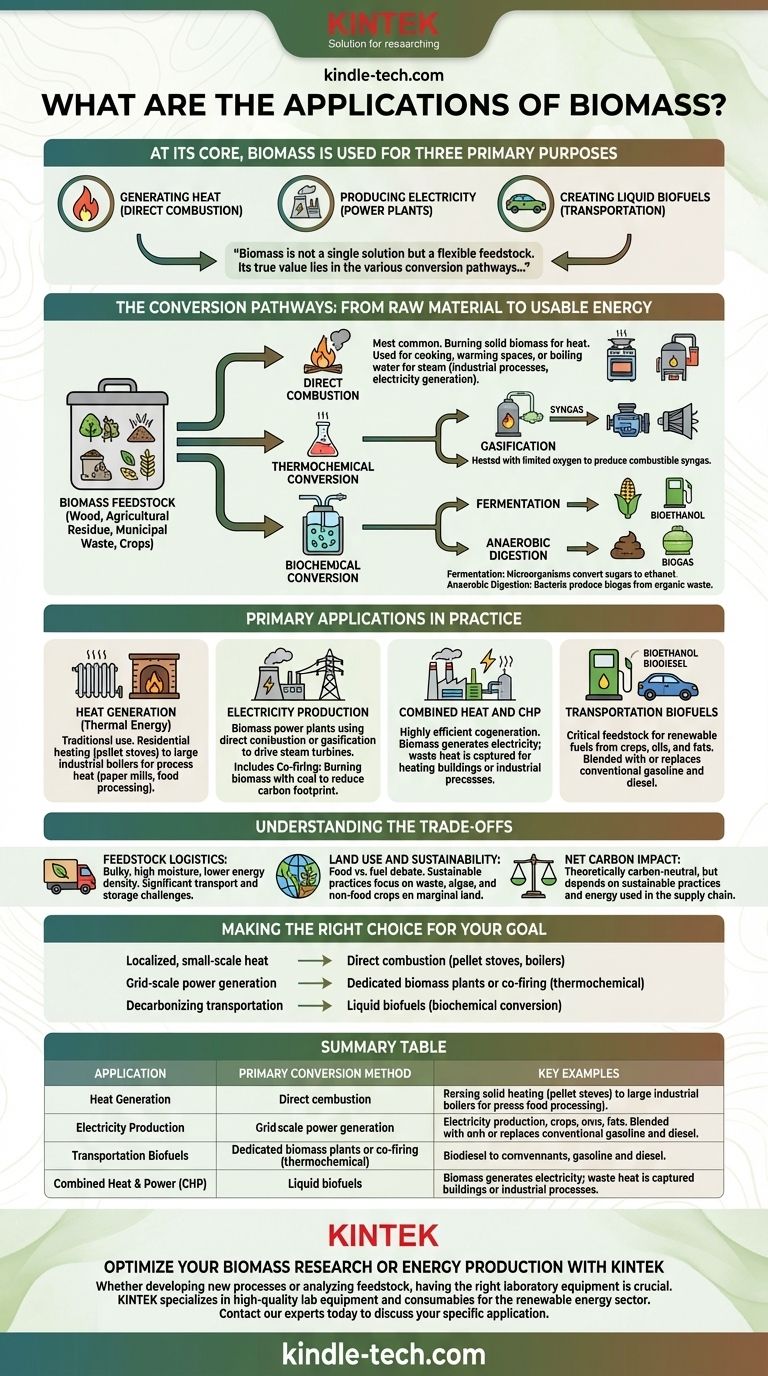
At its core, biomass is used for three primary purposes. This organic matter—derived from plants and animals—serves as a versatile renewable energy source for generating heat through direct combustion, producing electricity in power plants, and creating liquid biofuels for transportation. Its applications range from simple residential cooking stoves to complex industrial-scale energy production.
Biomass is not a single solution but a flexible feedstock. Its true value lies in the various conversion pathways that transform raw organic material into the specific energy form required—whether it's direct heat, electricity, or liquid fuel.

The Conversion Pathways: From Raw Material to Usable Energy
Before biomass can be used, it must be converted into a more practical form of energy. The specific application depends entirely on the conversion method chosen.
Direct Combustion
This is the most straightforward and common method. It involves simply burning solid biomass, such as wood, agricultural residue, or municipal solid waste, to produce heat.
This heat can be used directly for cooking and warming spaces or to boil water, creating steam. That steam can then be used for industrial processes or to spin a turbine to generate electricity.
