The primary advantages of using Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) for Carbon Nanotube (CNT) production are its superior scalability, cost-effectiveness, and precise control over the final product's structure. These factors have made it the dominant commercial process, eclipsing older methods like arc discharge and laser ablation which are largely confined to laboratory-scale research.
While other methods can produce high-quality CNTs, CVD is the only technique that bridges the gap between laboratory discovery and industrial-scale manufacturing, making real-world applications economically feasible.

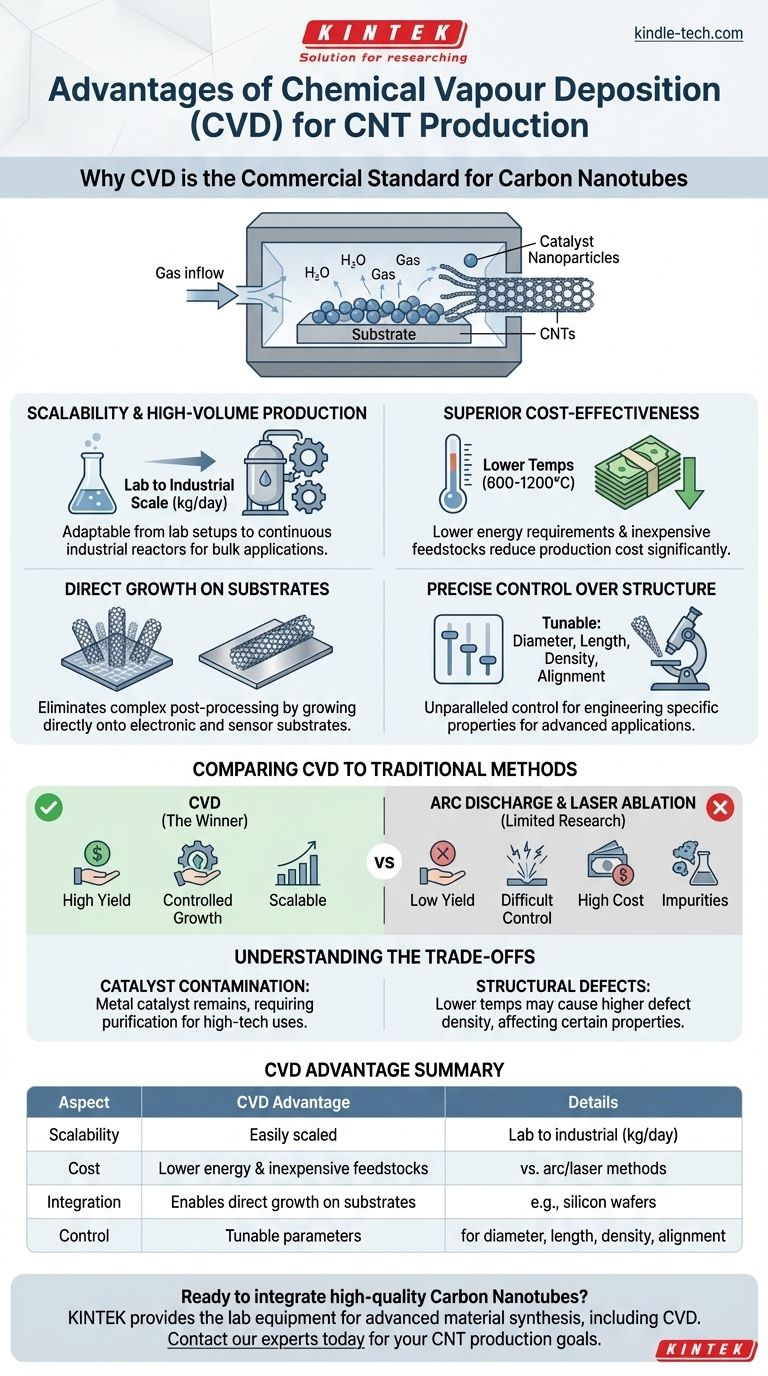
Why CVD Became the Commercial Standard
The shift to CVD was driven by the practical demands of manufacturing. For CNTs to move from a scientific curiosity to a functional material, they needed to be produced reliably, in large quantities, and at a reasonable cost.
