industrial applications where production volume and efficiency directly impact cost, such as in creating decorative coatings or simple electrical contacts.
Material Versatility
The technique is compatible with a wide array of materials, including single metals like aluminum and silver, as well as various non-metallic compounds.
It is particularly well-suited for materials with low melting points and organic materials, such as those used in OLED displays, which might be damaged by higher-energy deposition processes.
Excellent Directionality and Uniformity
The process occurs in a high vacuum, allowing evaporated atoms to travel in a straight, "line-of-sight" path to the substrate. This creates a highly directional deposition.
When combined with hardware like planetary substrate fixturing or uniformity masks, this directionality enables excellent film uniformity across large surface areas.
How the Process Enables These Advantages
The underlying physics and hardware of thermal evaporation are directly responsible for its benefits.
The Role of High Vacuum
Deposition is performed in a vacuum chamber, typically at pressures between 10⁻⁵ and 10⁻⁹ Torr. This environment is crucial for two reasons.
First, it minimizes gaseous contaminants, preventing unwanted reactions with the evaporated material. Second, it allows for a long "mean free path," meaning atoms travel from the source to the substrate with virtually no collisions, ensuring the directional coating.
Compatibility with Advanced Techniques
Thermal evaporation systems can be enhanced with additional tools. For example, they are compatible with ion-assist sources.
An ion source can be used to bombard the substrate during deposition, which helps compact the film. This improves film density and quality, bridging the gap between thermal evaporation and more complex PVD methods.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technique is perfect. The simplicity and speed of thermal evaporation come with important limitations that must be considered.
Film Purity and Density
Of all the major PVD methods, thermal evaporation tends to produce films with the highest impurity levels. The simple heating of a source can cause outgassing from the crucible and surrounding hardware.
The resulting films are often less dense and have more structural defects than those produced by sputtering. While this can be improved with ion-assist, the baseline quality is lower.
Material Limitations
The technique is not suitable for materials with very high melting points, as reaching the required evaporation temperature becomes difficult and inefficient with simple resistive heating.
Furthermore, creating alloy films from multiple source materials can be challenging. It requires precise and independent temperature control of each crucible to manage the different vapor pressures of the constituent materials.
Choosing Thermal Evaporation for Your Application
The decision to use thermal evaporation hinges on a clear understanding of your project's primary goal.
- If your primary focus is speed and cost: Thermal evaporation is an excellent choice for applications like EMI/RFI shielding, decorative coatings, or depositing simple metallic contacts where maximum purity is not required.
- If your primary focus is high-purity, dense films: You should consider alternative methods like sputtering or e-beam evaporation, especially for demanding optical coatings or critical semiconductor layers.
- If your primary focus is depositing low-temperature or organic materials: Thermal evaporation is a leading candidate, as its gentle process is ideal for sensitive materials used in OLEDs and some solar cells.
By understanding this balance of speed versus purity, you can confidently determine if thermal evaporation is the right tool for your specific engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Feature | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Simplicity & Cost | Straightforward equipment & operation | Budget-conscious R&D and production |
| High Deposition Rate | Faster coating than sputtering | High-volume industrial applications |
| Material Versatility | Compatible with low-melting-point metals & organics | OLEDs, simple electrical contacts |
| Directionality & Uniformity | Line-of-sight deposition in high vacuum | Uniform coatings on large areas |
Ready to enhance your lab's thin-film capabilities?
Thermal evaporation is a powerful tool for depositing coatings quickly and cost-effectively. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including thermal evaporation systems, to meet your specific research and production needs. Whether you're working on electronics, decorative coatings, or sensitive organic materials, our solutions are designed for reliability and performance.
Let's discuss how thermal evaporation can benefit your projects. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between sputtering and thermal evaporation? Choose the Right PVD Method for Your Thin Film
- What is thermal effect via evaporation? A Simple Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the meaning of thermal evaporation? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective Thin Film Coating
- What is thermal evaporation technique thin film deposition? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective PVD
- What is the thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition for Your Lab


















