The choice of catalyst is pivotal for efficiently converting raw biomass into valuable fuels and chemicals. The primary catalysts fall into three broad categories: homogeneous acids and bases, heterogeneous solid catalysts such as zeolites and metal oxides, and biocatalysts like enzymes. Each class is suited for different biomass feedstocks, reaction conditions, and desired end products.
The central challenge in biomass conversion is not finding a catalyst, but selecting the right catalyst. The optimal choice is a carefully balanced trade-off between reaction efficiency, product selectivity, operational stability, and economic viability for a specific conversion pathway.

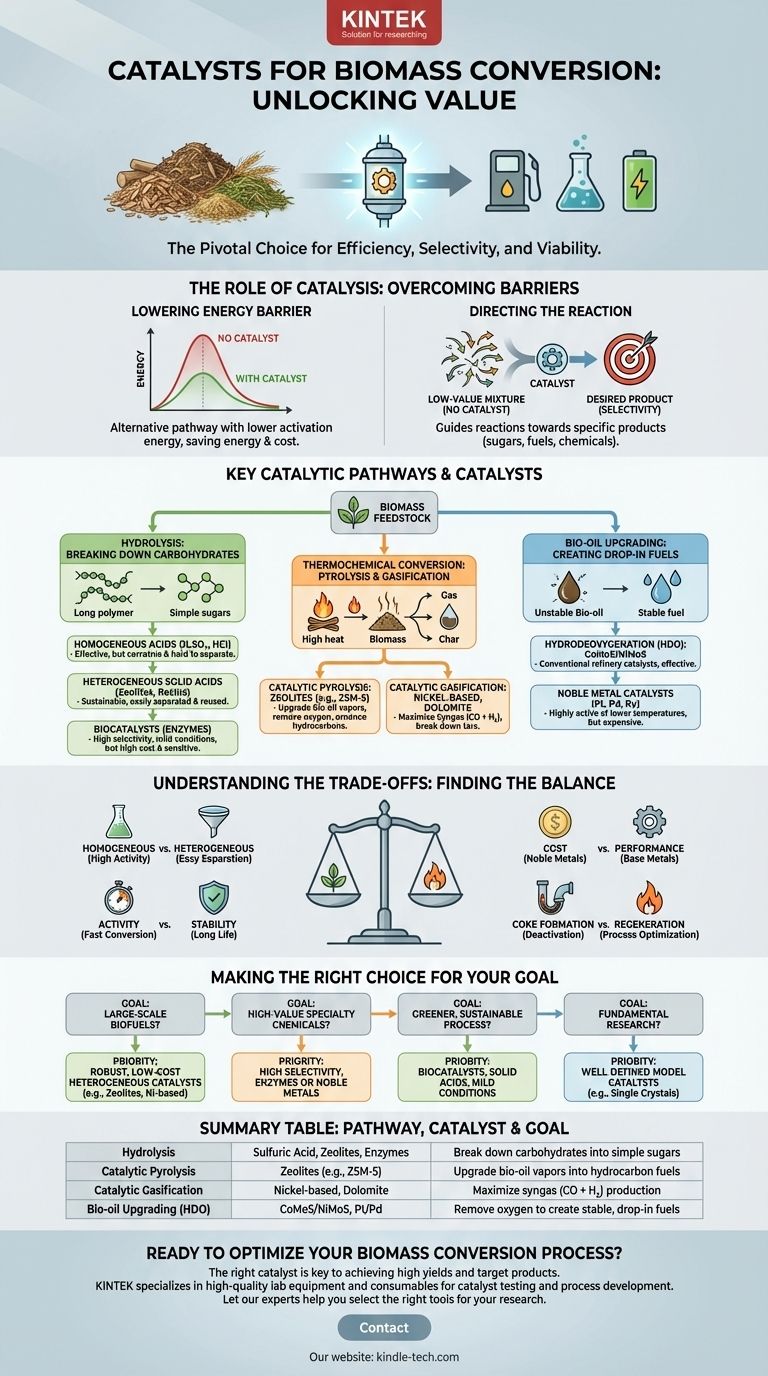
The Role of Catalysis in Biomass Conversion
Biomass—composed of complex polymers like cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin—is inherently stable and resistant to degradation. Catalysts are essential for breaking it down under practical conditions.
Lowering the Energy Barrier
Catalysts provide an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy. This allows complex biomass molecules to be broken down at lower temperatures and pressures, saving significant energy and cost.
Directing the Reaction
Without a catalyst, heating biomass often results in a complex, low-value mixture of hundreds of compounds. Catalysts provide selectivity, guiding the chemical reactions toward a specific, desired product, whether it's a sugar, a fuel molecule, or a platform chemical.
Key Catalytic Pathways and Their Catalysts
Different conversion technologies target different components of biomass and require distinct catalytic systems.
Hydrolysis: Breaking Down Carbohydrates to Sugars
The goal of hydrolysis is to break down cellulose and hemicellulose into simple sugars (e.g., glucose, xylose).
- Homogeneous Acids: Mineral acids like sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) and hydrochloric acid (HCl) are highly effective. However, they are corrosive, difficult to separate from the sugar products, and create significant waste treatment challenges.
