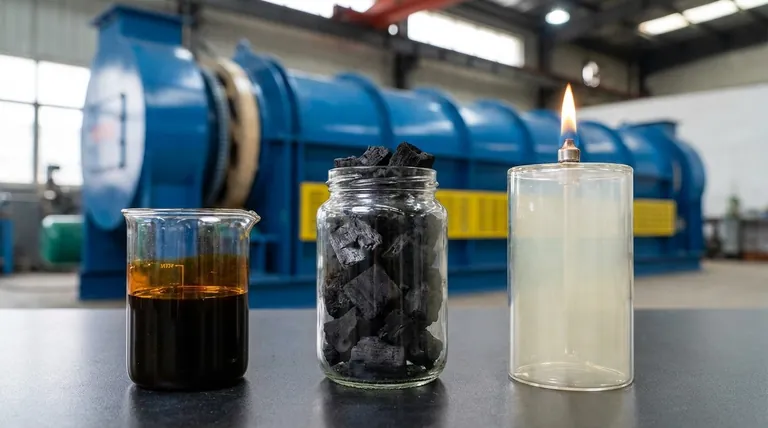
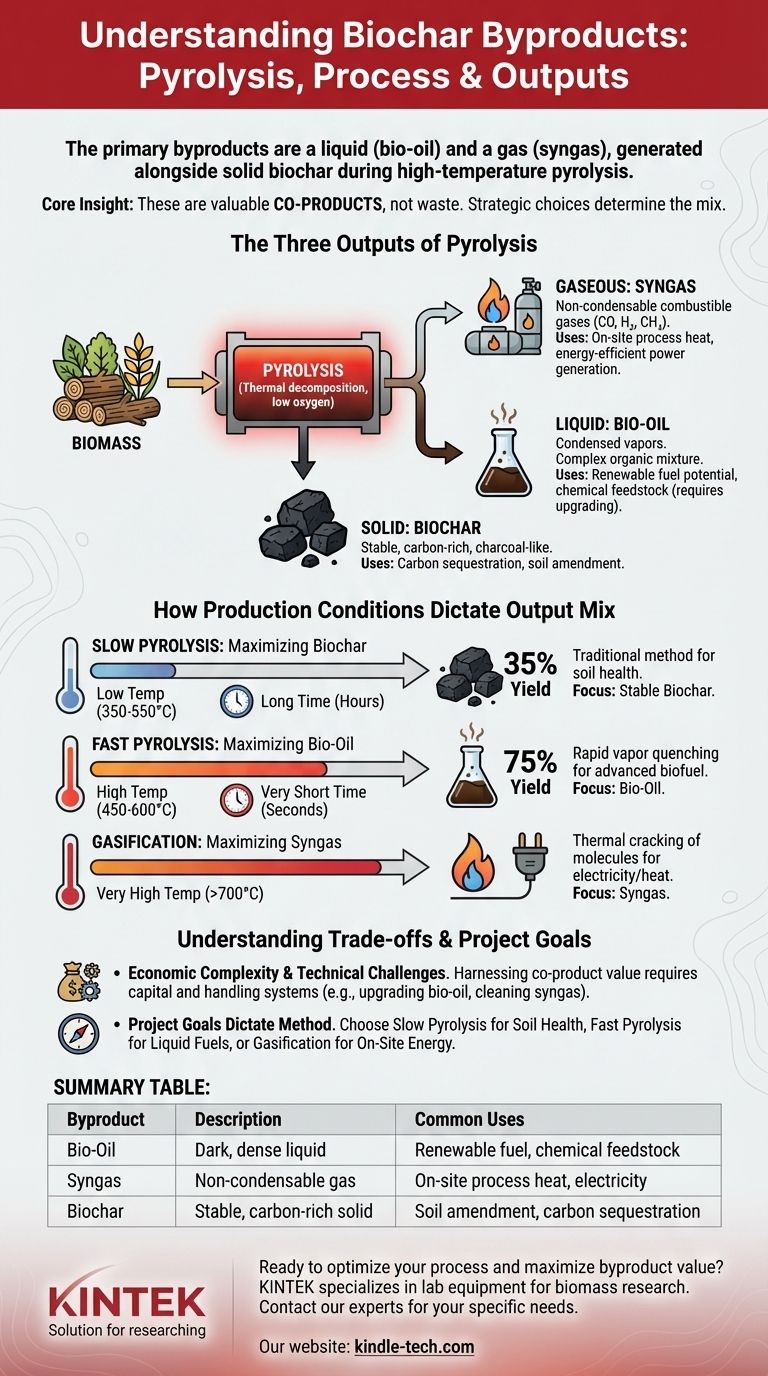
The primary byproducts of biochar production are a liquid known as bio-oil and a non-condensable gas called syngas. These are not waste products but are co-products generated alongside the solid biochar during a high-temperature process called pyrolysis. The exact amount and composition of these byproducts are directly controlled by the production conditions, namely temperature and processing time.
