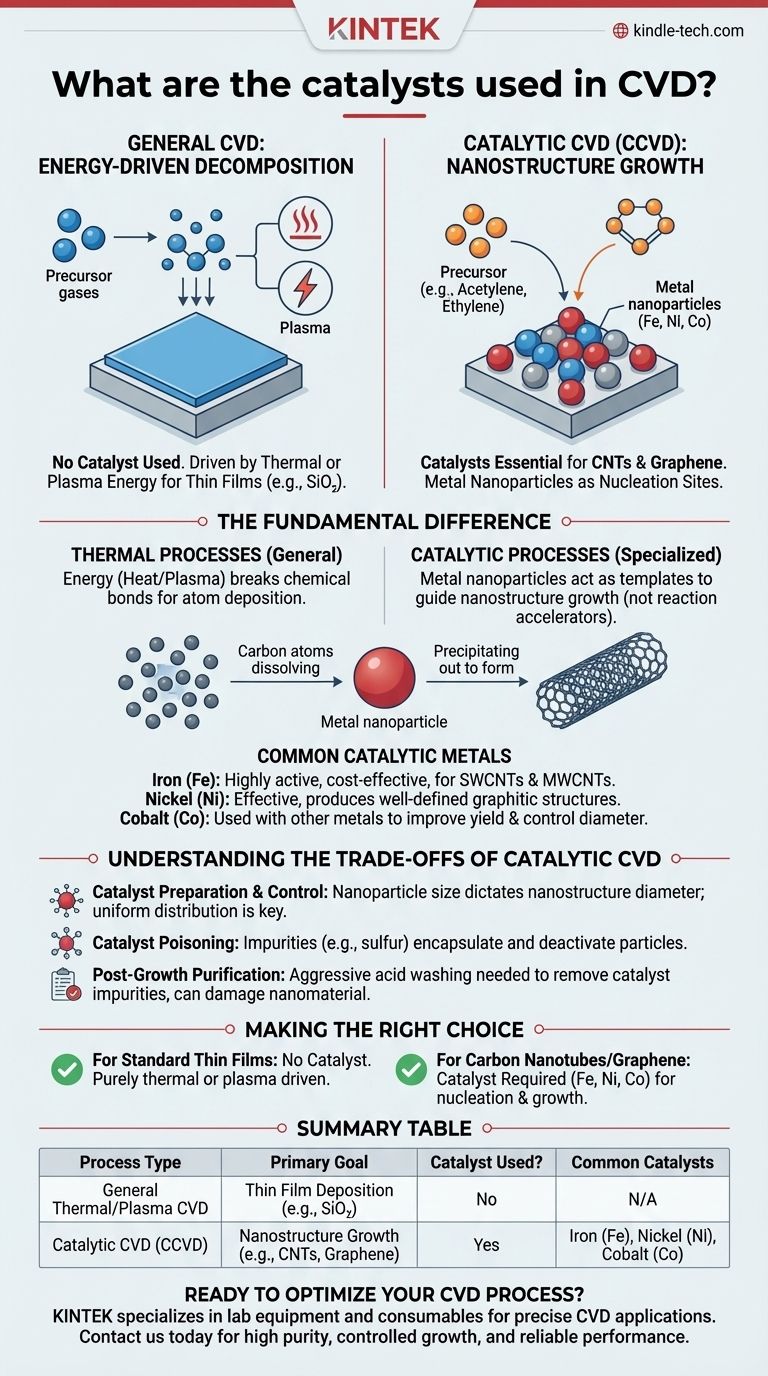
Contrary to a common assumption, most Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) processes are not catalytic. They are primarily driven by thermal energy, where high temperatures break down precursor gases to deposit a thin film onto a substrate. However, a critical sub-field, often called Catalytic CVD (CCVD), relies on metal catalysts for the specific purpose of growing one-dimensional or two-dimensional nanostructures like carbon nanotubes and graphene.
The core distinction is this: general CVD for thin films uses energy (heat, plasma) to drive reactions, whereas specialized CVD for nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes uses metal nanoparticles (typically iron, nickel, or cobalt) as nucleation sites to template and guide growth.

