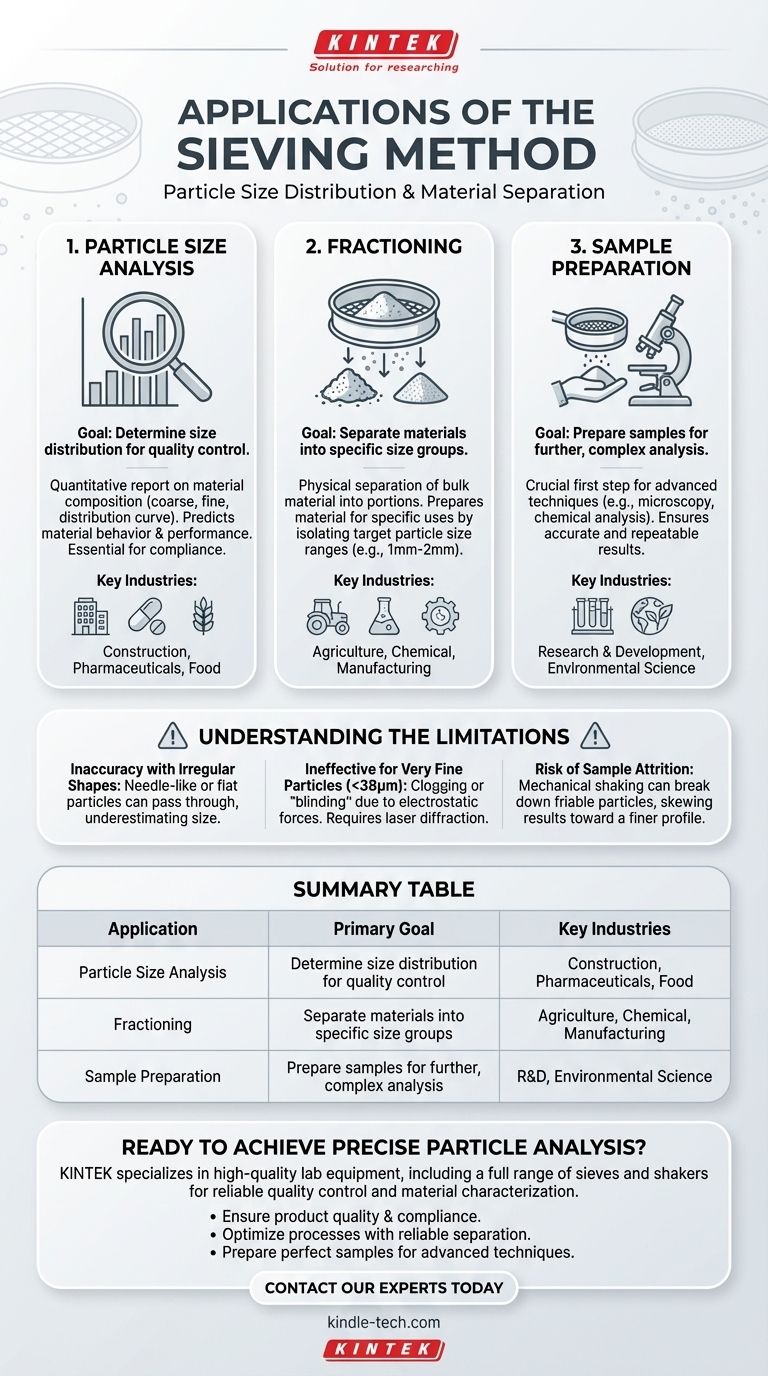
In short, the sieving method has three primary applications. It is used to analyze the distribution of particle sizes within a sample, to separate materials into specific size groups (a process called fractioning), and to prepare samples for further, more complex types of analysis. These applications are fundamental across numerous scientific and industrial fields.
The core purpose of sieving is not just to sort materials, but to gain critical data for quality control and material characterization. Understanding a material's particle size distribution is essential for predicting its physical behavior, performance, and compliance with industry standards.

The Role of Particle Size Analysis
Sieving is one of the oldest and most intuitive methods for separating materials. The process involves passing a granular sample through a series of screens, or sieves, with progressively smaller mesh openings to determine the proportion of particles within specific size ranges.
The Goal: Particle Size Distribution
The most common application is to determine a sample's particle size distribution. This isn't simply about sorting; it's about generating a quantitative report on the composition of the material.
This analysis answers critical questions: What percentage of the sample is coarse? What percentage is fine? Is the distribution curve narrow or wide? This data is vital for predicting how a material will behave.
