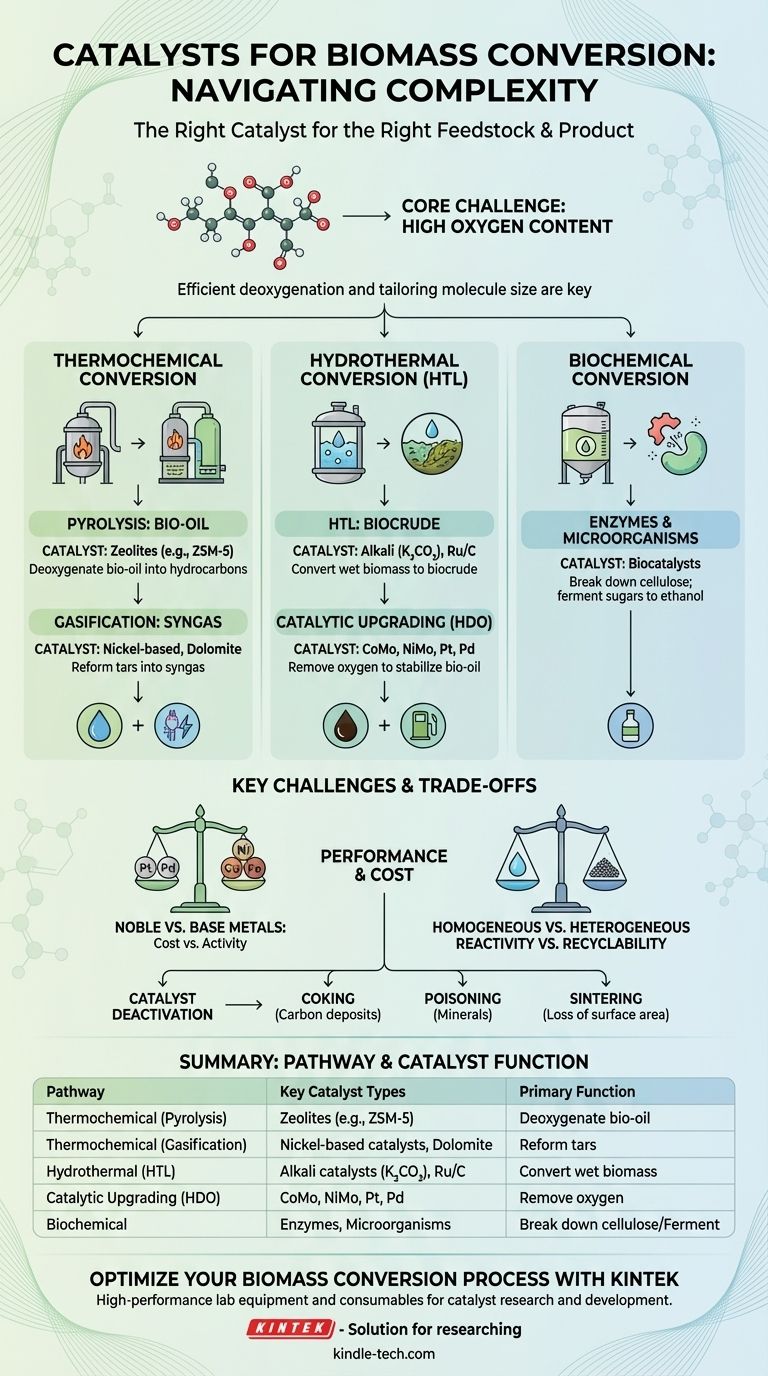
In the field of biorefining, there is no single "biomass catalyst." The correct catalyst is entirely dependent on the biomass feedstock (e.g., wood, algae, waste oils) and the desired end product (e.g., gasoline, jet fuel, plastics). Catalysts for biomass conversion are broadly categorized into three families: heterogeneous solids like zeolites and supported metals, homogeneous acids and bases, and highly specific biocatalysts like enzymes.
The central challenge in biomass conversion is its high oxygen content, which lowers its energy value and makes it unstable. Therefore, the primary job of a biomass catalyst is to efficiently remove oxygen (deoxygenation) and tailor the molecule size, a fundamentally different task than the one faced in traditional petroleum refining.

The Core Challenge: Why Biomass Needs Special Catalysts
Traditional catalysts used in oil refineries are often unsuitable for biomass. This is due to the unique chemical nature of bio-based feedstocks, which presents three main hurdles.
High Oxygen Content
Biomass is rich in oxygenates—molecules containing oxygen atoms. This oxygen adds weight without contributing to energy content, makes the derived liquids (like pyrolysis oil) acidic and corrosive, and causes them to be thermally unstable.
Catalysis is essential for deoxygenation, the process of removing this oxygen, typically as H₂O, CO, or CO₂.
Complexity of Feedstocks
Unlike crude oil, biomass is not uniform. It's often a complex composite of three main components: cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin.
Each of these components breaks down under different conditions and requires a specific catalytic strategy to be converted into useful products.
The Inevitable Presence of Water
Biomass is inherently wet, and many conversion processes use water as a solvent (e.g., hydrothermal liquefaction).
Many conventional catalysts, such as those used for fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) in refineries, are rapidly deactivated by water. Biomass catalysis requires water-tolerant materials.
Matching the Catalyst to the Conversion Pathway
The choice of catalyst is inseparable from the chosen conversion technology. Different pathways are optimized for different feedstocks and products, each relying on a specific class of catalyst.
For Thermochemical Conversion (Pyrolysis & Gasification)
Pyrolysis thermally decomposes biomass in the absence of oxygen, creating a liquid known as bio-oil. This bio-oil is unstable and must be upgraded.
