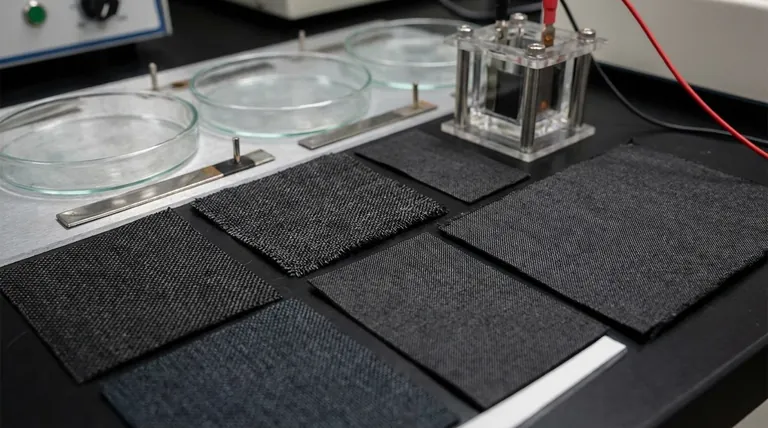
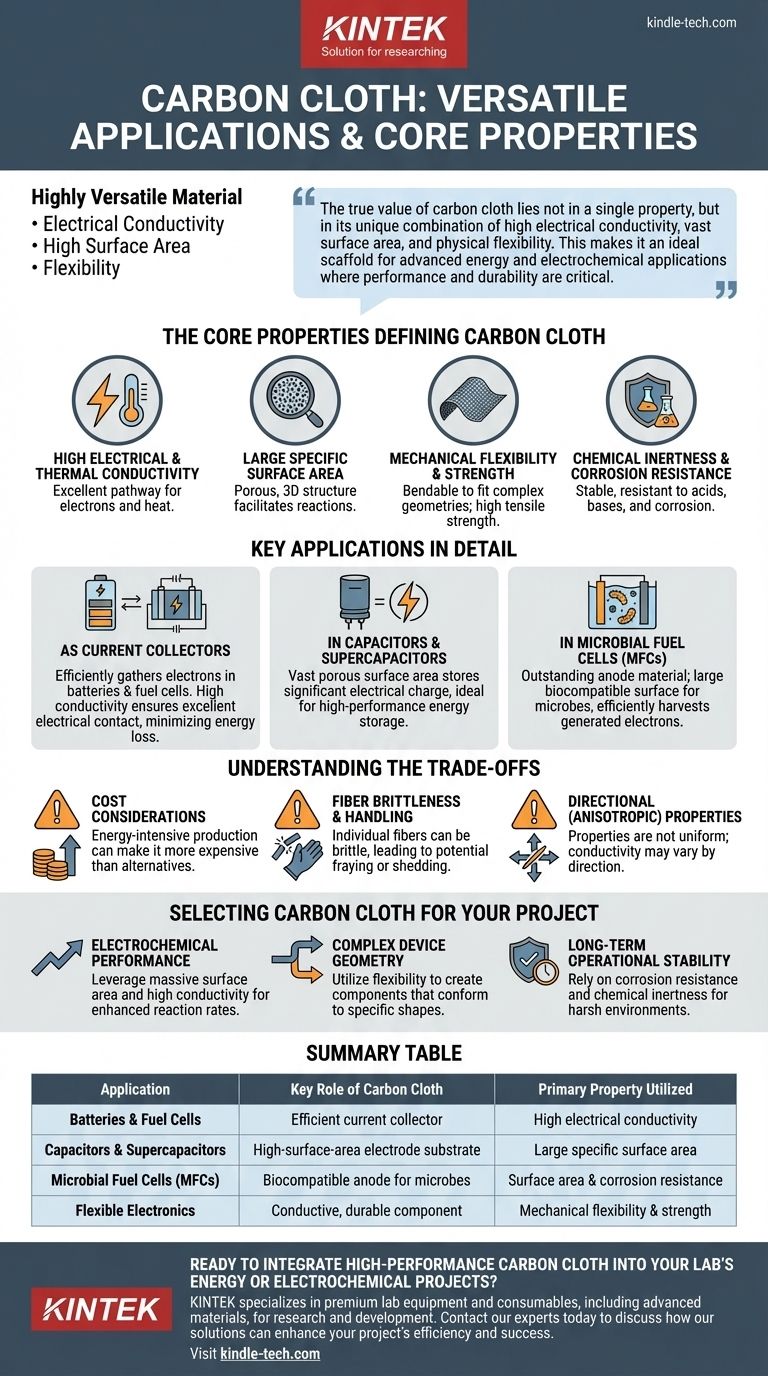
Carbon cloth is a highly versatile material used primarily where electrical conductivity, high surface area, and flexibility are required. Its most common applications are as current collectors in batteries and fuel cells, as electrode substrates for capacitors, and as a foundational component in microbial fuel cell (MFC) reactors.
The true value of carbon cloth lies not in a single property, but in its unique combination of high electrical conductivity, vast surface area, and physical flexibility. This makes it an ideal scaffold for advanced energy and electrochemical applications where performance and durability are critical.

