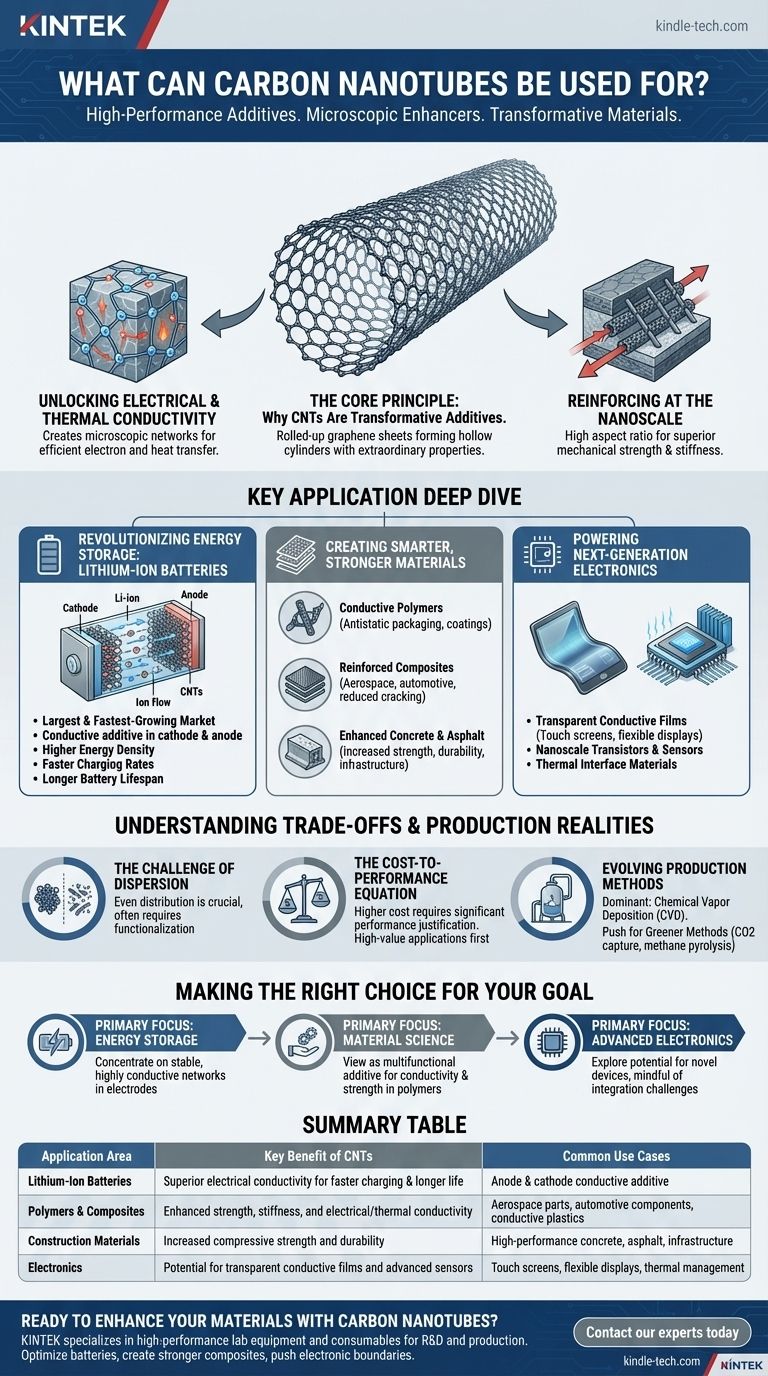
At their core, carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are primarily used as high-performance additives. Their most significant commercial application today is in lithium-ion batteries, where they act as a conductive additive to improve performance and charging speeds. They are also widely used to enhance the properties of materials, creating stronger and more conductive polymers, composites, concrete, and tires.
The true value of carbon nanotubes is not as a standalone product, but as a microscopic enhancer. By integrating them into existing materials, we unlock significant improvements in electrical conductivity, mechanical strength, and thermal performance that were previously unattainable.

The Core Principle: Why CNTs Are Transformative Additives
Carbon nanotubes derive their power from their unique physical structure. They are essentially rolled-up sheets of graphene, forming hollow cylinders that are incredibly small but possess extraordinary properties.
Unlocking Electrical and Thermal Conductivity
The structure of CNTs allows electrons and heat to move along their length with very little resistance. When mixed into a non-conductive material like a polymer, they form a microscopic, interconnected network that allows the entire composite to conduct electricity and dissipate heat.