Scalability and High-Volume Production
CVD is a highly scalable process. It can be adapted from small laboratory setups to large, continuous, or semi-continuous industrial reactors capable of producing kilograms of CNTs per day.
This ability to scale up is a fundamental requirement for commercial viability, allowing CNTs to be used in bulk applications like polymer composites, coatings, and energy storage devices.
Superior Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to its predecessors, CVD is significantly more economical. It typically operates at lower temperatures (600-1200°C) than arc discharge or laser ablation, which require temperatures exceeding 3000°C.
This lower energy requirement, combined with the use of relatively inexpensive hydrocarbon feedstocks like methane or ethylene, drastically reduces the overall production cost per gram of CNTs.
Direct Growth on Substrates
A key strategic advantage of CVD is its ability to grow CNTs directly onto a desired substrate, such as a silicon wafer, metal foil, or ceramic plate.
This capability is critical for applications in electronics, sensors, and catalysis, as it eliminates the difficult and often damaging post-processing steps of purifying, sorting, and depositing the nanotubes.
Precise Control Over Structure
CVD offers unparalleled control over the final CNT structure. By carefully tuning process parameters—such as temperature, pressure, gas composition, and catalyst type—it is possible to influence the nanotubes' diameter, length, density, and alignment.
This level of control is essential for engineering CNTs with specific properties tailored for advanced applications, a feat that is nearly impossible with the chaotic environments of arc discharge or laser ablation.
Comparing CVD to Traditional Methods
Understanding the limitations of older methods clarifies why the industry moved so decisively toward CVD.
The Limitations of Arc Discharge
This method involves striking an electric arc between two graphite electrodes. While it can produce high-quality CNTs, the output is a low-yield, tangled soot containing significant impurities. The process is difficult to control and virtually impossible to scale for mass production.
The Challenge of Laser Ablation
In this process, a high-power laser vaporizes a graphite target. It yields very high-purity CNTs but is extremely slow, energy-intensive, and prohibitively expensive. Its production rate is far too low for anything beyond specialized research samples.
Understanding the Trade-offs of CVD
Despite its advantages, CVD is not without its challenges. Objectively assessing these trade-offs is crucial for any application.
Catalyst Contamination
CVD relies on metal catalyst nanoparticles (e.g., iron, nickel, cobalt) to initiate CNT growth. These metallic particles can remain in the final product as impurities.
For many bulk applications, this is acceptable. However, for high-performance electronics or biomedical uses, these impurities can be detrimental and require extensive, costly purification steps.
Potential for Structural Defects
The lower synthesis temperatures of CVD can sometimes result in CNTs with a higher density of structural defects compared to those produced by higher-temperature methods.
While often sufficient for most applications, this can impact properties like electrical conductivity and mechanical strength, creating a trade-off between production cost and ultimate material perfection.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best production method is entirely dependent on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial production for composites or coatings: CVD is the only commercially viable choice due to its scalability and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible material purity for fundamental research: Laser ablation or specialized arc-discharge methods may be superior, despite their low yield and high cost.
- If your primary focus is integrating CNTs directly into electronic devices: CVD's ability to grow nanotubes directly on substrates makes it the most practical and efficient approach.
Ultimately, Chemical Vapor Deposition is the foundational technology that enabled carbon nanotubes to become a true industrial material.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | CVD Advantage |
|---|---|
| Scalability | Easily scaled from lab to industrial production (kg/day) |
| Cost | Lower energy use & inexpensive feedstocks vs. arc/laser methods |
| Integration | Enables direct growth on substrates (e.g., silicon wafers) |
| Control | Tunable parameters for diameter, length, density, and alignment |
Ready to integrate high-quality Carbon Nanotubes into your research or product development? KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables needed for advanced material synthesis, including CVD processes. Our expertise can help you achieve precise control and scalability for your specific application, from composites to electronics. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's CNT production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What function does CVD equipment serve in rhodium-modified coatings? Achieve Deep Diffusion and Microstructural Precision
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- What role does Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) equipment play in the preparation of C/C composites? Expert Analysis



















