At its core, thermal evaporation is a foundational thin-film deposition technique used across a vast range of industries. It is most commonly applied to create the thin metallic layers essential for electronics like OLED displays and solar cells, simple electrical contacts, and functional or decorative coatings on products from automotive reflectors to sporting goods.
The decision to use thermal evaporation hinges on a critical trade-off. It is an exceptionally simple, fast, and cost-effective method for depositing materials with low melting points, but this comes at the cost of material limitations and potential contamination from the heating source.
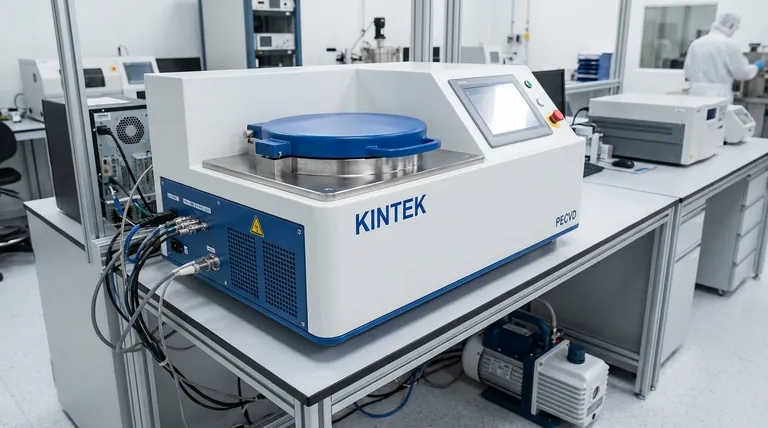

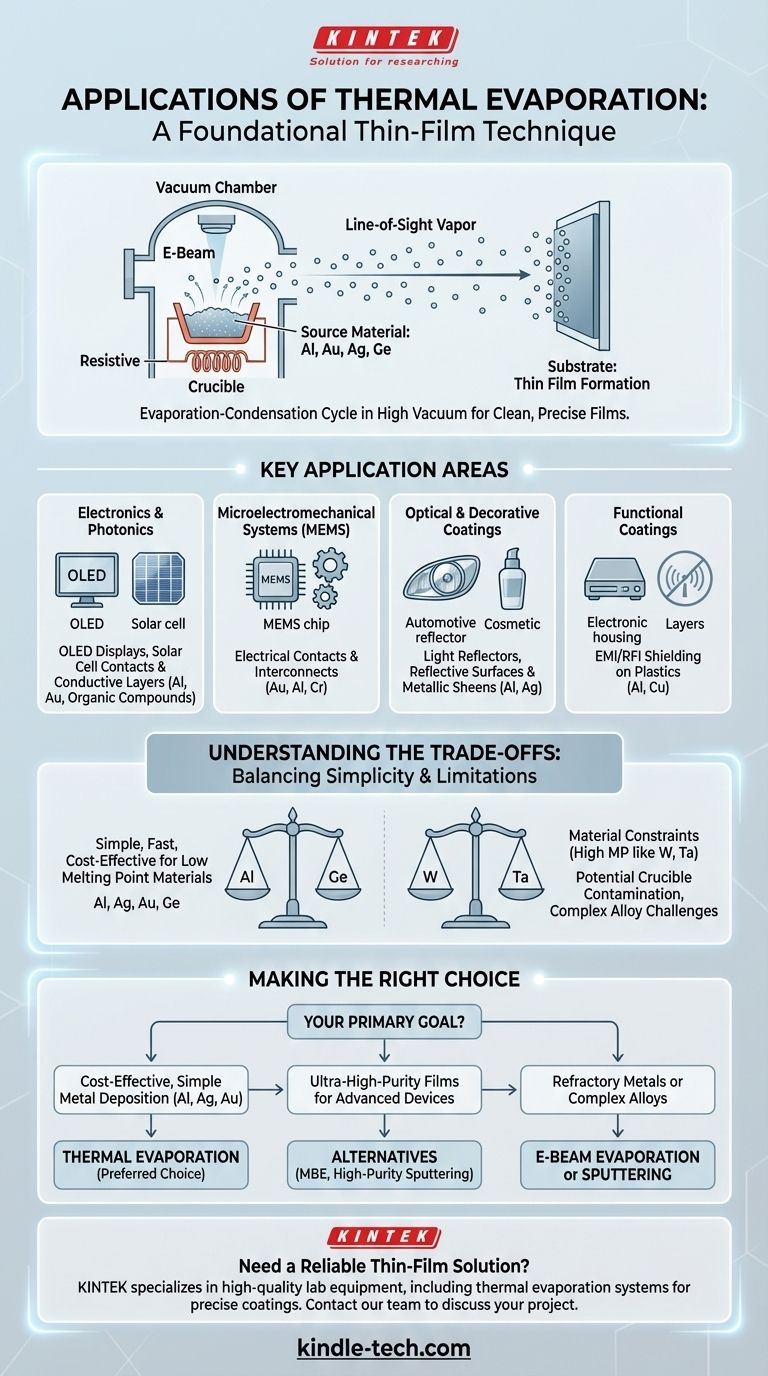
How Thermal Evaporation Works
Thermal evaporation is a type of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) that operates on a simple principle of changing a material's physical state.
