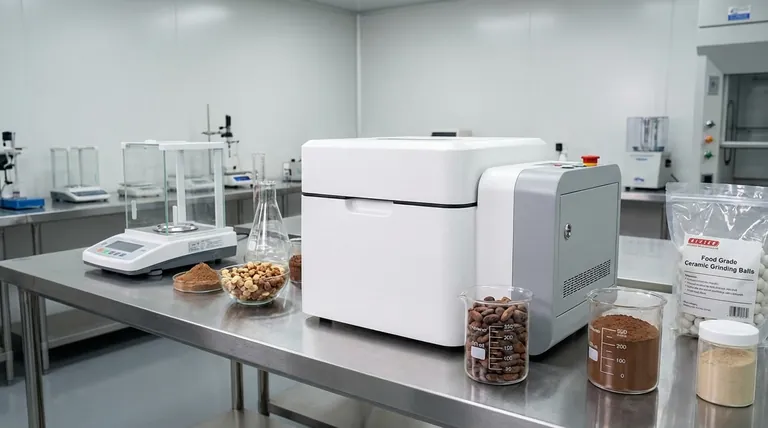
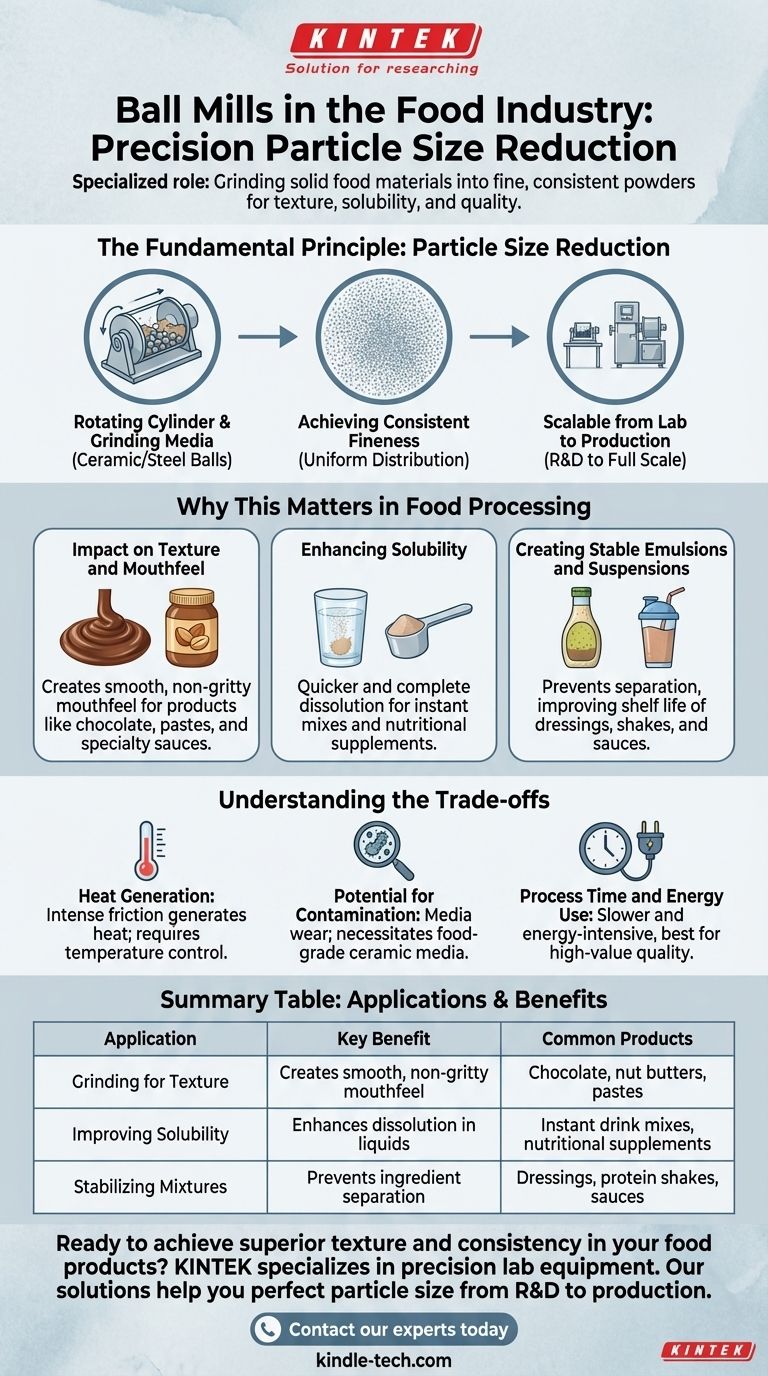
Although not as widely publicized as in mining or ceramics, ball mills serve a critical, specialized role in the food industry centered on precise particle size reduction. Their primary application is to grind solid food materials into extremely fine, consistent powders, which directly impacts the final product's texture, solubility, and overall quality.
