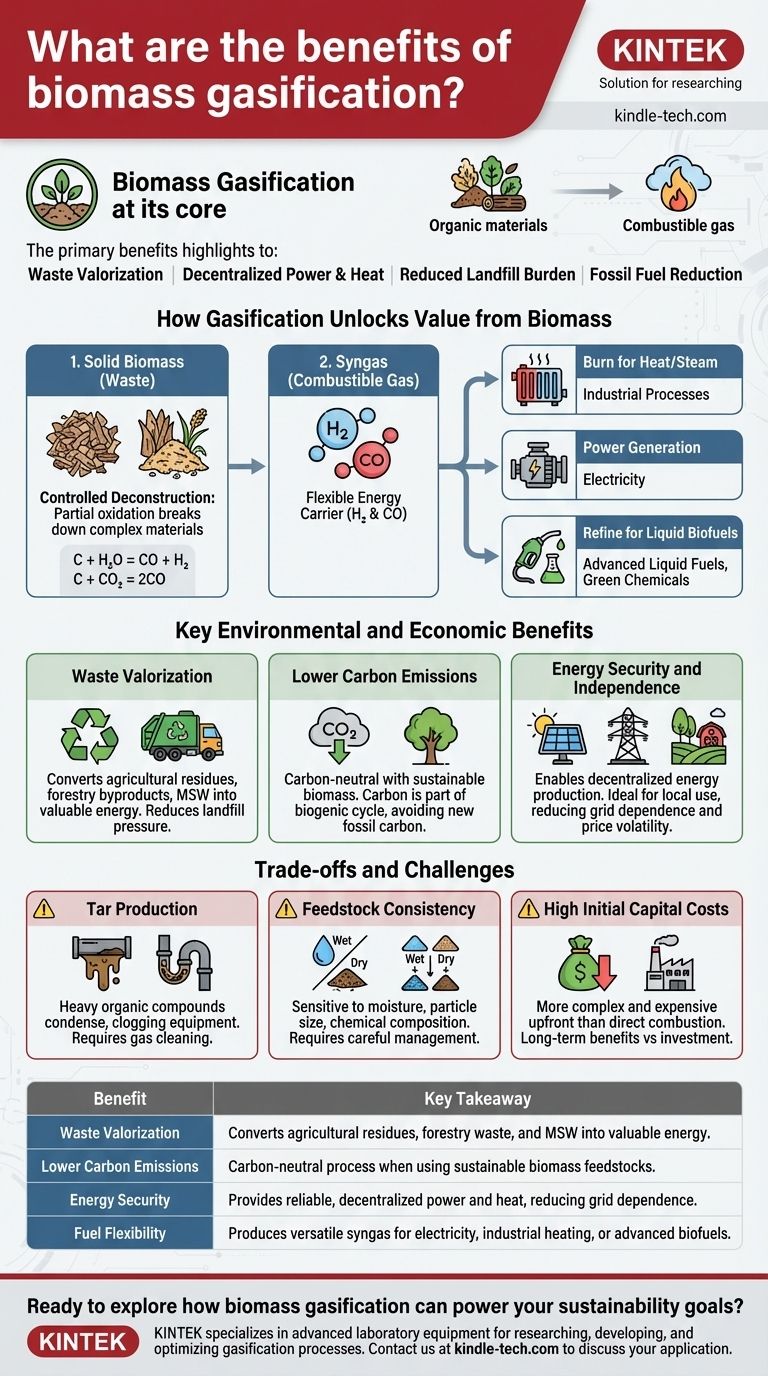
At its core, biomass gasification is a thermochemical process that converts organic materials into a valuable, combustible gas. Its primary benefits are the ability to create renewable energy from low-value waste streams and to provide a decentralized, reliable source of power and heat, reducing both landfill burden and reliance on fossil fuels.
While often viewed simply as a waste-to-energy method, the true advantage of biomass gasification is its flexibility. It transforms diverse organic feedstocks into a clean, versatile fuel gas—known as syngas—that can be used for electricity generation, industrial heating, or as a building block for advanced liquid fuels.

How Gasification Unlocks Value from Biomass
To understand the benefits, you must first understand the process. Gasification is not simple burning; it is a controlled, partial oxidation of solid fuel at high temperatures.
The Core Process: Controlled Deconstruction
Instead of fully combusting biomass with excess oxygen, gasification intentionally starves the reaction of oxygen. This breaks down the complex organic material into its more basic chemical components.
Think of it less like a bonfire and more like a chemical refinery. You are not just releasing heat; you are deconstructing the solid biomass to create a new, more useful gaseous fuel.