The Evaporation-Condensation Cycle
The source material, such as a metal like aluminum or gold, is placed inside a container called a crucible within a high-vacuum chamber. This crucible is heated, causing the source material to sublimate or evaporate into a vapor.
This vapor then travels in a straight line through the vacuum and condenses onto a cooler target object, known as the substrate, forming a thin, solid film.
The Critical Role of Vacuum
The process is performed in a high vacuum to ensure the vaporized atoms can travel from the source to the substrate with minimal collisions with air or other gas molecules. This line-of-sight travel is what allows for the creation of a clean, well-defined film.
Heating the Source Material
Heat is typically generated in one of two ways. In resistive evaporation, an electrical current passes through the crucible or a nearby refractory metal boat, heating it like a filament in a light bulb. In electron-beam evaporation, a focused beam of high-energy electrons directly heats the source material.
Key Application Areas
The unique characteristics of thermal evaporation—its simplicity, speed, and compatibility with low-melting-point materials—make it ideal for several specific domains.
Electronics and Photonics
Thermal evaporation is a workhorse for producing consumer electronics. It is used to deposit the thin layers of metals and organic compounds that form OLED displays, and it's also used to create the metallic contacts and conductive layers in solar cells.
Microelectromechanical Systems (MEMS)
In MEMS and other micro-fabrication processes, thermal evaporation is used to deposit single-metal films for electrical contacts and interconnects. The ability to deposit metals like gold (Au), aluminum (Al), or chromium (Cr) quickly and cheaply is a major advantage.
Optical and Decorative Coatings
The process is widely used to create highly reflective surfaces. This includes manufacturing light reflectors for automotive headlamps, medical lighting, and aerospace components. It is also used for purely decorative applications, such as adding metallic sheens to cosmetic packaging or sporting goods.
Functional Coatings
A thin, conductive metal film can effectively block electromagnetic and radio-frequency interference. Thermal evaporation is a common method for applying these EMI/RFI shielding layers onto plastic housings for sensitive electronic devices.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, thermal evaporation is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly.
The Material Constraint: Low Melting Points
The primary limitation is temperature. The process is best suited for materials with relatively low melting points, such as aluminum, silver, gold, and germanium. It is not suitable for depositing materials that require very high temperatures to vaporize, such as refractory metals like tungsten or tantalum.
The Purity Problem: Crucible Contamination
Because the crucible is heated to extreme temperatures along with the source material, there is a risk that atoms from the crucible itself can become incorporated into the vapor stream. This introduces impurities into the final thin film, which can be unacceptable for high-performance applications.
The Challenge of Complex Alloys
While it is possible to co-deposit multiple materials by using several crucibles at different temperatures, precisely controlling the final composition of a complex alloy can be difficult. Other PVD methods, like sputtering, often offer superior control for creating films with specific multi-elemental stoichiometries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition method requires aligning the process capabilities with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective deposition of simple metals: Thermal evaporation is an excellent, often preferred, choice for its speed and simplicity with materials like Al, Ag, or Au.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high-purity films for advanced devices: Consider alternatives like molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) or high-purity sputtering to avoid the risk of crucible contamination.
- If your primary focus is depositing refractory metals or complex alloys: You must use a different method, such as e-beam evaporation or sputtering, which can handle higher-temperature materials and offer better compositional control.
Ultimately, understanding thermal evaporation's strengths and weaknesses empowers you to select the most effective tool for your specific engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Common Uses | Key Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics & Photonics | OLED displays, solar cell contacts | Aluminum (Al), Gold (Au), Organic compounds |
| MEMS | Electrical contacts, interconnects | Gold (Au), Aluminum (Al), Chromium (Cr) |
| Optical & Decorative Coatings | Automotive reflectors, packaging | Aluminum (Al), Silver (Ag) |
| Functional Coatings | EMI/RFI shielding on plastics | Aluminum (Al), Copper (Cu) |
Need a reliable thin-film deposition solution for your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including thermal evaporation systems, to help you achieve precise and cost-effective coatings for electronics, MEMS, and optical applications. Our experts can help you select the right tool for your specific materials and purity requirements.
Contact our team today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
People Also Ask
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the components of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition Systems
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition


















