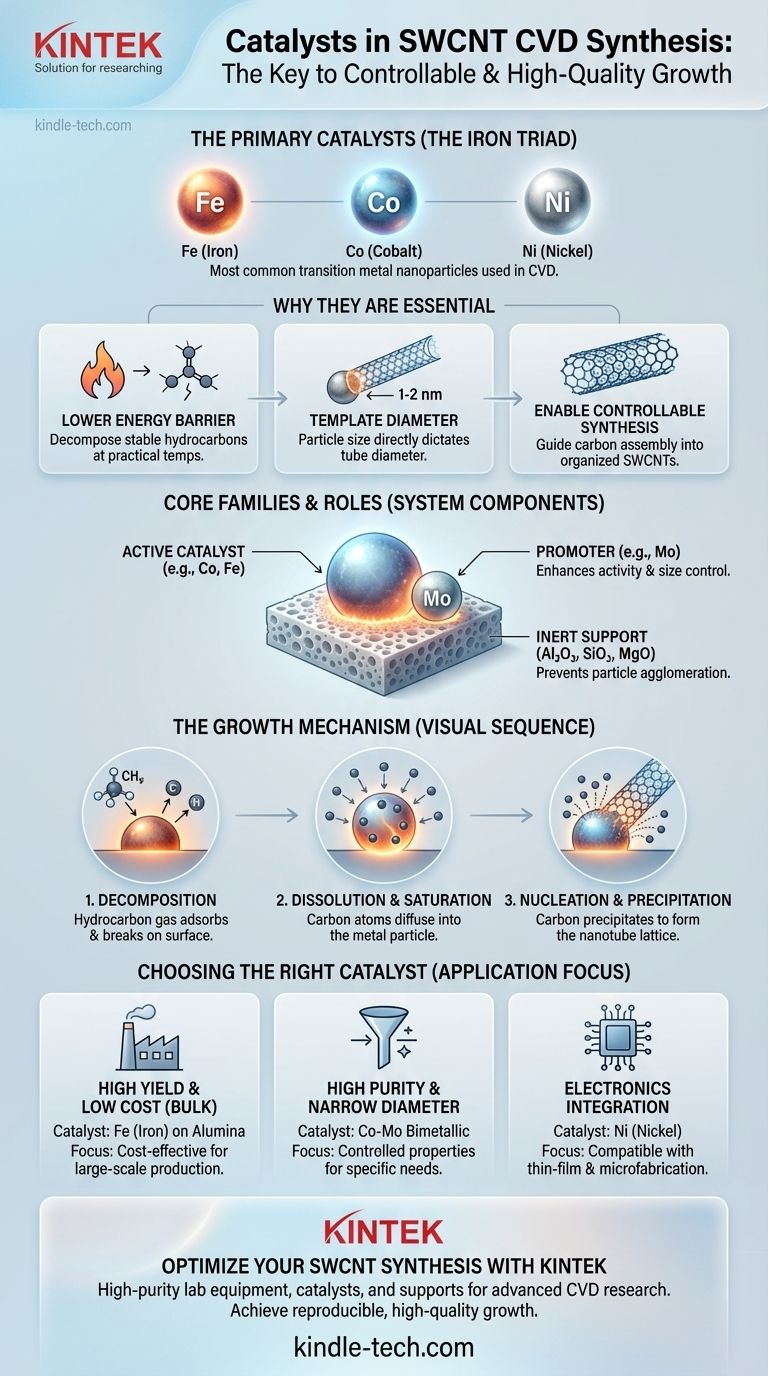
The most common catalysts used in chemical vapor deposition (CVD) for preparing single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) are transition metals. Specifically, nanoparticles of iron (Fe), cobalt (Co), and nickel (Ni) are the primary catalysts employed. These are often used individually or in bimetallic combinations, sometimes with a promoter like molybdenum (Mo), to achieve high selectivity and yield.
The choice of catalyst is not just about a specific element; it's about creating precisely sized nanoparticles that can effectively crack hydrocarbon precursors and template the growth of a single-walled tube. The catalyst's state, size, and interaction with its support are the most critical factors determining the final SWCNT structure and quality.

Why Catalysts are Essential for SWCNT Growth
Catalytic Chemical Vapor Deposition (CCVD) has become the dominant method for producing carbon nanotubes due to its controllability and cost-effectiveness. The catalyst is not an optional additive; it is the central component that makes the entire process possible.
Lowering the Energy Barrier
Stable hydrocarbon gases, such as methane or ethylene, do not break down on their own at moderate temperatures. The catalyst's role is to dramatically lower the energy required to decompose these precursor gases, releasing carbon atoms needed for nanotube formation at practical and energy-efficient temperatures.
Templating the Nanotube Diameter
For SWCNTs, there is a direct and critical relationship between the size of the catalyst particle and the diameter of the resulting nanotube. To grow a SWCNT with a diameter of 1-2 nanometers, you must start with a catalyst nanoparticle of a similar size.
Enabling Controllable Synthesis
Without a catalyst, any carbon deposition would be disordered and amorphous. The catalyst particle provides a nucleation site and a physical template that guides the carbon atoms to assemble into the specific, cylindrical graphitic structure of a nanotube.
