The primary challenges of plastic pyrolysis are rooted in feedstock contamination, the low quality and instability of the resulting fuel oil, significant economic hurdles, and pressing environmental concerns. The process is far more complex than simply melting plastic; it involves a series of technical and financial obstacles that prevent it from being a straightforward solution to the plastic waste crisis.
While presented as a high-tech solution to plastic waste, pyrolysis is not a silver bullet. Its viability is fundamentally limited by the chemical complexity of real-world plastic waste and the economic challenge of producing a low-grade product that requires costly upgrades to be useful.
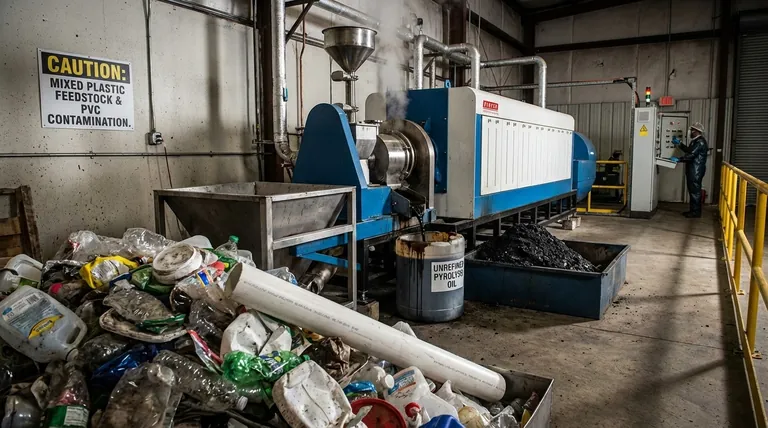

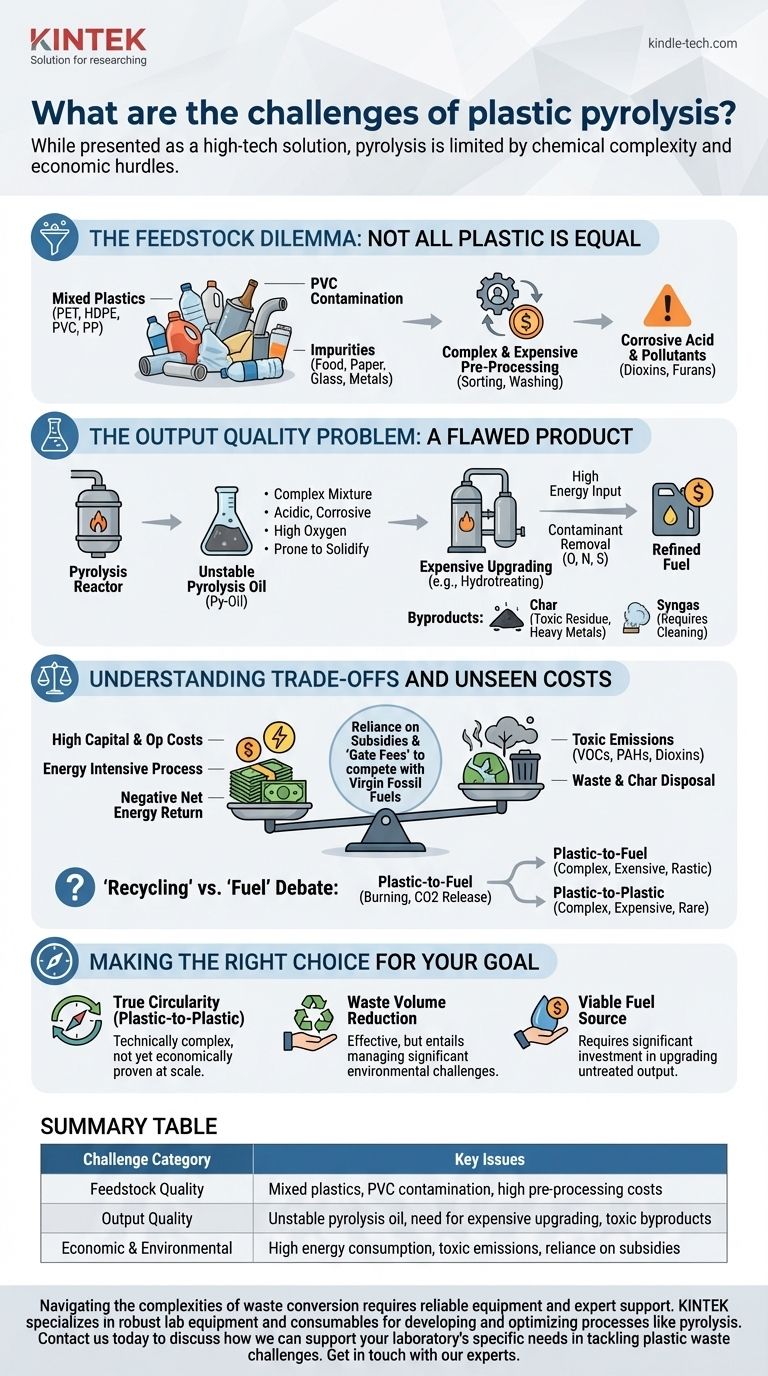
The Feedstock Dilemma: Not All Plastic is Equal
The single greatest challenge begins before the process even starts: the plastic waste itself. Real-world municipal waste is a chaotic mixture that undermines the efficiency and safety of pyrolysis.