From Solid Waste to Valuable Syngas
This controlled process triggers a series of chemical reactions, including C + H₂O = CO + H₂ (water-gas shift) and C + CO₂ = 2CO (Boudouard reaction).
These reactions convert the solid carbon (C) in the biomass into a mixture of combustible gases. The resulting product is syngas, which is primarily composed of hydrogen (H₂) and carbon monoxide (CO), with smaller amounts of methane (CH₄).
The Flexibility of Syngas
Once produced, syngas is a remarkably versatile energy carrier. It can be:
- Burned directly in a boiler to produce steam and heat for industrial processes.
- Used as fuel in an internal combustion engine or gas turbine to generate electricity.
- Further refined through processes like Fischer-Tropsch synthesis to create liquid biofuels, such as renewable diesel or sustainable aviation fuel.
The Key Environmental and Economic Benefits
This unique ability to convert solid waste into a flexible gas fuel is the source of gasification's main advantages.
Waste Valorization
Gasification transforms materials often considered waste—such as agricultural residues (corn stover, rice husks), forestry byproducts, and the organic fraction of municipal solid waste—into a valuable energy resource. This reduces landfill pressure and creates a new revenue stream from waste.
Lower Carbon Emissions
When using sustainable biomass, the process is considered low-carbon or carbon-neutral. The carbon dioxide released during the eventual combustion of the syngas is part of the natural biogenic carbon cycle, meaning it was recently captured from the atmosphere by the growing biomass. This avoids adding new, fossil-derived carbon to the atmosphere.
Energy Security and Independence
Because biomass is often locally available, gasification enables decentralized energy production. This is ideal for farms, rural communities, or industrial sites seeking to reduce their dependence on a centralized electrical grid and volatile fossil fuel prices. It provides a source of reliable, baseload power that intermittent renewables like solar and wind cannot always offer.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
No technology is a silver bullet. An objective assessment requires acknowledging the technical hurdles associated with gasification.
The Problem of Tar
One of the most significant challenges in biomass gasification is the production of tar. These are complex, heavy organic compounds that can condense at lower temperatures, clogging downstream equipment, fouling engines, and increasing maintenance costs. Effective and often expensive gas cleaning systems are required to remove tar before the syngas can be used.
Feedstock Consistency is Critical
Gasification systems are sensitive to the properties of their fuel. The moisture content, particle size, and chemical composition of the biomass feedstock must be carefully managed for stable and efficient operation. A system designed for dry wood chips may not function properly with wet agricultural waste without significant pre-treatment.
High Initial Capital Costs
Compared to direct combustion (burning), a gasification plant is more complex and has a higher upfront capital cost. The reactor, feeding systems, and especially the gas cleanup equipment represent a significant investment that must be weighed against the long-term fuel cost savings and environmental benefits.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the suitability of biomass gasification depends entirely on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is sustainable waste management: Gasification is a superior alternative to landfilling or simple incineration, as it converts organic waste into a high-value, flexible energy product.
- If your primary focus is reliable, off-grid power: A well-designed gasification system can provide consistent, 24/7 electricity and heat, making it an excellent choice for industries or communities needing energy independence.
- If your primary focus is producing advanced biofuels: Gasification is a foundational technology, providing the essential syngas feedstock required for creating next-generation liquid fuels and green chemicals.
By understanding both its powerful benefits and its technical realities, you can effectively determine if biomass gasification aligns with your energy and sustainability objectives.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Waste Valorization | Converts agricultural residues, forestry waste, and MSW into valuable energy. |
| Lower Carbon Emissions | Carbon-neutral process when using sustainable biomass feedstocks. |
| Energy Security | Provides reliable, decentralized power and heat, reducing grid dependence. |
| Fuel Flexibility | Produces versatile syngas for electricity, industrial heating, or advanced biofuels. |
Ready to explore how biomass gasification can power your sustainability goals?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced laboratory equipment to help you research, develop, and optimize gasification processes. Whether you're analyzing feedstock, testing syngas composition, or scaling up your technology, our solutions provide the precision and reliability you need.
Let KINTEK be your partner in renewable energy innovation. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover the right equipment for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What is the necessity of using an autoclave for pre-treating culture media? Ensure Accurate Ag2O/TiO2 Testing
- What are the advantages of using an autoclave equipped with a stirring device for molten salt testing? Dynamic Accuracy
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- What is the primary function of a laboratory autoclave in the pre-treatment of medical plastic waste for liquid fuel?



















