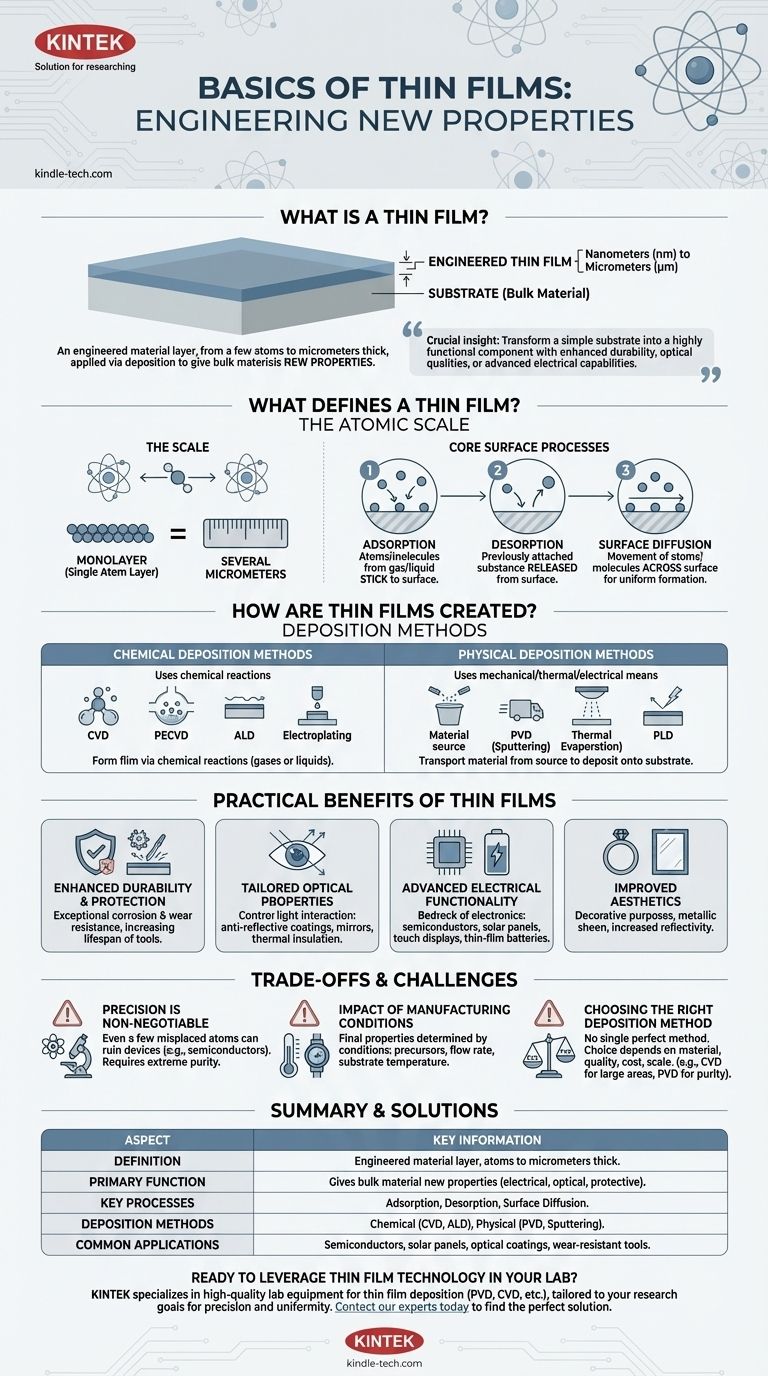
At its core, a thin film is an engineered layer of material ranging from just a few atoms to several micrometers in thickness. These films are applied to a surface, or substrate, through a process called deposition. This controlled synthesis is not merely a coating but a fundamental step in creating countless modern products, from semiconductor chips to advanced optics.
The crucial insight is that thin films are designed to give a bulk material entirely new properties. By precisely controlling material layers at an atomic or molecular scale, we can transform a simple substrate into a highly functional component with enhanced durability, specific optical qualities, or advanced electrical capabilities.

What Defines a Thin Film?
A thin film's behavior is dictated by its incredibly small scale and the physics that dominate at the atomic level. Understanding these principles is key to understanding their function.