The core value of a ball mill in food processing is its ability to achieve a uniform, ultra-fine particle size that is difficult to obtain with other methods. This makes it a strategic tool for enhancing product quality in specific, high-value applications rather than a universal piece of equipment.

The Fundamental Principle: Particle Size Reduction
A ball mill is fundamentally a grinder. It uses a rotating cylinder filled with grinding media—typically ceramic or steel balls—to reduce the size of solid materials through impact and attrition.
Achieving Consistent Fineness
The key advantage of this method is its ability to produce a very fine and highly uniform particle size distribution. This consistency is maintained over long production runs, ensuring product quality remains stable.
A Reliable and Simple Process
The technology is valued for its reliability, safety, and simplicity. The mechanics are straightforward, making the equipment durable and relatively easy to service, which is a significant benefit in a production environment.
Scalable from Lab to Production
Ball mills are available in a wide range of sizes. This includes small planetary or mixer mills for laboratory-scale research and development, up to large horizontal rolling mills with capacities of several hundred liters for full-scale production.
Why This Matters in Food Processing
The ability to control particle size with such precision unlocks specific benefits for food products, directly influencing the consumer experience and product performance.
Impact on Texture and Mouthfeel
For products like chocolate, specialty sauces, or pastes, an extremely fine particle size is essential for a smooth, non-gritty mouthfeel. Ball milling can grind ingredients like cocoa solids or nuts to a level where the individual particles are undetectable on the palate.
Enhancing Solubility
In products like instant drink mixes or nutritional supplements, finer particles dissolve much more quickly and completely in liquids. Ball milling can dramatically improve the solubility and bioavailability of certain ingredients.
Creating Stable Emulsions and Suspensions
Reducing particle size is crucial for creating stable mixtures of ingredients that would otherwise separate. Fine grinding helps keep solids suspended in liquids for longer, improving the shelf life and visual appeal of products like dressings or protein shakes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, ball milling is not a universal solution and requires careful consideration of its potential downsides, particularly in the context of food safety and quality.
Heat Generation
The intense friction and impact during milling generate heat. For heat-sensitive ingredients like certain vitamins, spices, or flavor compounds, this can lead to degradation. Temperature control is often a necessary consideration.
Potential for Contamination
The grinding media (the "balls") wear down over time. This introduces a risk of microscopic contamination from the media material into the food product. Using food-grade ceramic media is essential to mitigate this risk.
Process Time and Energy Use
Ball milling can be a relatively slow and energy-intensive process compared to other grinding methods. It is best suited for applications where the final particle size and consistency justify the time and cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if a ball mill is the appropriate tool, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is creating an ultra-fine, smooth texture: A ball mill is an excellent choice for products where mouthfeel is paramount, such as premium chocolates, nut butters, or certain pastes.
- If your primary focus is improving the solubility of a powder: For nutritional supplements or instant beverage mixes, ball milling can significantly enhance how well the product dissolves.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Laboratory-scale planetary ball mills offer precise, repeatable results for testing new formulations and ingredient characteristics.
Ultimately, choosing a ball mill is a decision to prioritize final product quality and consistency over processing speed.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Common Products |
|---|---|---|
| Grinding for Texture | Creates smooth, non-gritty mouthfeel | Chocolate, nut butters, pastes |
| Improving Solubility | Enhances dissolution in liquids | Instant drink mixes, nutritional supplements |
| Stabilizing Mixtures | Prevents ingredient separation | Dressings, protein shakes, sauces |
Ready to achieve superior texture and consistency in your food products?
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment, including ball mills for food processing. Our solutions help you perfect particle size reduction from R&D to production, ensuring your products meet the highest standards of quality and performance.
Contact our experts today to find the ideal ball mill for your specific food application needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Double Tank Type
- High Energy Vibratory Laboratory Ball Mill Grinding Mill Single Tank Type
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the ball mill based on the principle of? Impact and Attrition for Efficient Grinding
- What is the benefit of using tungsten carbide (WC) milling jars and balls? Achieve High-Energy Milling Efficiency
- Why are zirconia (ZrO2) milling jars recommended for sulfide electrolytes? Ensure Purity in Li6PS5Cl Synthesis
- Why are excellent sealing and corrosion resistance required for WC-10Co ball milling? Ensure High-Purity Mixing Results
- Why are tungsten carbide grinding jars and balls preferred for high-purity lithium ceramic powders? Ensure Peak Purity.



















