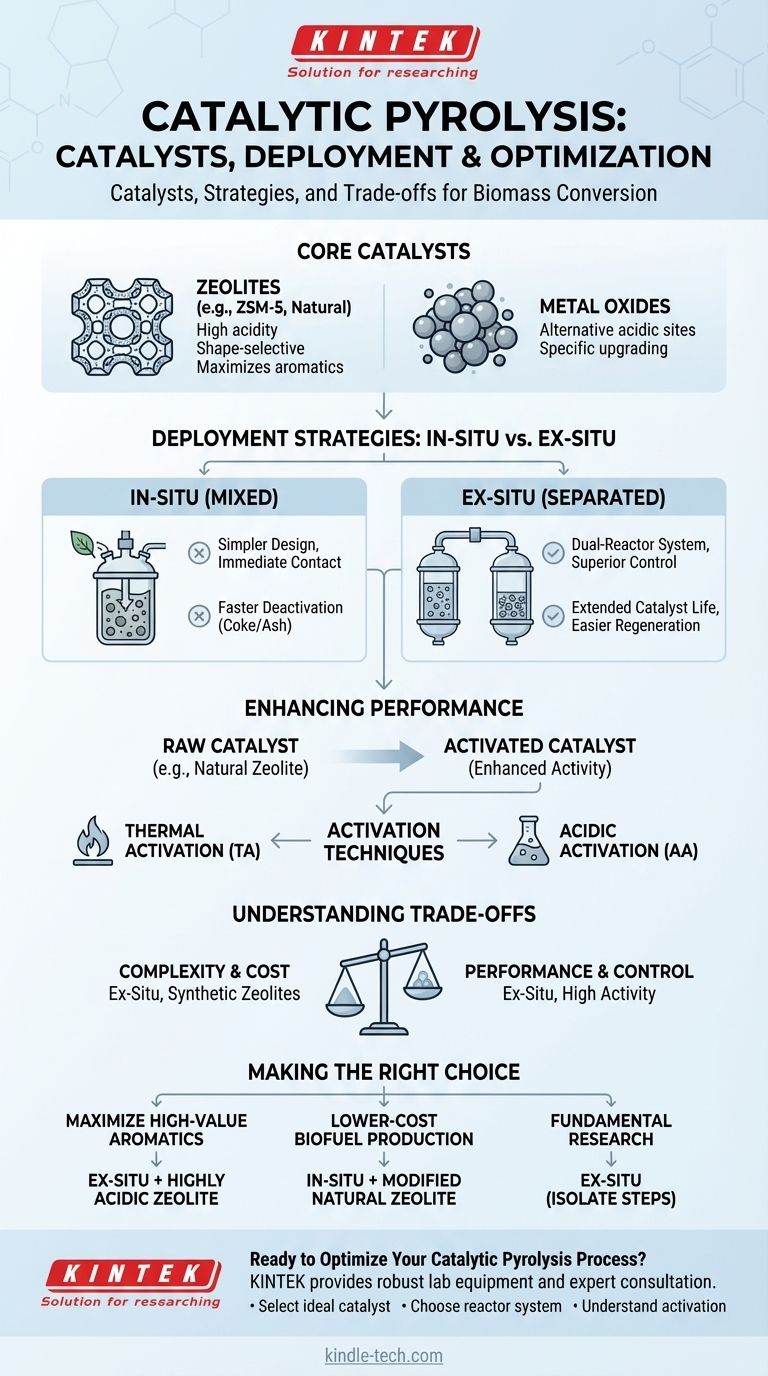
In catalytic pyrolysis, the most common catalysts are porous acidic solids, with zeolites being the predominant choice due to their unique structural and chemical properties. Other materials like metal oxides are also used, but zeolites are the workhorse for upgrading biomass vapors into valuable chemicals and fuels.
The choice of a catalyst is only one part of the equation. How the catalyst is prepared and where it is placed in the reactor—either mixed directly with the biomass (in-situ) or in a separate bed (ex-situ)—are equally critical decisions that dictate the process efficiency and final product composition.

How Catalysts Are Deployed: In-Situ vs. Ex-Situ
The physical arrangement of the catalyst relative to the biomass fundamentally changes the reaction environment. This is the first major decision in designing a catalytic pyrolysis process.
In-Situ Catalysis: Mixed for Simplicity
In the in-situ method, the catalyst is physically mixed with the biomass feedstock before or during heating. This ensures immediate contact between the initial pyrolysis vapors and the catalyst's active sites.