The Fundamental Difference: Thermal vs. Catalytic Processes
The term "CVD" covers a wide range of processes. Understanding whether a catalyst is needed depends entirely on the material you intend to create.
How General CVD Works: Energy-Driven Decomposition
Most CVD processes are used to deposit uniform thin films, such as silicon dioxide on a computer chip.
In this context, there is no catalyst. The reaction is initiated by adding energy to precursor gases inside a chamber. This energy, usually from heat (Thermal CVD) or plasma (PECVD), breaks the chemical bonds in the gas molecules, allowing the desired atoms to deposit onto the heated substrate.
Where Catalysts Become Essential: Nanostructure Growth
The need for a catalyst arises when growing highly specific, crystalline structures, most famously carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and graphene.
Here, the goal isn't just to deposit a uniform layer of atoms. The process must be controlled to form a specific atomic arrangement—a rolled-up sheet for a nanotube or a flat lattice for graphene. This is where metal catalyst particles become indispensable.
The Role of the "Catalyst" in Nanomaterial Growth
In the context of growing CNTs or graphene, the "catalyst" is typically a metal nanoparticle that acts as a seed for growth. The most common metals are from the transition group.
The Mechanism: A Nucleation Site, Not a Reaction Accelerator
The metal particle isn't a catalyst in the traditional sense of lowering the activation energy for the entire reaction. Instead, it serves as a liquid or semi-liquid site where carbon-containing precursor gases (like acetylene or ethylene) can decompose.
Carbon atoms dissolve into the metal nanoparticle until it becomes supersaturated. The carbon then precipitates out to form the highly ordered graphitic structure of a nanotube or graphene sheet. The particle essentially templates the growth.
Common Catalytic Metals
The choice of metal is critical for controlling the resulting nanostructure. The most widely used catalysts are:
- Iron (Fe): Highly active and cost-effective, often used for growing both single-walled and multi-walled CNTs.
- Nickel (Ni): Another highly effective catalyst, known for producing well-defined graphitic structures.
- Cobalt (Co): Often used in combination with other metals (like Fe or Molybdenum) to improve yield and control the diameter of single-walled CNTs.
These metals are typically deposited onto a substrate (like silicon or quartz) as a thin film, which then de-wets upon heating to form the necessary nanoparticles.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Catalytic CVD
While essential for nanomaterial synthesis, using catalysts introduces unique challenges that are not present in standard thin-film deposition.
Catalyst Preparation and Control
The size of the metal nanoparticle directly dictates the diameter of the carbon nanotube. Creating a uniform distribution of nanoparticles to grow uniform CNTs is a significant engineering challenge.
Catalyst Poisoning
Impurities in the precursor gases (such as sulfur) can "poison" the catalyst particles, causing them to become encapsulated in amorphous carbon. This deactivates the particle and stops the growth process.
Post-Growth Purification
After growth is complete, the final product contains both the desired carbon nanostructures and the metal catalyst particles. For most electronic or biomedical applications, these metallic impurities must be removed through aggressive acid washing, which can damage the nanomaterial.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Whether you need a catalyst is determined entirely by your desired end product.
- If your primary focus is growing carbon nanotubes or graphene: You will need to use metal catalysts like iron, nickel, or cobalt to serve as nucleation and growth sites.
- If your primary focus is depositing a standard thin film (e.g., silicon dioxide, silicon nitride, or amorphous silicon): You will not use a catalyst; the reaction will be driven entirely by external energy like heat or plasma.
Ultimately, your material goal dictates whether the CVD process is purely thermal or requires a catalyst to guide its structure.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Primary Goal | Catalyst Used? | Common Catalysts |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Thermal/Plasma CVD | Thin Film Deposition (e.g., SiO₂) | No | N/A |
| Catalytic CVD (CCVD) | Nanostructure Growth (e.g., CNTs, Graphene) | Yes | Iron (Fe), Nickel (Ni), Cobalt (Co) |
Ready to optimize your CVD process for nanomaterials or thin films? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the precise tools and expertise needed for both catalytic and thermal CVD applications. Whether you're growing carbon nanotubes or depositing uniform thin films, our solutions ensure high purity, controlled growth, and reliable performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs and accelerate your research!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods



