The Scale: Nanometers to Micrometers
A thin film's thickness can be as small as a single layer of atoms (monolayer) or extend up to several micrometers. This precise control over thickness is what enables their specialized properties.
The Core Processes at the Surface
Three phenomena govern how a thin film forms and interacts with its environment:
- Adsorption: The process where atoms or molecules from a gas or liquid stick to the substrate's surface.
- Desorption: The opposite of adsorption, where a previously attached substance is released from the surface.
- Surface Diffusion: The movement of atoms and molecules across the surface, which is critical for forming a uniform, high-quality film.
How Are Thin Films Created? The Deposition Process
Creating a thin film involves depositing material onto a substrate using highly controlled methods. These techniques are broadly divided into two families: chemical and physical.
Chemical Deposition Methods
These methods use chemical reactions to form the film on the substrate. The precursors are often gases or liquids.
Common examples include Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD), Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD), and electroplating.
Physical Deposition Methods
These techniques use mechanical, thermal, or electrical means to transport material from a source and deposit it onto the substrate's surface.
This category includes Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) methods like sputtering and thermal evaporation, as well as Pulsed Laser Deposition (PLD).
The Practical Benefits of Thin Films
Applying a thin film fundamentally alters the surface of a material, providing a wide range of functional and aesthetic advantages.
Enhanced Durability and Protection
One of the most common uses is to protect the underlying substrate. Thin films provide exceptional corrosion and wear resistance, significantly increasing the lifespan and durability of tools and components.
Tailored Optical Properties
Multiple layers of thin films can be engineered to control how light interacts with a surface. This is the principle behind anti-reflective coatings on eyeglasses, mirrors on reflector lamps, and thermal insulation on architectural glass.
Advanced Electrical Functionality
Thin films are the bedrock of modern electronics. They are used to create semiconductors, thin-film photovoltaic cells (solar panels), touch-panel displays, and even next-generation thin-film batteries.
Improved Aesthetics
Beyond function, thin films are used for decorative purposes. They can enhance a substrate's appearance with a metallic sheen, as seen on jewelry or bathroom fittings, or make it more reflective.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While the benefits are significant, the process of creating high-quality thin films is demanding and fraught with challenges. The choice of method involves critical trade-offs.
Precision is Non-Negotiable
The quality of the thin film is paramount. In applications like semiconductors, even a few misplaced atoms can render the entire device useless. This requires manufacturing environments with extreme purity and control.
The Impact of Manufacturing Conditions
The final properties of the film are determined by the specific conditions during deposition. Factors like the type of precursor chemicals, their flow rate onto the surface, and the substrate temperature must be precisely managed to achieve the desired outcome.
Choosing the Right Deposition Method
No single deposition method is perfect for all applications. Chemical methods like CVD can provide excellent uniformity over large areas, while physical methods like PVD are valued for their purity. The choice depends on the material, desired quality, cost, and scale of production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate thin film strategy depends entirely on the intended application and performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics: You need atomic-level precision, making methods like Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) or Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE) critical.
- If your primary focus is protecting a large surface from corrosion: Cost-effective and scalable methods like electroplating or certain types of sputtering are often the best choice.
- If your primary focus is creating specialized optical coatings: Deposition techniques that offer precise control over layer thickness, such as various forms of CVD or PVD, are essential.
Understanding these fundamentals allows you to see thin films not just as coatings, but as a foundational technology for manipulating the properties of matter.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Information |
|---|---|
| Definition | Engineered material layer, from atoms to micrometers thick, applied to a substrate. |
| Primary Function | Gives a bulk material new properties (electrical, optical, protective). |
| Key Processes | Adsorption, Desorption, Surface Diffusion. |
| Deposition Methods | Chemical (CVD, ALD) and Physical (PVD, Sputtering). |
| Common Applications | Semiconductors, solar panels, anti-reflective coatings, wear-resistant tools. |
Ready to leverage thin film technology in your lab?
Whether you are developing next-generation electronics, creating specialized optical coatings, or need to enhance the durability of your components, choosing the right deposition equipment is critical. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment for thin film deposition, including systems for PVD, CVD, and more.
We provide solutions tailored to your specific research and production goals, helping you achieve the precision, uniformity, and performance your projects demand.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and find the perfect thin film solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition



