Zeolites, particularly ZSM-5, are used in a process called catalytic fast pyrolysis. Their acidic, shape-selective pores are highly effective at deoxygenating the bio-oil and converting it directly into aromatic hydrocarbons, which are valuable as gasoline blendstock and chemical precursors.
Gasification converts biomass into syngas (a mixture of CO and H₂). A major byproduct is tar, which clogs equipment. Nickel-based catalysts or inexpensive minerals like dolomite and olivine are used downstream to reform these tars into more syngas.
For Hydrothermal Conversion (HTL)
Hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL) uses hot, compressed water to break down wet biomass into a more energy-dense "biocrude."
The water itself acts as a reactant and a catalyst, but others are added to improve yield and quality. Homogeneous alkali catalysts (like potassium carbonate, K₂CO₃) are common. For upgrading the biocrude, heterogeneous supported metal catalysts like Ruthenium on a carbon support (Ru/C) are highly effective.
For Catalytic Upgrading & Deoxygenation
This is often a second, crucial step after initial conversion via pyrolysis or HTL. The goal is to stabilize the bio-oil or biocrude and make it resemble conventional crude oil.
The primary method is hydrodeoxygenation (HDO), which uses hydrogen to remove oxygen as water. Catalysts for this are similar to those in conventional hydrotreating, such as Cobalt-Molybdenum (CoMo) or Nickel-Molybdenum (NiMo) on an alumina support.
However, these traditional catalysts can be poisoned by biomass contaminants and require sulfur to remain active. This has driven research into noble metals like Platinum (Pt) and Palladium (Pd) on carbon supports, which are more robust but also more expensive.
For Biochemical Conversion
This pathway operates at or near ambient temperatures and pressures, using biological agents as catalysts.
Enzymes (biocatalysts) like cellulases are used to break down cellulose into simple sugars with extremely high specificity.
Microorganisms, such as yeast or bacteria, are then used to ferment these sugars into products like ethanol. This is the established industrial process for producing corn ethanol.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Challenges
Selecting a catalyst involves balancing performance, cost, and lifespan. The harsh conditions of biomass processing present significant challenges that must be considered.
Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous Catalysts
Homogeneous catalysts (acids, bases) dissolve in the reaction medium. They are often highly active but suffer from major practical drawbacks, including difficulty in separating them from the product, reactor corrosion, and challenges with recycling.
Heterogeneous catalysts (solids) are the preferred choice for most industrial-scale processes because they are easily separated, regenerated, and reused, simplifying reactor design.
Catalyst Deactivation: The Achilles' Heel
Biomass catalysts have a finite lifespan and are prone to deactivation. This is a primary driver of operating costs.
Common deactivation mechanisms include coking (carbon deposits blocking active sites), poisoning by minerals present in biomass ash (like potassium and sodium), and sintering (loss of surface area at high temperatures).
Cost vs. Performance: Noble Metals vs. Base Metals
Noble metals (Pt, Pd, Ru) exhibit excellent activity and stability, especially for HDO, and are often more resistant to deactivation. However, their extremely high cost can make a process economically unviable.
Base metals (Ni, Cu, Fe) are orders of magnitude cheaper and can be effective for certain reactions, like tar reforming or HDO. Their main drawback is lower stability, as they are more susceptible to poisoning and sintering.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of catalyst is a strategic decision that defines your entire process. To make an informed choice, align the catalyst system with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is producing drop-in liquid fuels (gasoline, diesel): You will need a multi-step process involving pyrolysis or HTL followed by hydrodeoxygenation using supported metal catalysts like NiMo, CoMo, or noble metals.
- If your primary focus is creating high-value aromatic chemicals: Catalytic fast pyrolysis using zeolites like ZSM-5 is the most direct and well-researched route.
- If your primary focus is converting sugars or starches with high specificity: Biocatalysts, such as enzymes for hydrolysis and microorganisms for fermentation to alcohols, are the established industrial standard.
- If your primary focus is producing syngas for further synthesis: You will need gasification combined with a robust, inexpensive catalyst like nickel-based materials or dolomite to clean the gas by reforming tars.
Ultimately, selecting the right catalyst is not just a chemical choice; it is the central engineering decision that dictates the efficiency, economics, and success of your entire biorefinery concept.
Summary Table:
| Conversion Pathway | Key Catalyst Types | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Thermochemical (Pyrolysis) | Zeolites (e.g., ZSM-5) | Deoxygenate bio-oil into hydrocarbons |
| Thermochemical (Gasification) | Nickel-based catalysts, Dolomite | Reform tars into syngas |
| Hydrothermal (HTL) | Alkali catalysts (e.g., K₂CO₃), Ru/C | Convert wet biomass to biocrude |
| Catalytic Upgrading (HDO) | CoMo, NiMo, Pt, Pd | Remove oxygen to stabilize bio-oil |
| Biochemical | Enzymes, Microorganisms | Break down cellulose; ferment sugars to ethanol |
Optimize Your Biomass Conversion Process with KINTEK
Navigating the complexities of catalyst selection is critical for the efficiency and economic viability of your biorefinery. Whether you are developing drop-in biofuels, high-value chemicals, or syngas, the right catalyst system is the cornerstone of your success.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance laboratory equipment and consumables essential for your biomass catalysis research and development. From reactors for testing catalyst performance to analytical tools for monitoring deactivation, our solutions help you make informed decisions and scale your process effectively.
Ready to enhance your catalyst testing and process development? Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's lab equipment can support your specific biomass conversion goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Buchner Funnel and Triangular Funnel
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing



