The Process: Fractioning a Sample
Fractioning is the physical act of separating a bulk material into two or more portions based on particle size.
While analysis is about gathering data, fractioning is about preparing a material for a specific use. For example, a process might require only the particles that are between 1mm and 2mm, and sieving is the direct way to isolate that specific fraction.
Key Applications in Practice
The principles of sieving are applied daily in fields where the physical properties of powders, grains, and aggregates are critical to performance and safety.
Quality Control in Construction
The strength and durability of concrete depend directly on the size and distribution of the aggregates (sand, gravel) used. Civil engineers use sieve analysis to ensure these materials meet strict engineering standards.
Pharmaceutical and Food Production
In pharmaceuticals, the particle size of a powder can affect how quickly a drug dissolves in the body. In the food industry, the particle size of flour, sugar, or spices determines the texture and consistency of the final product.
Agriculture and Environmental Science
Sieving is used to sort seeds by size to ensure uniform germination and crop growth. Geologists and environmental scientists also sieve soil and sediment samples to understand their composition, which impacts everything from agricultural fertility to water drainage patterns.
Preparing Samples for Further Tests
Many advanced analytical instruments require samples to be within a specific particle size range to function correctly. Sieving is often a crucial first step to prepare a material for techniques like microscopy or chemical analysis, ensuring the subsequent results are accurate and repeatable.
Understanding the Limitations
While sieving is a robust and cost-effective technique, it's essential to recognize its limitations to avoid misinterpreting results.
Inaccuracy with Irregular Shapes
Sieves are calibrated for roughly spherical particles. Long, needle-like, or flat, flaky particles can pass through mesh openings end-on or diagonally, leading to an underestimation of their true size.
Ineffective for Very Fine Particles
For extremely fine powders (typically below 38 microns), physical sieving becomes impractical. Electrostatic forces can cause particles to clump together and clog, or "blind," the sieve mesh, making separation impossible. Other methods like laser diffraction are required for these materials.
Risk of Sample Attrition
The mechanical shaking involved in sieving can sometimes break down friable or brittle particles. This process, known as attrition, can alter the particle size distribution during the test itself, skewing the results toward a finer profile.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your reason for using a sieving method will determine how you approach the process and interpret the results.
- If your primary focus is quality control: Sieving is a direct, reliable pass/fail test to ensure a material meets a specific size requirement.
- If your primary focus is detailed material characterization: Using a stack of sieves with different mesh sizes provides a cost-effective way to generate a full particle size distribution curve for research or product development.
- If your primary focus is sample preparation: Sieving is an essential first step to isolate the particle size fraction needed to ensure the validity of other, more sensitive analytical tests.
Ultimately, sieving provides a clear and physical method to control and understand the fundamental properties of any particulate material.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Goal | Key Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size Analysis | Determine size distribution for quality control | Construction, Pharmaceuticals, Food |
| Fractioning | Separate materials into specific size groups | Agriculture, Chemical, Manufacturing |
| Sample Preparation | Prepare samples for further, complex analysis | Research & Development, Environmental Science |
Ready to achieve precise particle analysis and separation in your lab?
The right sieving equipment is fundamental to reliable quality control and material characterization. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality lab equipment, including a full range of sieves and shakers, designed to deliver accurate and repeatable results for your specific needs.
We help you:
- Ensure product quality and compliance with industry standards.
- Optimize your processes with reliable separation and analysis.
- Prepare perfect samples for advanced analytical techniques.
Let's discuss your application. Contact our experts today to find the perfect sieving solution for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine for Dry and Wet Three-Dimensional Sieving
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Wet Three-Dimensional Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
People Also Ask
- What is sieving filtering? Master the Key Differences for Accurate Material Separation
- What are the sieve sizes for particle size distribution? A Guide to ASTM and ISO Standards
- What is the sieve method for particle size determination? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective Analysis
- What are the limitations of sieve size analysis? Avoid Costly Errors in Particle Characterization
- How do you calculate sieve analysis in a lab report? A Step-by-Step Guide to Accurate Particle Size Distribution
- What are the precautions for sieve analysis? Ensure Accurate Particle Size Distribution Results
- What is the purpose of sieving in chemistry? Master Particle Size Control for Better Reactions & Quality
- What role do crushing and sieving systems play in plastic photoreforming? Master Pre-treatment for Maximum Yield



