Reinforcing at the Nanoscale
CNTs are one of the strongest and stiffest materials ever discovered relative to their weight. Their high aspect ratio (the ratio of their length to their diameter) means even a small amount can act like nanoscale rebar, drastically increasing the strength and durability of materials like concrete or fiber-reinforced composites.
Key Application Deep Dive
While the potential applications are vast, the current market is dominated by a few key areas where CNTs provide a clear and justifiable performance benefit.
Revolutionizing Energy Storage: Lithium-Ion Batteries
This is the largest and fastest-growing market for CNTs. They are added to both the cathode and anode of lithium-ion batteries to create a highly efficient electrical pathway. This improves ion and electron transfer, leading to higher energy density, faster charging rates, and a longer battery lifespan.
Creating Smarter, Stronger Materials
CNTs are used as a multifunctional additive in a wide range of composites.
- Conductive Polymers: Adding CNTs to plastics can make them electrically conductive, which is essential for applications like antistatic packaging for electronics, conductive coatings, and components for fuel systems.
- Reinforced Composites: In aerospace and high-performance automotive parts, CNTs are added to carbon fiber composites to improve strength and reduce the risk of cracking between layers.
- Enhanced Concrete & Asphalt: A small amount of CNTs can significantly increase the compressive strength and durability of concrete, potentially leading to longer-lasting infrastructure.
Powering Next-Generation Electronics
While still emerging, the use of CNTs in electronics holds immense promise. They are being used to develop transparent conductive films as a potential replacement for indium tin oxide (ITO) in touch screens and flexible displays. Researchers are also using them to build nanoscale transistors, sensors, and thermal interface materials to cool high-performance computer chips.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Production Realities
Despite their incredible properties, CNTs are not a universal solution. Their adoption involves navigating practical and economic challenges.
The Challenge of Dispersion
One of the biggest hurdles is ensuring CNTs are distributed evenly within a host material. They naturally tend to clump together, which negates their benefits. Significant effort goes into functionalization and mixing processes to achieve proper dispersion.
The Cost-to-Performance Equation
CNTs are more expensive than the conventional additives they replace. Therefore, their use must be justified by a significant and necessary performance improvement that provides a return on the investment. This is why they are first adopted in high-value applications like batteries and aerospace.
Evolving Production Methods
The dominant commercial production method is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), which offers the best balance of quality, quantity, and cost. However, there is a strong push toward greener production, including methods that use captured carbon dioxide or the pyrolysis of methane as a feedstock, aligning the technology with sustainability goals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When evaluating carbon nanotubes, your decision should be guided by your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is energy storage: Concentrate on CNTs' ability to create stable, highly conductive networks within battery electrodes to boost charge rates and cycle life.
- If your primary focus is material science: View CNTs as a multifunctional additive for imparting conductivity and exceptional mechanical strength to polymers and composites.
- If your primary focus is advanced electronics: Explore their potential for novel devices like sensors and transparent films, but remain mindful of current integration and manufacturing challenges.
Ultimately, understanding carbon nanotubes means seeing them not as a final product, but as a fundamental building block for enhancing the materials of the future.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Benefit of CNTs | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium-Ion Batteries | Superior electrical conductivity for faster charging & longer life | Anode & cathode conductive additive |
| Polymers & Composites | Enhanced strength, stiffness, and electrical/thermal conductivity | Aerospace parts, automotive components, conductive plastics |
| Construction Materials | Increased compressive strength and durability | High-performance concrete, asphalt, infrastructure |
| Electronics | Potential for transparent conductive films and advanced sensors | Touch screens, flexible displays, thermal management |
Ready to enhance your materials with carbon nanotubes?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for developing and testing next-generation materials. Whether you're optimizing battery performance, creating stronger composites, or pushing the boundaries of electronics, our solutions support your R&D and production needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you integrate CNT technology and achieve your material science goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Conductive Carbon Cloth Carbon Paper Carbon Felt for Electrodes and Batteries
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- Electrode Polishing Material for Electrochemical Experiments
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
People Also Ask
- What are 3 products that carbon nanotubes can be used in? Enhancing Batteries, Tires, and Composites
- How should carbon cloth used for high-temperature electrolysis be handled after operation? Prevent Irreversible Oxidative Damage
- What are the material properties of carbon paper? Unlocking High Conductivity & Porosity for Your Lab
- What applications is carbon felt suitable for? Ideal for High-Performance Electrochemical Systems
- What are the four main types of sensors? A Guide to Power Source and Signal Type



