- Heterogeneous Solid Acids: These are a more sustainable alternative. Zeolites (like H-ZSM-5), sulfonated carbons, and functionalized resins can effectively break down carbohydrates while being easily filtered and reused.
- Biocatalysts (Enzymes): Cellulase and hemicellulase enzymes offer extremely high selectivity under very mild conditions (low temperature and neutral pH). Their main drawbacks are high cost and sensitivity to temperature and contaminants.
Thermochemical Conversion: Pyrolysis and Gasification
These high-temperature processes break down all biomass components into vapors, liquids (bio-oil), or gases (syngas).
- Catalytic Pyrolysis: The primary goal is to upgrade the quality of bio-oil vapors in real-time. Zeolites, particularly ZSM-5, are the industry standard. They excel at removing oxygen (deoxygenation) and converting the vapors into aromatic hydrocarbons, the building blocks of gasoline.
- Catalytic Gasification: This process aims to maximize the production of syngas (CO + H₂). Nickel-based catalysts are common for breaking down unwanted tar byproducts. Cheaper, naturally occurring minerals like dolomite and olivine are also widely used, though they are generally less active than nickel.
Bio-oil Upgrading: Creating Drop-in Fuels
Raw bio-oil is acidic, unstable, and has a high oxygen content. Catalytic upgrading is required to make it a usable "drop-in" fuel.
- Hydrodeoxygenation (HDO): This is the most common upgrading method, which uses hydrogen to remove oxygen. Conventional refinery catalysts like cobalt-molybdenum sulfide (CoMoS) and nickel-molybdenum sulfide (NiMoS) are effective.
- Noble Metal Catalysts: Supported precious metals like platinum (Pt), palladium (Pd), and ruthenium (Ru) are highly active for HDO at lower temperatures but come at a significantly higher cost.
Understanding the Trade-offs
There is no single "best" catalyst. The selection is always a compromise based on the specific goals of the process.
Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous
Homogeneous catalysts often show higher activity because they are perfectly mixed with reactants. However, their recovery from the product stream is a major engineering and economic hurdle. Heterogeneous catalysts are the preferred choice for most industrial-scale processes due to their ease of separation and potential for regeneration.
Activity vs. Stability
Highly active catalysts can convert biomass quickly but may also be prone to deactivation. The harsh environment of biomass conversion—with high temperatures and contaminants like alkali metals and sulfur—can quickly poison a catalyst. A key challenge is finding a catalyst that is robust enough to maintain its performance over long operational cycles.
The Problem of Coking
One of the most common modes of deactivation is coking, where carbon deposits form on the catalyst's active sites, blocking them. Catalyst design and process conditions must be optimized to minimize coke formation and allow for periodic regeneration (e.g., by burning the coke off with air).
Cost vs. Performance
Noble metals like platinum offer exceptional performance but can be prohibitively expensive. In contrast, base metals like nickel and iron or natural minerals like dolomite are far cheaper but may offer lower activity or require more frequent replacement. The final choice depends on the value of the end product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of catalyst should be dictated by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is large-scale biofuel production: Prioritize robust, low-cost heterogeneous catalysts like zeolites (for pyrolysis) or nickel-based systems (for gasification) that can withstand deactivation and be regenerated.
- If your primary focus is producing high-value specialty chemicals: The high selectivity offered by enzymes or precisely engineered noble metal catalysts may justify their higher cost and more delicate operating conditions.
- If your primary focus is creating a greener, more sustainable process: Explore biocatalysts (enzymes) or solid acid catalysts that can operate in water under milder conditions, minimizing energy input and harsh chemical use.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research: Use well-defined model catalysts (e.g., single crystals or precisely synthesized nanoparticles) to understand reaction mechanisms, even if they are not commercially scalable.
Ultimately, selecting the right catalyst is a strategic engineering decision that balances chemical efficiency with economic reality.
Summary Table:
| Conversion Pathway | Common Catalysts | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrolysis | Sulfuric Acid, Zeolites, Cellulase Enzymes | Break down carbohydrates into simple sugars |
| Catalytic Pyrolysis | Zeolites (e.g., ZSM-5) | Upgrade bio-oil vapors into hydrocarbon fuels |
| Catalytic Gasification | Nickel-based catalysts, Dolomite | Maximize syngas (CO + H₂) production |
| Bio-oil Upgrading (HDO) | CoMoS/NiMoS, Platinum/Palladium | Remove oxygen to create stable, drop-in fuels |
Ready to optimize your biomass conversion process? The right catalyst is key to achieving high yields and target products, whether you're producing biofuels or high-value chemicals. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for catalyst testing and process development. Our experts can help you select the right tools to evaluate catalyst performance, stability, and selectivity for your specific biomass feedstock and goals.
Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your research and scale-up efforts.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
People Also Ask
- What function does a high-speed rotor-stator homogenizer perform in biomass processing? Optimize Structural Disruption
- What is the difference between mixer and disperser? Choose the Right Tool for Your Process
- Why is a rotary mechanical homogenizer used for extended periods for forsterite-spinel? Achieve Peak Ceramic Uniformity
- What is grinder in chemistry? A Guide to Precision Sample Preparation
- Why is precision mixing required for concrete corrosion studies? Ensure Data Integrity through Homogenization



