The core insight is that "byproducts" is a misleading term. The liquids and gases produced during pyrolysis are valuable co-products. The decision to prioritize biochar, bio-oil, or syngas is a strategic choice determined by the specific temperature and speed of the production process.
The Three Outputs of Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of biomass (like wood, manure, or crop residue) in a low-oxygen environment. This process fundamentally breaks down the material into three distinct product streams: a solid, a liquid, and a gas.
The Solid Product: Biochar
This is the stable, carbon-rich, charcoal-like material that is the primary target in many operations. Its intended use is typically for carbon sequestration and soil amendment.
The Liquid Co-Product: Bio-Oil
Often called pyrolysis oil, this is a dark, dense liquid that results from cooling and condensing the volatile vapors released from the biomass. It is a complex mixture of hundreds of organic compounds and water.
Bio-oil has significant potential as a renewable fuel or as a source for specialty chemicals, but it is acidic and unstable, often requiring further upgrading before use.
The Gaseous Co-Product: Syngas
Syngas, or synthesis gas, is the stream of non-condensable gases that remain after the bio-oil has been condensed. It is a mixture of combustible gases, primarily carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), methane (CH4), and carbon dioxide (CO2).
This gas has a low-to-medium energy value and is almost always used on-site to provide the heat required to run the pyrolysis process, making the system more energy-efficient.
How Production Conditions Dictate the Output Mix
The ratio of biochar, bio-oil, and syngas is not fixed. It is a direct function of the process parameters, particularly temperature and the time the biomass is exposed to that heat (residence time).
Slow Pyrolysis: Maximizing Biochar
By using lower temperatures (around 350-550°C) and long residence times (hours), the process favors the production of the solid biochar. This is the traditional method when the primary goal is to create a soil amendment. Yields of biochar can be around 35% by weight.
Fast Pyrolysis: Maximizing Bio-Oil
Using higher temperatures (around 450-600°C) with a very short residence time (seconds) and then rapidly quenching the vapors maximizes the bio-oil yield. This process can convert up to 75% of the biomass weight into liquid, making it ideal for advanced biofuel production.
Gasification: Maximizing Syngas
At even higher temperatures (above 700°C), the larger organic molecules are thermally "cracked" into the smaller gaseous molecules that make up syngas. While some char is still produced, the primary output becomes this combustible gas, which can be used to generate electricity or heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Viewing the outputs of pyrolysis as a flexible system is key, but it comes with practical trade-offs that dictate the economic and environmental viability of an operation.
Economic Complexity
While bio-oil and syngas are valuable, harnessing that value requires capital investment. A system designed to capture and refine bio-oil is far more complex and expensive than a simple kiln designed only to produce biochar. The market for these co-products must justify the added complexity.
Technical and Handling Challenges
Bio-oil is not a drop-in replacement for petroleum. It is corrosive, chemically unstable, and must be upgraded to be used in conventional engines or refineries. Likewise, syngas must be cleaned of tars and particulates before it can be used in more sensitive equipment like gas engines.
Applying This to Your Project
The right approach depends entirely on your end goal. There is no single "best" method; there is only the best method for your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is soil health and carbon sequestration: Choose slow pyrolysis to maximize your yield of stable, high-quality biochar.
- If your primary focus is producing renewable liquid fuels or chemical feedstocks: Choose fast pyrolysis to maximize your bio-oil yield, but plan for the necessary downstream processing and upgrading.
- If your primary focus is generating on-site heat or electricity from biomass: Choose gasification to maximize syngas production, or configure a pyrolysis system to efficiently burn its gaseous co-products.
Ultimately, understanding that you are managing a portfolio of potential products—not just making biochar—is the key to designing an effective and economically sound system.

Summary Table:
| Byproduct | Description | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Bio-Oil | Dark, dense liquid from condensed vapors | Renewable fuel, chemical feedstock |
| Syngas | Non-condensable gas (CO, H₂, CH₄) | On-site process heat, electricity generation |
| Biochar | Stable, carbon-rich solid | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process and maximize the value of your byproducts? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced biomass research. Whether you're developing a slow pyrolysis system for biochar or a fast pyrolysis setup for bio-oil, our solutions help you analyze and control process conditions with precision. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs in renewable energy and sustainable materials research.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
People Also Ask
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products



