The Core Catalyst Families and Their Roles
While many metals have been investigated, a small group has proven most effective for SWCNT synthesis due to a unique combination of catalytic activity and carbon solubility.
The Iron Triad: Fe, Co, and Ni
Iron (Fe), Cobalt (Co), and Nickel (Ni) are by far the most widely used catalysts. They share a key property: they can dissolve a certain amount of carbon at high temperatures. This ability to absorb and then precipitate carbon is fundamental to the growth mechanism.
The Importance of Catalyst Supports
Catalyst nanoparticles are not used in isolation. They are dispersed on a high-surface-area, inert ceramic support material like alumina (Al₂O₃), silica (SiO₂), or magnesia (MgO). The support prevents the tiny metallic nanoparticles from clumping together (agglomerating) at high temperatures, which would lead to the growth of undesirable multi-walled nanotubes or no growth at all.
Bimetallic Systems and Promoters
To further improve performance, catalysts are often used in pairs, such as a Co-Mo (Cobalt-Molybdenum) or Fe-Mo (Iron-Molybdenum) system. In this arrangement, Co or Fe acts as the primary active catalyst, while Mo serves as a promoter that enhances activity and helps maintain a small, uniform particle size distribution.
Understanding the Growth Mechanism
The process by which a catalyst particle transforms gas into a solid nanotube is an elegant, self-assembling sequence.
Step 1: Precursor Decomposition
A hydrocarbon gas molecule (like methane, CH₄) adsorbs onto the surface of the hot metal nanoparticle and breaks apart, depositing its carbon atom onto the catalyst.
Step 2: Carbon Dissolution and Saturation
Carbon atoms diffuse into the bulk of the metal particle. As more precursor gas decomposes, the concentration of carbon within the particle increases until it reaches a state of supersaturation.
Step 3: Nanotube Nucleation and Precipitation
To relieve this supersaturated state, the dissolved carbon precipitates out onto the surface of the particle. Guided by the particle's geometry, the carbon atoms form the hexagonal lattice structure that becomes the wall of the single-walled nanotube, which then grows outwards from the catalyst particle.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While essential, the use of catalysts introduces significant practical challenges that must be managed to produce high-quality material.
Controlling Catalyst Particle Size
The single biggest challenge in SWCNT synthesis is creating a uniform population of catalyst nanoparticles in the 1-2 nm size range. Even small variations in particle size lead to a mixture of different nanotube diameters in the final product.
Catalyst Deactivation
Over time, the catalyst particle can become encapsulated in a layer of amorphous carbon or poisoned by trace impurities in the gas feed. This deactivates the catalyst and stops nanotube growth, limiting the achievable length and overall process yield.
Post-Synthesis Purification
The final SWCNT product is inherently a composite material contaminated with residual metal catalyst particles and the ceramic support. These impurities must be removed through aggressive acid treatments, a process which adds cost, generates chemical waste, and can introduce defects into the nanotubes themselves.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal catalyst system is not universal; it is highly dependent on the desired outcome of the synthesis.
- If your primary focus is high yield and low cost: An iron (Fe) catalyst on an alumina support is often the most cost-effective starting point for bulk production.
- If your primary focus is high purity and specific structures: A cobalt-molybdenum (Co-Mo) system is frequently used as it can produce a narrower diameter distribution, which is a prerequisite for controlling properties.
- If your primary focus is direct integration with electronics: Nickel (Ni) is often explored due to its well-understood properties in thin-film deposition and compatibility with existing microfabrication processes.
Ultimately, successful SWCNT synthesis relies on precisely controlling the catalyst's state to manage the delicate balance between carbon decomposition, diffusion, and precipitation.
Summary Table:
| Catalyst | Key Role & Characteristics | Common Support Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Iron (Fe) | Cost-effective; high yield; good for bulk production | Alumina (Al₂O₃), Silica (SiO₂) |
| Cobalt (Co) | High purity; often used with Mo for narrow diameter distribution | Silica (SiO₂), Alumina (Al₂O₃) |
| Nickel (Ni) | Compatible with electronics; good for thin-film integration | Magnesia (MgO), Silica (SiO₂) |
| Bimetallic (e.g., Co-Mo) | Enhanced activity and size control; improved selectivity | Alumina (Al₂O₃), Silica (SiO₂) |
Ready to Optimize Your SWCNT Synthesis?
Choosing the right catalyst is critical for achieving the desired yield, purity, and structure of your Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. KINTEK specializes in providing high-purity lab equipment and consumables, including catalyst materials and support systems tailored for advanced materials research like CVD.
We can help you:
- Source high-purity transition metal catalysts and supports.
- Select the right equipment for controlled CVD processes.
- Achieve reproducible and high-quality SWCNT growth.
Let's discuss your specific application needs. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- What function does CVD equipment serve in rhodium-modified coatings? Achieve Deep Diffusion and Microstructural Precision
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques
- What role does Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) equipment play in the preparation of C/C composites? Expert Analysis
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit



