Thermochemical Conversion
This category involves using heat and chemical processes to break down biomass into more valuable energy products.
Gasification is a key process where biomass is heated with a limited amount of oxygen. Instead of burning completely, it produces a combustible gas mixture known as syngas, which can fuel engines and turbines for electricity generation.
Biochemical Conversion
This pathway uses biological processes, such as fermentation and anaerobic digestion, to break down the organic matter.
The most common application is fermentation, which uses microorganisms to convert plant sugars into ethanol, a biofuel often blended with gasoline. Anaerobic digestion uses bacteria to produce biogas (renewable natural gas) from wet organic waste like manure or sewage.
Primary Applications in Practice
The conversion pathways enable a wide range of real-world applications, from small-scale residential use to large-scale industrial facilities.
Heat Generation (Thermal Energy)
This is the most traditional use of biomass. It includes everything from wood-burning fireplaces and modern pellet stoves for residential heating to large boilers that provide process heat for industries like paper mills and food processing plants.
Electricity Production
Biomass power plants operate much like conventional fossil fuel plants. The biomass is burned (direct combustion) or gasified to produce steam or syngas, which then drives a turbine connected to a generator to create electricity.
A common practice is co-firing, where biomass is burned alongside coal in existing power plants. This reduces the overall carbon footprint without requiring entirely new infrastructure.
Combined Heat and Power (CHP)
Also known as cogeneration, CHP is a highly efficient application. In a CHP facility, the biomass is used to generate electricity, and the waste heat from that process—which would normally be lost—is captured and used for heating buildings or industrial processes.
Transportation Biofuels
Biomass is a critical feedstock for producing renewable transportation fuels. This includes bioethanol from crops like corn and sugarcane and biodiesel produced from vegetable oils and animal fats. These biofuels can be blended with or fully replace conventional gasoline and diesel.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While versatile, biomass is not without its challenges. Objectivity requires acknowledging its limitations.
Feedstock Logistics
Biomass is often bulky, has a high moisture content, and a lower energy density compared to fossil fuels. This makes transportation and storage from its source to a processing facility a significant logistical and economic challenge.
Land Use and Sustainability
The debate over "food versus fuel" is a major concern, especially for first-generation biofuels made from food crops like corn. Sustainable biomass practices focus on using waste products, algae, or non-food energy crops grown on marginal land to avoid competing with food production.
Net Carbon Impact
Biomass is considered carbon-neutral because the carbon dioxide released when it is burned is theoretically offset by the CO2 absorbed by the plants during their growth. However, this depends heavily on sustainable harvesting practices and the energy used to grow, collect, and transport the feedstock.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best application of biomass depends entirely on the scale and objective of your energy needs.
- If your primary focus is localized, small-scale heat: Direct combustion in high-efficiency pellet stoves or boilers is the most accessible and cost-effective approach.
- If your primary focus is grid-scale power generation: Dedicated biomass power plants or co-firing at existing facilities using thermochemical conversion are the most viable paths.
- If your primary focus is decarbonizing transportation: Investing in the production of liquid biofuels through biochemical conversion remains the dominant strategy.
Ultimately, biomass serves as a flexible and essential component within a diversified portfolio of renewable energy solutions.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Conversion Method | Key Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Generation | Direct Combustion | Residential heating, industrial boilers |
| Electricity Production | Direct Combustion, Gasification | Biomass power plants, co-firing with coal |
| Transportation Biofuels | Biochemical Conversion (Fermentation) | Bioethanol, Biodiesel |
| Combined Heat & Power (CHP) | Thermochemical Conversion | Cogeneration facilities |
Optimize Your Biomass Research or Energy Production with KINTEK
Whether you are developing new biofuel conversion processes or analyzing biomass feedstock, having the right laboratory equipment is crucial for accuracy and efficiency. KINTEK specializes in supplying high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to the needs of researchers and engineers in the renewable energy sector.
We can provide the reliable tools you need to advance your biomass projects. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific application and help you achieve your energy goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are quartz tubes preferred for chromium powder combustion? Superior Heat Resistance & Optical Clarity
- What is the role of a tube furnace in the thermal treatment of argyrodite electrolytes? Master Ionic Conductivity
- What is the function of quartz tubes and vacuum sealing systems? Secure Your High-Purity Solid Solution Synthesis
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in hBN synthesis? Optimize Your Chemical Vapor Deposition Results
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.



