This approach benefits from a simpler, single-reactor design. However, it can lead to faster catalyst deactivation from coke and mineral deposition.
Ex-Situ Catalysis: Separated for Control
The ex-situ method uses a dual-reactor system. The first reactor performs the initial pyrolysis of the biomass, and the resulting vapors are then passed over a separate, fixed bed of the catalyst in a second reactor.
This separation allows for independent optimization of both the pyrolysis and the catalytic upgrading temperatures, offering greater process control and making catalyst regeneration easier.
Enhancing Catalyst Performance
The raw catalyst material is often not in its most effective form. Pre-treatment, or activation, is a critical step to enhance its catalytic properties and improve the yield of desired products.
The Role of Natural Zeolites
Natural zeolites (NZ) are a cost-effective option for catalytic pyrolysis. However, their performance in their natural state can be limited.
Activation: Unlocking a Catalyst's Potential
To improve effectiveness, catalysts like natural zeolite undergo activation. These methods modify the catalyst's surface area, pore structure, and acidity, which are the primary drivers of its performance.
Common techniques include thermal activation (TA), which involves heating the catalyst to high temperatures, and acidic activation (AA), which uses an acid wash to alter its chemical properties. These novel methods significantly boost catalytic activity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a catalytic strategy involves balancing complexity, cost, and performance. There is no single "best" approach; the optimal choice depends on the specific goal.
In-Situ: Efficiency vs. Catalyst Lifespan
The direct mixing in an in-situ process maximizes contact time and can improve yields in a simple setup. The primary trade-off is significant catalyst deactivation from direct contact with char and ash, requiring more frequent regeneration or replacement.
Ex-Situ: Control vs. System Complexity
An ex-situ setup provides superior control over reaction conditions and extends catalyst life. This flexibility, however, comes at the cost of a more complex and expensive dual-reactor system.
Catalyst Choice: Cost vs. Activity
Highly active synthetic zeolites (like ZSM-5) are excellent for producing specific chemicals like aromatics but are expensive. Cheaper options like modified natural zeolites offer a good balance of cost and performance, making them suitable for bulk fuel production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of catalyst and process configuration should be driven directly by your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximizing high-value aromatic chemicals: An ex-situ reactor with a highly acidic, shape-selective zeolite like ZSM-5 is the standard approach.
- If your primary focus is developing a lower-cost process for biofuel production: An in-situ configuration using an abundant, activity-enhanced catalyst like modified natural zeolite is a more practical path.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research and process optimization: The ex-situ method is superior, as it allows you to isolate and study the pyrolysis and catalytic upgrading steps independently.
Ultimately, the catalyst and its implementation strategy are the most powerful levers for directing the outcome of the biomass conversion process.
Summary Table:
| Catalyst Type | Common Examples | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zeolites | ZSM-5, Natural Zeolite (NZ) | High acidity, shape-selective pores | Maximizing aromatic chemicals |
| Metal Oxides | Various oxides | Alternative acidic sites | Specific upgrading reactions |
| Activated Catalysts | Acid/Heat-treated NZ | Enhanced activity, cost-effective | Lower-cost biofuel production |
Ready to Optimize Your Catalytic Pyrolysis Process?
The right catalyst and reactor configuration are critical for achieving your target yields of biofuels or high-value chemicals. KINTEK specializes in providing robust lab equipment and expert consultation to help you design, test, and scale your pyrolysis process efficiently.
We help our laboratory customers:
- Select the ideal catalyst for your specific biomass feedstock and desired products.
- Choose between in-situ and ex-situ reactor systems for maximum control and efficiency.
- Understand catalyst activation techniques to enhance performance and lifespan.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how our solutions can accelerate your research and development. Let's turn your biomass into value together.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Tweezers
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Rubber Vulcanizer Vulcanizing Machine Plate Vulcanizing Press for Lab
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using PTFE molds for epoxy resin flame retardant samples? Ensure High-Purity Material Testing
- How are PTFE gaskets utilized for POEGMA electrolyte conductivity? Ensure Precision in Electrochemical Measurements
- Why is it necessary to utilize PTFE sample holders in electroless nickel plating? Ensure Process Integrity
- Why is a PTFE casing used in liquid tin stability experiments? Achieve Superior Thermal Isolation and Precision
- What are the advantages of using PTFE jars for RuTi alloy mixing? Ensure Chemical Purity and High Yield



