The Core Properties Defining Carbon Cloth
To understand why carbon cloth is chosen for these specific roles, we must first examine its fundamental characteristics, which stem from its construction of woven carbon fibers.
High Electrical and Thermal Conductivity
Because it is composed almost entirely of carbon, the cloth provides an excellent pathway for electrons and heat. This conductivity is essential for its role in electrical devices.
Large Specific Surface Area
The woven nature of the fibers creates a porous, three-dimensional structure. This results in an exceptionally large surface area relative to its volume, which is crucial for facilitating chemical and electrochemical reactions.
Mechanical Flexibility and Strength
Unlike rigid graphite plates, carbon cloth can be bent, shaped, or layered to fit complex device geometries. Despite this flexibility, the underlying carbon fibers provide high tensile strength and durability.
Chemical Inertness and Corrosion Resistance
Carbon is a very stable element that does not readily react with most acids, bases, or organic solvents. This makes carbon cloth highly resistant to corrosion and chemical degradation, ensuring long-term performance in harsh environments.
Key Applications in Detail
These core properties directly translate into its effectiveness in several advanced technical applications.
As Current Collectors
In batteries and fuel cells, a current collector's job is to efficiently gather electrons from an electrode and guide them to the external circuit. Carbon cloth's high conductivity and large surface area ensure excellent electrical contact, minimizing energy loss.
In Capacitors and Supercapacitors
The performance of a capacitor is directly related to the surface area of its electrodes. Carbon cloth's vast, porous surface allows it to store a significant amount of electrical charge, making it an ideal substrate for high-performance supercapacitors.
In Microbial Fuel Cells (MFCs)
Carbon cloth serves as an outstanding anode material in MFCs. Its large, biocompatible surface provides an ideal habitat for electricity-producing microbes to colonize. Its conductivity efficiently harvests the electrons they generate, while its corrosion resistance ensures it survives long-term within the microbial environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, carbon cloth is not the solution for every problem. An objective analysis requires understanding its limitations.
Cost Considerations
The process of producing high-purity carbon fibers is energy-intensive. Consequently, carbon cloth is often more expensive than alternative materials like graphite foils or certain metal meshes, which can be a limiting factor for large-scale or cost-sensitive projects.
Fiber Brittleness and Handling
Although the cloth itself is flexible, the individual carbon fibers can be brittle. This can lead to fraying at the edges or shedding of fiber fragments during handling, which may be a concern in highly sensitive systems where particulate contamination must be avoided.
Directional (Anisotropic) Properties
Because it is a woven material, its properties are not always uniform in every direction. For example, electrical conductivity might be higher along the length of the fiber bundles (the warp and weft) than it is through the thickness of the cloth. This must be accounted for in device design.
Selecting Carbon Cloth for Your Project
The decision to use carbon cloth should be driven by your primary technical goal.
- If your primary focus is electrochemical performance: Leverage its massive surface area and high conductivity, as these directly enhance reaction rates and energy storage capacity.
- If your primary focus is complex device geometry: Utilize its unique flexibility and strength to create components that conform to specific shapes without sacrificing electrical performance.
- If your primary focus is long-term operational stability: Rely on its inherent corrosion resistance and chemical inertness for applications in harsh environments where other materials would quickly degrade.
Understanding these core principles allows you to effectively harness carbon cloth's potential in advanced material design.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Role of Carbon Cloth | Primary Property Utilized |
|---|---|---|
| Batteries & Fuel Cells | Efficient current collector | High electrical conductivity |
| Capacitors & Supercapacitors | High-surface-area electrode substrate | Large specific surface area |
| Microbial Fuel Cells (MFCs) | Biocompatible anode for microbes | Surface area & corrosion resistance |
| Flexible Electronics | Conductive, durable component | Mechanical flexibility & strength |
Ready to integrate high-performance carbon cloth into your lab's energy or electrochemical projects?
KINTEK specializes in providing premium lab equipment and consumables, including advanced materials like carbon cloth, to meet the precise needs of research and development laboratories. Our products are selected for their reliability and performance in demanding applications, from battery research to microbial fuel cell development.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your project's efficiency and success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Conductive Carbon Cloth Carbon Paper Carbon Felt for Electrodes and Batteries
- Hydrophilic Carbon Paper TGPH060 for Battery Lab Applications
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Conductive Carbon Fiber Brush for Static Removal and Cleaning
- Battery Lab Equipment 304 Stainless Steel Strip Foil 20um Thick for Battery Test
People Also Ask
- What are the four main types of sensors? A Guide to Power Source and Signal Type
- What are 3 products that carbon nanotubes can be used in? Enhancing Batteries, Tires, and Composites
- What applications is carbon felt suitable for? Ideal for High-Performance Electrochemical Systems
- What can carbon nanotubes be used for? Unlock Superior Performance in Batteries & Materials
- Why are high surface area materials preferred for BES anodes? Maximize Microbial Power and Efficiency