The Problem of Mixed Plastics
Pyrolysis reactors require a consistent, clean stream of specific plastic types to operate effectively. However, post-consumer waste is a blend of PET (bottles), HDPE (jugs), PVC (pipes), PP (containers), and more.
Each polymer breaks down at different temperatures and yields different products, making process control extremely difficult and the final output unpredictable.
The PVC Contamination Threat
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a critical contaminant. When heated, PVC releases chlorine, which forms highly corrosive hydrochloric acid.
This acid aggressively attacks reactor components, leading to expensive maintenance and operational downtime. More dangerously, the chlorine can also form dioxins and furans, which are potent, long-lasting environmental pollutants.
Impurities and Pre-Processing Costs
Plastic waste is never pure. It is contaminated with organic matter (food residue), paper, glass, and metals.
These impurities must be meticulously removed through costly and energy-intensive sorting and washing processes. Failure to do so results in a lower-quality output and can damage the pyrolysis equipment.
The Output Quality Problem: A Flawed Product
Even with ideal feedstock, the products of pyrolysis are not drop-in replacements for conventional fuels or chemical feedstocks. They require significant and expensive secondary processing.
Understanding Pyrolysis Oil (Py-Oil)
The primary liquid output, often called pyrolysis oil or py-oil, is not equivalent to crude oil. It is a complex, unstable mixture that is acidic, corrosive, and contains a high percentage of oxygen and contaminants.
This oil is prone to polymerization, meaning it can thicken and solidify into a sludge-like material over time, creating storage and transportation challenges.
The Need for Expensive Upgrading
Before py-oil can be used in a traditional refinery, it must undergo a costly and energy-intensive upgrading process, such as hydrotreating.
This step is necessary to remove contaminants like oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur and to stabilize the molecules. This secondary processing is a major hidden cost that significantly impacts the overall economic viability.
Managing Char and Syngas Byproducts
Pyrolysis also produces a solid residue called char and a non-condensable gas called syngas.
The char can contain heavy metals, toxic organic compounds, and other contaminants from the original plastic feedstock, making its disposal an environmental concern. While the syngas can be burned to provide energy for the process, it too must be cleaned of pollutants before use or release.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Unseen Costs
Viewing pyrolysis as a simple solution ignores its significant energy, environmental, and economic trade-offs. A clear-eyed assessment reveals a process burdened by inherent inefficiencies.
High Energy Consumption
Pyrolysis is an energy-intensive process that requires heating large volumes of plastic to temperatures between 400°C and 600°C.
The net energy return—the energy value of the produced fuel minus the energy required to run the process—is often low and can even be negative, especially when accounting for collection, sorting, and upgrading.
The Risk of Toxic Emissions
Improper process control or the presence of contaminants like PVC can lead to the formation and release of hazardous air pollutants.
These include volatile organic compounds (VOCs), polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), and the previously mentioned dioxins and furans, all of which pose risks to human health and the environment.
Economic Volatility and Reliance on Subsidies
The high capital and operational costs, combined with the low value of the unrefined py-oil, make the economics of pyrolysis challenging.
Many operations struggle to compete with the low cost of virgin fossil fuels and often depend on government subsidies or "gate fees"—being paid to take plastic waste—to remain solvent.
The "Recycling" vs. "Fuel" Debate
A major point of contention is whether pyrolysis is truly "recycling." Most current facilities operate on a plastic-to-fuel model, where the end product is burned.
Critics argue this is not a circular solution but rather a complex way to turn plastic back into a fossil fuel, releasing CO2 and other pollutants upon combustion. True plastic-to-plastic recycling via pyrolysis is technically possible but far more complex and expensive, and it is not the common operational model.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Evaluating pyrolysis requires aligning its capabilities with a specific, well-defined objective. The technology's suitability is entirely dependent on the problem you intend to solve.
- If your primary focus is true circularity (plastic-to-plastic): Recognize that current pyrolysis technology largely creates fuel, and the pathway to creating new plastics is technically complex and not yet economically proven at scale.
- If your primary focus is waste volume reduction: Pyrolysis effectively converts solid plastic into other forms, but you must account for the significant costs and environmental challenges of managing the toxic char, wastewater, and air emissions.
- If your primary focus is creating a viable fuel source: Be prepared for significant capital investment in upgrading and refining the raw pyrolysis oil to meet industry standards, as the untreated output is unsuitable for most applications.
Ultimately, a clear-eyed assessment of these technical and economic hurdles is essential before investing in pyrolysis as a definitive solution for plastic waste.
Summary Table:
| Challenge Category | Key Issues |
|---|---|
| Feedstock Quality | Mixed plastics, PVC contamination, high pre-processing costs |
| Output Quality | Unstable pyrolysis oil, need for expensive upgrading, toxic byproducts |
| Economic & Environmental | High energy consumption, toxic emissions, reliance on subsidies |
Navigating the complexities of waste conversion requires reliable equipment and expert support. KINTEK specializes in providing robust lab equipment and consumables for researchers and engineers developing and optimizing processes like pyrolysis. Whether you are analyzing feedstock, testing outputs, or scaling up your operations, our solutions are designed for precision and durability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs in tackling plastic waste challenges. Get in touch with our experts
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds



















